File - Doctorswriting
advertisement

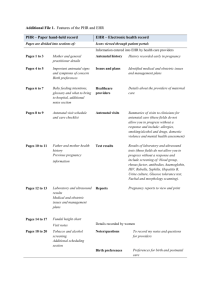
Tasmanian Department of Health and Human Services Royal Hobart Hospital Clinical Guidelines Note: The electronic version of this document is the version currently in use. Any printed version can not be assumed to be current. Please remember to read our disclaimer. Rh D IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Anti – D) ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINE (WACS) Introduction Objectives Related Documents Staff Scope Routine Antenatal Care Dosage Indications for Administration MAT-1-0024 Alerts Forms & Equipment Preparation and Administration Procedure Refusal for Consent of Treatment References Introductions Rh D negative women are at risk of alloimmunisation resulting in the development of haemolytic antiD antibodies that are able to cross the placenta to such an extent that a Rh D positive foetus and newborn are at risk of serious morbidity and mortality. The administration of passive anti-D at times of actual and potential foeto-maternal haemorrhage (FMH) and routine antenatal prophylaxis has been shown to reduce the rate of alloimmunisation. Guidelines have been established for the recommended use of anti-D in pregnancy and post-partum and are endorsed by the RANZCOG ARCBSNHMRC and ANZSBT Objectives To prevent Rhesus iso-immunisation in women who are Rh D negative with no preformed anti-D antibodies in the following situations: After the birth of an Rh D positive infant. After termination or miscarriage at any stage of pregnancy After an event which may provoke a transplacental haemorrhage during pregnancy (e.g. amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, ectopic pregnancy, antepartum haemorrhage, external version or significant abdominal trauma). By antenatal prophylaxis to reduce the rate of unexpected antibody formation from approximately 1.5% to 0.2% in Rh D negative women carrying an Rh D positive baby despite appropriate use of postnatal prophylaxis. Custodian: WACS Authorised by: Haematology / Obstetric Depts Document File Name: STAHS Clinical Guideline.doc Effective Date: September 2014 Review Date: September 2017 Page 1 of 7 Tasmanian Department of Health and Human Services Royal Hobart Hospital Clinical Guidelines Note: The electronic version of this document is the version currently in use. Any printed version can not be assumed to be current. Please remember to read our disclaimer. Rh D IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Anti – D) ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINE (WACS) MAT-1-0024 Related Documents To be read in conjunction with: Transfusion - THO South - Clinical Protocol RHH COC 47 Blood Component Transfusion RHH IC2-04 Sharps Handling and Disposal RHH IC2-09 Blood and Body Substance – Spills Management RHH Refusal of Procedure/Treatment form Staff Scope Registered Nurse Registered Midwife Midwifery Students Medical Officers Transfusion Laboratory staff. Routine Antenatal Care Pathology A blood sample should be taken from all pregnant women at their first antenatal visit to test for the presence of red cell antibodies and to establish ABO and Rh D blood group. This group and antibody screen should be repeated at the first antenatal visit in each pregnancy even for known Rh D negative women because clinically significant antibodies to red cell antigens other than Rh D may have developed since the previous pregnancy. The antibody screen should then be repeated prior to the 28 week prophylactic dose of Rh D Immunoglobulin. A post natal Kleihauer-Betke test should be done on all Rh D negative women with Rh D positive babies.NOTE: All babies born to women with an Rh D negative blood group must have cord blood taken at birth (or if unavailable a blood sample from the baby must be taken) to determine the baby's blood group. Anti-D will be issued by the RHH Transfusion Laboratory on blood work from external laboratories but the RHH laboratory makes a disclaimer that if it has not done the blood group – it takes no responsibility for the results of other laboratories work. A very small number of women are found to have antibodies which are likely to affect the baby (e.g. Custodian: WACS Authorised by: Haematology / Obstetric Depts Document File Name: STAHS Clinical Guideline.doc Effective Date: September 2014 Review Date: September 2017 Page 2 of 7 Tasmanian Department of Health and Human Services Royal Hobart Hospital Clinical Guidelines Note: The electronic version of this document is the version currently in use. Any printed version can not be assumed