File
advertisement

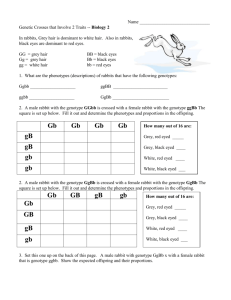
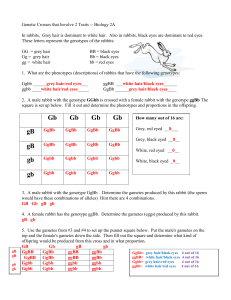
Sex- Linked Practice Problems Name: 1) Which sex is more likely have a recessive, sex-linked trait? Male Female 2) Which parent do sons inherit recessive, sex-linked traits from? Mother Father 3) Which type of sex chromosome do you find most sex-linked traits on? X Y 4) The gene for colorblindness is carried on the X chromosome and is recessive. A man whose father was colorblind has a colorblind daughter. a) Is this man colorblind? How do you know? b) Must the fathers of all colorblind girls be colorblind? Why? Daughter = XcXc Father= XcY a. Yes- because he gave his daughter 1 Xc so he must have 1 Xc, since men cant carry a gene on the X, he must be colourblind b. Yes. Because men can’t carry a trait on the X chromosome without having the trait 5) A man whose parents were normal with respect for color vision marries a woman of normal vision. One of their daughters is colorblind. Give the genotypes of this daughter, her parents, and paternal grandparents. Is the girl's father colorblind? Colourblind daughter= XcXc Father XcY, his parents were normal so the grandparents are XY and Xc. Mother was normal so her genotype is XXc 6) Cross a woman carrier for hemophilia (XXh) to a hemophiliac man (XhY). a) What fraction of the offspring will be carrier females? 1/4 b) What fraction will be hemophiliac females? 1/4 c) How many different genotypes are possible among the offspring? 4 XhXh, XXh, XhY, XY, 4) Brown eyes are dominant over blue eyes (B= brown, b=blue so BB or Bb= brown, bb=blue). This is NOT a sex-linked trait. Cross a brown-eyed colorblind male (whose mother had blue eyes (mother= bb)) (man=BbXcY) with a normal blue-eyed female (whose father was colorblind father= XcY)(bbXXc). a) What is the probability of getting offspring that are blue-eyed carrier females? 1/8 b) What is the probability of getting offspring that are colorblind? 1/2 5) If a husband and wife have a girl heterozygous for colorblindness (XXc), a normal boy (XY), a colorblind girl (XcXc), and a colorblind boy (XcY), what would be the genotypes of the parents? Because they have a colourblind girl (XcXc) each parent has one Xc The fathers other chromosome is a Y because he’s male = XcY The mothers other chromosome is X because one of the male children is normal (XY) he had to get the normal X from his mom so she is (XcX) 6) In fruit flies, eye color is carried on the X chromosome. The allele for red eyes is dominant (XR) over its recessive allele, white eyes (X). Cross a homozygous red-eyed female (XRXR) to white-eyed male (XY). a) How many genotypes are possible among the offspring? 2 XRY, XRX b) What is the probability of getting offspring that are white-eyed females? 0 7) In fruit flies, normal wings (N) are dominant over vestigial wings (n). This is not a sex-linked trait. What offspring would be expected if a heterozygous normal winged white eyed male (NnXY) were mated with a female who has vestigial wings and is heterozygous red-eyed (nnXRX)? [G] NnXY x nnXRX [A] NX, NY, nX, nY / nXR, nX, nXR, nX [S] [R] 1/8 each of NnXRX normal winged red eyed female NnXX normal winged white eyed female Practice Problems NnXRY normal winged red eyed male NnXY normal winged white eyed male nnXRX vestigial winged red eyed female nnXX vestigial winged white eyed female nnXRY vestigial winged red eyed male nnXY vestigial winged white eyed male 8) In alley cats, the coat color is determined by a gene carried on the X chromosome. At the same time, the alleles are expressed in co-dominant inheritance. Genotypes and color are as follows: Females: XbXb = yellow Males: XbY = yellow XBXb = calico XBY = black XBXB = black 9) A calico cat (XB Xb) has a litter of eight kittens: one yellow male (Xb Y), two black males (XB Y), two yellow