Human Impact on Ecosystems Worksheet
advertisement

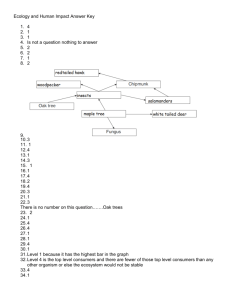
B10: ANSWERS Human influences on the Ecosystem 1. Read “Deforestation” pages 240-241. 2. Use the “key points” on page 241 to complete these sentences. Deforestation is due to the world demand for TIMBER and PAPER. The land is also cleared for FARMS, CATTLE RANCHES and new ROADS. 3. List the undesirable effects of deforestation in the table below. An example has been completed for you. Effect Description Soil erosion Thin soils in rainforests will be washed away when not held together by vegetation. This forms gullies and causes loss of plant nutrients. Severe storms Loss of trees in forests can cause changes in weather patterns (wind etc), which can increase frequency and severity of storms. Flooding Water runs off the land faster when it is not absorbed by plants and transpired back into the atmosphere. Destruction of habitats and extinction Some plants and animals live only in certain areas. If the forests that are their homes are cut down, this can cause extinction of many species. Carbon When the chopped down trees are burnt, the CO2 is dioxide build released into the atmosphere, increasing the concentration up of this greenhouse gas. 4. Pollution is the harm done to the environment by the release of substances produced by human activities. Pollutants affect the air, ecosystems on land and aquatic ecosystems like rivers and the sea. Use page 242 to give examples of sources of water and air pollution. Water pollution can be caused by sewage and chemical waste. Sources include: FERTILISERS, SEWAGE, INDUSTRIAL CHEMICAL WASTE, PESTICIDES AND HERBICIDES. Air pollution by greenhouse gases are contributing to global warming. Greenhouse gases include METHANE and CARBON DIOXIDE. 5. Read “Pollutions of rivers and seas” pages 248-249. 6. Define the term ‘eutrophication’, and explain how it occurs. definition: the enrichment of waters with plant nutrients that can stimulate the growth of algae and plants. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. FERTILISERS ARE LEACHED INTO RIVERS AND STREAMS FROM THE SOIL The fertilisers cause the growth of algae in the water Consumers of the algae cannot eat enough to limit the algal population Algae populations grow large enough to cover the lake surface, preventing light from reaching the plants below the surface The water plants die as they are not getting enough light to photosynthesise, they rot on the lake/river bed Algae from below the surface populations also die as they are not able to compete against the large surface population Decomposers feed on the dead plants and algae The decomposers use up oxygen in the water as they respire anaerobically The lower levels of dissolved oxygen kills off fish and invertebrates as they cannot respire Changing the balance of one orgnaism in the food web can have a flow-on affect to the rest of the populations. In this case, increasing the success of the algae by providing it with added nutrients ultimately caused the collapse of the entire ecosystem. 7. Read “Acid rain” pages 246-247. 8. Draw a diagram to show the causes and effects of acid rain. See figure 19.6.1 on p246 9. Complete the ‘summary questions 1-2’ on page 247 to summarise the causes and effects of acid rain, and the measures that may be taken to reduce its incidence. 1. Fossil fuels; dioxide; nitrogen oxides; nitric; sulfuric; acid 2. a rain water dissolves atmospheric carbon dioxide to form carbonic acid (slightly acidic) b sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides c fossil fuels and exhaust fumes d i) kills leaves and affects ability to fight disease ii) on soils containing hard rocks like granite, there is nothing to neutralise the acid (unlike limestone based soils which are basic), causing plant nuturints like potassium and calcium to wash out of the soil iii) acid rain washes into lakes and rivers, causing the aluminium levels to rise and lowering the pH, killing many fish and invertebrates e use low sulphur fuels; remove the sulfur from power station chimneys; fit catalytic converters to car exhausts 10. Read “The Greenhouse Effect” pages 244-245. 11. Complete the table below about the sources and effects of greenhouse gases. Gas Carbon dioxide Sources Effect Respiration; Combustion of fossil fuels Water vapour Respiration; combustion Methane Cattle; bacteria in wetlands and rice fields; rotting material in landfills; extraction of oil and natural gas Excess heat energy is trapped in the atmosphere, causing global temperature rises 12. List some of the likely consequences of global warming. Polar ice caps could melt Increase sea levels Flooding of low-lying land areas Changes to weather patterns Change to agricultural areas and flow on effect to political and economic stability 13. Read “Conservation” pages 250-251 and define the following terms: 1. Conservation: the management of ecosystems and resources to meet changing conditions and needs 2. Species: a group of organisms with similar characteristics which are capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring 3. Habitat: area where a population lives 4. Endangered: at risk of becoming extinct; may have low genetic diversity 5. Biodiversity: catalogue of all the species in an area, country or the world; as well as the habitats and genetic diversity of the species 14. Give three reasons why humans should conserve ecosystems: i. ii. iii. Provide us with areas for recreation, medicines and methods for water treatment Maintain nutrient cycles Keep pests and diseases in check by not disrupting species interactions 15. Give three ways that humans are conserving ecosystems and habitats: i. ii. iii. Marine reserves and parks (fishing areas) National parks Rescuing and breeding endangered animals and plants Natural resources like water and non-renewable fossil fuels should also be conserved. Fossil fuels form over millions of years; when the current supply is finished, there will be none left. We can use more efficient machines to conserve fossil fuels and investigate alternative energy supplies. Water should not be wasted and care should be taken to keep water free of pollution.