to be current. Please remember to read our disclaimer. Rh D IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Anti – D) ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINE (WACS) MAT-1-0024 anti-D, anti-c, anti-K). More frequent samples need to be requested if these antibodies are present, or if there is any other cause for concern regarding the baby’s well being. Dosage Strength 250 IU Product Rh D Immunoglobulin INDICATION 1st trimester (less than 12 weeks) sensitizing events, single pregnancy 625 IU Rh D Immunoglobulin 1st trimester sensitizing events, multiple pregnancy 625 IU Rh D Immunoglobulin 2nd & 3rd trimester sensitizing events 625 IU Rh D Immunoglobulin Routine prophylaxis at 28 weeks 625 IU Rh D Immunoglobulin Routine prophylaxis at 34 weeks 625 IU Rh D Immunoglobulin Post partum if baby Rh D positive 250-625 IU Rh D Immunoglobulin As determined by Kleihauer testing Indications for Administration A. SENSITISING EVENTS 1.1 First Trimester (up to and including Week 12 of gestation) 1.2 A dose of 250 IU (50 micrograms) Rh D Immunoglobulin should be offered to every Rh D negative woman with no pre-existing anti-D antibodies to ensure adequate protection against immunization for sensitizing events: Miscarriage Termination of pregnancy Ectopic pregnancy Ultrasound needle guided procedures e.g. chorionic villus sampling Antepartum haemorrhage A dose of 250 IU Rh D Immunoglobulin is sufficient to prevent immunization by FMH of 2.5 ml red cells (i.e. 5ml whole blood) Custodian: WACS Authorised by: Haematology / Obstetric Depts Document File Name: STAHS Clinical Guideline.doc Effective Date: September 2014 Review Date: September 2017 Page 3 of 7 Tasmanian Department of Health and Human Services Royal Hobart Hospital Clinical Guidelines Note: The electronic version of this document is the version currently in use. Any printed version can not be assumed to be current. Please remember to read our disclaimer. Rh D IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Anti – D) ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINE (WACS) MAT-1-0024 1.3 Multiple pregnancies require a dose of 625 IU 1.4 In the event of transfusion of Rh D positive blood products the recommended dose of Anti-D is 100 IU per 1 ml Rh D positive blood. 2 Second and Third Trimester Sensitising Events 2.1 A dose of 625 IU (125 micrograms) should be offered to every Rh D negative woman with no preformed Anti-D antibodies to ensure adequate protection against immunization for the following indications: Genetic studies (chorionic villous sampling, amniocentesis, cordocentesis) Abdominal trauma sufficient enough to cause FMH Each occasion of revealed or concealed antepartum haemorrhage. Where the patient suffers unexplained uterine pain, the possibility of antepartum haemorrhage should be considered, with a view to immunoprophylaxis. Recurrent bleeds. B. Routine Antenatal Prophylaxis At 28 and 34 weeks gestation universal prophylaxis with Rh D immunoglobulin administered to Rh D negative women with no preformed anti-D antibodies, is regarded as best practice. The dose given should be 625 IU (125 micrograms). C. Post Natal Administration All babies born to women with an Rh D negative blood group must have cord blood taken at birth (or if unavailable a blood sample from the baby must be taken) to determine the baby's blood group. 1.1 All Rh D negative women delivering an Rh D positive infant will require Anti-D administration within 72 hours of birth: 625 I U 1.2 All Rh D negative women with Rh D positive babies should have a Kleihauer-Betke test as soon as possible following delivery, to determine the degree of feto-maternal haemorrhage. The test results will determine whether an additional dose of Anti-D is required to inhibit formation of Rh antibodies in the mother and prevent Rh disease in future Rh D positive children. 1.3 The Obstetric medical officer must review the pathology results of the Kleihauer-Betke test of all Rh D negative women prior to discharge to ensure that additional Rh D immunoblogulin is administered if required. If patients are discharged prior to test results being available it is the responsibility of the medical officer to follow up results and recall the patient if required. 