females (Xb Xb), and three calico females (XB Xb). What is the color of the father of the litter? XbXb tells you each parent had an Xb allele soothe father must be Xb Y 10) A yellow (Xb Xb )cat has a litter of four kittens: one yellow, and three calicos (XBXb). Assuming a single father for the litter, what is the sex of the yellow kitten? The calico kitten ad to get the XB from the father so the father is XBY so the yellow kitten must be female 1. Practice setting up keys for the phenotypes listed in each set. Remember that the "medium" trait must always be heterozygous. a) Birds can be blue (CBCB), white(CWCW), or white with blue-tipped feathers(CBCW). b) Flowers can be white(WW), pink(RW), or red(RR). c) A Whoo can have curly hair(HCHC), spiked hair(HSHS), or a mix of both curly and spiked(HSHC). d) A Sneech can be tall(TT), medium(TS), or short(SS). e) A Bleexo can be spotted(CWCB), black(CBCB), or white(CWCB). 2. Now, can you figure out in the above list, which of the letters represent co-dominant traits and which are incomplete. Co-dominant __a,c,e_______ Incompletely Dominant ____b,d______ 3. If a tall sneech is crossed with a medium sneech what will be the height of the offspring? TT x TS 1/2 TS Medium 1/2 TT Tall 4. In rabbits, grey hair is dominant to white hair (G= grey g=white). Also in rabbits, black eyes are dominant to red eyes (B=black eyes, b=red eyes). a) What are the phenotypes (descriptions) of rabbits that have the following genotypes: Ggbb _Grey red eyed___ ggBB ____white black eyed ggbb ___white red eye GgBb _____grey black eyed b) A male rabbit with the genotype GGbb is crossed with a female rabbit with the genotype ggBb. Determine the phenotypes ratios in the offspring. [G] GGbb [A] Gb, Gb, Gb, Gb x / ggBb gB, gb, gB, gb Practice Problems [R] 1/2 GgBb grey black eyed, 1/2 Ggbb grey red eyed c) A male rabbit with the genotype GgBb is crossed with a female rabbit with the genotype GgBb. Determine the phenotypic ratio of the offspring. Dihybrid cross- ratio is always 9;3;3;1 9 Grey black eyed, 3 white black eyed, 3 grey red eyed, 1 white red eyed 6. In fruit flies, eye color is carried on the X chromosome. The allele for red eyes is dominant over its recessive allele, white eyes (XR= red X=white). Normal wings (N) are dominant over vestigial wings (n). This is not a sex-linked trait. What offspring would be expected if a vestigial winged white eyed male (vvXY) were mated with a female who has homozygous normal wings and is heterozygous red-eyed (NNXRX)? [G] vvXY x NNXRX [A] vX, vY, vX, vY / NXR, NX, NXR, NX [R] ¼ each of NvXXR normal winged red eyed female, NvXRY Normal winged red eyed male, NvXX normal winged white eyed female, NvXY normal winged white eyed male 7. In a certain cactus, prickly spines can be two pronged (C2) or one pronged (C1) . If a true breeding one-pronged cactus (C1C1) is crossed with a true breeding two-pronged (C2C2) cactus, the F1 generation has a mixture of spines (C1C2), some are two-pronged, some are onepronged. a. Is this an example of codominance or incomplete dominance? Co-dominance b. Show the F2 generation (a cross between the two F1's). What are the phenotypes of the offspring and in what proportion? C1C2 x C1C2 offspring= 1/4 C1C1, 1/4 C2C2,1/2 C1C2 8. In this same cactus, if you cross a plant that has red (RR) flowers to one that has yellow(YY) flowers, you produce a plant that has orange flowers(RY). Is this codominance or incomplete dominance? Co-dominance Show the cross of an orange flowered plant to a red flowered plant. RY x RR= 1/2 RR red, 1/2 RY orange 9. A red flowered, two-pronged cactus (RRC2C2) is crossed with a yellow flowered one-pronged cactus (YYC1C1). What are the resulting offspring and in what proportion? [G] RRC2C2 x [A] RC2, RC2, RC2, RC2 / YYC1C1 YC1, YC1, YC1, YC1 [R] all RYC1C2 all orange 1 and 2 spiked