the NSM Primes Three Tables (DOC 82k)
advertisement

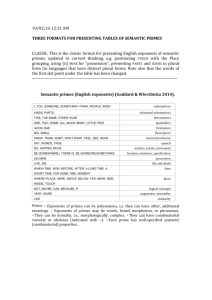
10/02/16 7:29 AM TABLES OF NSM SEMANTIC PRIMES, IN THREE FORMATS This is the classic format, updated to current thinking (e.g. positioning TOUCH with the Space grouping, using (BE) MINE for “possession”) —————————————————————————————————— Table: Semantic primes (English exponents) (Goddard & Wierzbicka 2014). I, YOU, SOMEONE, SOMETHING~THING, PEOPLE, BODY KIND, PART THIS, THE SAME, OTHER~ELSE ONE, TWO, MUCH~MANY, LITTLE~FEW, SOME, ALL Substantives Relational substantives Determiners Quantifiers GOOD, BAD Evaluators BIG, SMALL Descriptors THINK, KNOW, WANT, DON’T WANT, FEEL, SEE, HEAR SAY, WORDS, TRUE DO, HAPPEN, MOVE BE (SOMEWHERE), THERE IS, BE (SOMEONE/SOMETHING) (BE) MINE LIVE, DIE WHEN~TIME, NOW, BEFORE, AFTER, A LONG TIME, A Mental predicates Speech Actions, events, movement Location, existence, specification Possession Life and death Time SHORT TIME, FOR SOME TIME, MOMENT WHERE~PLACE, HERE, ABOVE, BELOW, FAR, NEAR, SIDE, Space INSIDE, TOUCH NOT, MAYBE, CAN, BECAUSE, IF VERY, MORE LIKE Logical concepts Augmentor, intensifier Similarity Notes: Primes exist as the meanings of lexical units (not at the level of lexemes) Exponents of primes may be words, bound morphemes, or phrasemes They can be formally, i.e., morphologically, complex They can have combinatorial variants or allolexes (indicated with ~) Each prime has well-specified syntactic (combinatorial) properties. This format is less technical, especially if the right hand column is omitted. Anna Wierzbicka used it for the first time in her 2014 book Imprisoned in English. —————————————————————————————————— Table: Semantic primes (English exponents) (after Goddard & Wierzbicka 2014; Wierzbicka 2014). I~ME, YOU, SOMEONE, SOMETHING, PEOPLE, BODY KIND, PARTS THIS, THE SAME, OTHER~ELSE ONE, TWO, MUCH~MANY, LITTLE~FEW, SOME, ALL GOOD, BAD, BIG, SMALL THINK, KNOW, WANT, DON’T WANT, FEEL, SEE, HEAR SAY, WORDS, TRUE DO, HAPPEN, MOVE BE (SOMEWHERE), THERE IS, BE (SOMEONE/SOMETHING), (BE) MINE LIVE, DIE WHEN~TIME, NOW, BEFORE, AFTER, A LONG TIME, A SHORT TIME, FOR SOME TIME, MOMENT Substantives Relational substantives Determiners Quantifiers Evaluators, descriptors Mental predicates Speech Actions, events, movement Location, existence, specification, possession Life and death Time WHERE~PLACE, HERE, ABOVE, BELOW, FAR, NEAR, SIDE, INSIDE, TOUCH NOT, MAYBE, CAN, BECAUSE, IF, VERY, MORE, LIKE~AS Space Logical concepts Primes exist as the meanings of lexical units (not at the level of lexemes) Exponents of primes may be words, bound morphemes, or phrasemes They can be formally, i.e., morphologically, complex They can have combinatorial variants or allolexes (indicated with ~) Each prime has well-specified syntactic (combinatorial) properties. I~ME, YOU, SOMEONE, SOMETHING, PEOPLE, BODY KIND, PARTS THIS, THE SAME, OTHER~ELSE ONE, TWO, MUCH~MANY, LITTLE~FEW, SOME, ALL GOOD, BAD, BIG, SMALL THINK, KNOW, WANT, DON’T WANT, FEEL, SEE, HEAR SAY, WORDS, TRUE DO, HAPPEN, MOVE BE (SOMEWHERE), THERE IS, BE (SOMEONE/SOMETHING), (BE) MINE LIVE, DIE WHEN~TIME, NOW, BEFORE, AFTER, A LONG TIME, A SHORT TIME, FOR SOME TIME, MOMENT WHERE~PLACE, HERE, ABOVE, BELOW, FAR, NEAR, SIDE, INSIDE, TOUCH NOT, MAYBE, CAN, BECAUSE, IF, VERY, MORE, LIKE~AS The next two tables are in a dual-language format. Each language has its own column or row, which can be presented in either order. The idea is to avoid any subliminal impression that one language (English) is primary or prior with respect to the other. —————————————————————————————————— Table: Semantic primes (English and Spanish), grouped into related categories (after Goddard & Wierzbicka (2014), Travis (2002)). I, YOU, SOMEONE, SOMETHING~THING, YO, TU, ALGUIEN~PERSONA, ALGO~COSA, PEOPLE, BODY GENTE, CUERPO KIND, PART TIPO, PARTE THIS, THE SAME, OTHER~ELSE ESTO, LO MISMO, OTRO ONE, TWO, MUCH~MANY, LITTLE~FEW, SOME, ALL UNO, DOS, MUCHO , POCO, ALGUNOS, TODO GOOD, BAD BUENO, MALO BIG, SMALL GRANDE, PEQUEÑO KNOW, THINK, WANT, FEEL, SEE, HEAR PENSAR, SABER, QUERER, SENTIR, VER, OÍR SAY, WORDS, TRUE DECIR, PALABRAS, VERDAD DO, HAPPEN, MOVE HACER, PASAR, MOVERSE BE (SOMEWHERE), THERE IS, BE ESTAR (EN ALGÚN LUGAR), HAY, SER (SOMEONE/SOMETHING) (ALGUIEN/ALGO) (BE) MINE (SER) MÍO LIVE, DIE VIVIR, MORIR WHEN~TIME, NOW, BEFORE, AFTER, A CUÁNDO~TIEMPO, AHORA, ANTES, DESPUÉS, LONG TIME, A SHORT TIME, FOR SOME MUCHO TIEMPO, POCO TIEMPO, POR UN TIME, MOMENT TIEMPO, MOMENTO WHERE~PLACE, HERE, ABOVE, BELOW, DÓNDE~LUGAR, AQUÍ, ARRIBA, DEBAJO, FAR, NEAR, SIDE, INSIDE, TOUCH CERCA, LEJOS, LADO, DENTRO , TOCAR NOT, MAYBE, CAN, BECAUSE, IF NO, TAL VEZ, PODER, PORQUE, SI VERY, MORE MUY, MÁS LIKE COMO substantives relational substantives determiners quantifiers evaluators descriptors mental predicates speech actions, events, movement location, existence, specification possession life and death time space logical concepts intensifier, augmentor similarity Notes: – Primes exist as the meanings of lexical units (not at the level of lexemes) – Exponents of primes may be words, bound morphemes, or phrasemes – They can be formally complex – They can have combinatorial variants or “allolexes” (indicated with ~) – Each prime has well-specified syntactic (combinatorial) properties. Table: Semantic primes (English and German exponents), grouped into related categories. I, YOU, SOMEONE, SOMETHING~THING, PEOPLE, BODY substantives ICH, DU, JEMAND, ETWAS~DING, MENSCHEN~LEUTE, KÖRPER KIND, PART relational substantives ART, TEIL THIS, THE SAME, OTHER~ELSE determiners DIESE(R), DASSELBE, ANDERE(R) ONE, TWO, SOME, ALL, MUCH~MANY, LITTLE~FEW quantifiers EINS, ZWEI, EINIGE, ALLE, VIEL~VIELE, WENIG~WENIGE GOOD, BAD evaluators GUT, SCHLECHT BIG, SMALL descriptors GROß, KLEIN KNOW, THINK, WANT, FEEL, SEE, HEAR mental predicates WISSEN, DENKEN, WOLLEN, FÜHLEN, SEHEN, HÖREN SAY, WORDS, TRUE speech SAGEN, WORT~WÖRTER, WAHR DO, HAPPEN, MOVE, TOUCH TUN, PASSIEREN, BEWEGEN, BERÜHREN BE (SOMEWHERE), THERE IS, BE (SOMEONE/SOMETHING) SEIN (IRGENDWO), ES GIBT, SEIN (JEMAND/ETWAS) (BE) MINE (SEIN) MINE LIVE, DIE LEBEN, STERBEN WHEN~TIME, NOW, BEFORE, AFTER, A LONG TIME, A SHORT TIME, FOR SOME TIME, MOMENT WENN~ZEIT, JETZT, VOR, NACH, EINE LANGE ZEIT, EINE KURZE ZEIT, EINIGE ZEIT, MOMENT WHERE~PLACE, HERE, ABOVE, BELOW, FAR, NEAR, SIDE, INSIDE WO~ORT, HIER, ÜBER, UNTER, WEIT, NAH, SEITE, INNEN NOT, MAYBE, CAN, BECAUSE, IF NICHT, VIELLEICHT, KÖNNEN, WEIL~WEGEN, WENN VERY, MORE SEHR, MEHR LIKE~AS~WAY WIE~ALS~WEISE actions, events, movement, contact location, existence, specification possession life and death time space logical concepts intensifier, augmentor similarity Notes: • Primes exist as the meanings of lexical units (not at the level of lexemes) • Exponents of primes may be words, bound morphemes, or phrasemes • They can be formally complex • They can have language-specific combinatorial variants (allolexes, indicated with ~) • Each prime has well-specified syntactic (combinatorial) properties.