1.4 Advice regarding additional doses can be obtained from the haematologist on call. Custodian: WACS Authorised by: Haematology / Obstetric Depts Document File Name: STAHS Clinical Guideline.doc Effective Date: September 2014 Review Date: September 2017 Page 4 of 7 Tasmanian Department of Health and Human Services Royal Hobart Hospital Clinical Guidelines Note: The electronic version of this document is the version currently in use. Any printed version can not be assumed to be current. Please remember to read our disclaimer. Rh D IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Anti – D) ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINE (WACS) MAT-1-0024 Alerts 1. Day of Surgery Admissions requiring Anti-D [refer 1.1 and 2.1]: The Obstetric and/or Gynaecology Medical Officer is responsible for the ordering of Anti-D for Rh D negative patients. 2. Rh D Positive Platelet Transfusion 2.1. Rh D negative patients should receive 250 IU prophylactic Anti-D when receiving Rh D positive platelets if they are: Women of child bearing age Men less than 25 years of age 2.2. Anti–D should be given subcutaneously to patients with low platelet counts due to the risk of haematoma. 2.3. For doses exceeding a volume of 5 ml, it is recommended to administer in divided doses at different sites. Anti–D need only be given on a weekly basis Forms and Equipment A Transfusion Medicine request form that includes indication for use and the gestation (in weeks). Human Anti-D Antibody Product Administration and patient consent form Patient information brochure Anti–D vial 5 ml syringe Interlink Vial access 21 and 23G needle Alco-wipes Gloves Preparation and Administration Procedure 1. Collect Anti-D from Pathology. A Transfusion Medicine Request form is required. Note if the product appears turbid or contains any sediment do not use it. The product must be used immediately after opening. Any unused solution should be discarded appropriately. 2. Patient Identification: check three points of identity with two registered nursing /midwifery staff (See RHH COC 40 Patient Identification Policy and Procedure). 3. Checklist [refer to Human Anti-D Antibody Product Administration form]: Mothers blood group Baby’s blood group (post partum) Custodian: WACS Authorised by: Haematology / Obstetric Depts Document File Name: STAHS Clinical Guideline.doc Effective Date: September 2014 Review Date: September 2017 Page 5 of 7 Tasmanian Department of Health and Human Services Royal Hobart Hospital Clinical Guidelines Note: The electronic version of this document is the version currently in use. Any printed version can not be assumed to be current. Please remember to read our disclaimer. Rh D IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Anti – D) ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINE (WACS) MAT-1-0024 Anti-D order by Medical Officer Record batch number in patient medical records on Human Anti-D Antibody Product Administration form Patient consent section signed 4. Apply universal precautions (wear gloves) 5. Prepare skin with alcohol wipe 6. Administer slowly as deep intramuscular injection as per Product Information (see alerts) 7. Observe injection site 8. Document: dose, route, batch number and sign Human Anti-D Antibody Product Administration form Refusal for Consent of Treatment Everyone has the right to decide whether or not to accept treatment before giving consent. It is important for mothers to understand why they are being offered treatment and the risks and benefits to them and their baby. If there the paternal rhesus (D) status is positive, an option for checking the fetal blood group and Rhesus status by the non-invasive prenatal testing may be discussed and offered to help with counselling. References 1. National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC): www.nhmrc.gov.au 2. Australian Society of Blood Transfusion Inc.(ASBT): www.anzsbt.org.au 3. Australian Red Cross Blood Service(ARCBS): www.transfusion.com.au 4. CSL Bioplasma: Rh(D) Immunoglobulin – VF, Product Information, 2007 5. Peninsula Health, Vic: Maternity Services Clinical procedure, Anti-RH(D) Immunoglogulin Antenatal and Postnatal Administration,2006 Custodian: WACS Authorised by: Haematology / Obstetric Depts Document File Name: STAHS Clinical Guideline.doc Effective Date: September 2014 Review Date: September 2017 Page 6 of 7 Tasmanian Department of Health and Human Services Royal Hobart Hospital Clinical Guidelines Note: The electronic version of this document is the version currently in use. Any printed version can not be assumed to be current. Please remember to read our disclaimer. Rh D IMMUNOGLOBULIN (Anti – D) ADMINISTRATION GUIDELINE (WACS) MAT-1-0024 6. NWGH, Tas: Rh(D) Immunoglobulin (Anti-D), 2007 Custodian: WACS Authorised by: Haematology / Obstetric Depts Document File Name: STAHS Clinical Guideline.doc Effective Date: September 2014 Review Date: September 2017 Page 7 of 7