Cosmology Prof. Yves Gaspar COURSE CONTENT Cosmology
advertisement

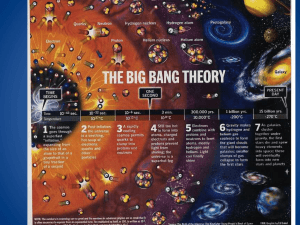
. - Cosmology PROF. YVES GASPAR COURSE CONTENT Cosmology corresponds to the part of physics that studies the origin and the evolution of the universe. In this field, various disciplines of physics, which are usually taught separately, are used in a unified framework. The course also contains a part dedicated to theoretical astrophysics, which studies the stars and their evolution, the general aim being the study of the problems inherent to black hole physics. The content of the course can be divided in the following way: a) Theoretical cosmology. - Review of general relativity and quantum physics, the Friedmann-LemaitreRobertson-Walker (FLRW) models, the dynamics and geometry of the FLRW models, the cosmological expansion, fundamental parameters, open, flat and closed models. A. Einstein’s cosmological constant and the impossibility of the static universe. - The basis of the Standard Hot Big Bang Model, elements of particle physics. The origin of matter: asymmetry between particles/antiparticles. Primordial nucleosinthesis: the “fossil” elements of the Big Bang. The “fossil” cosmic background radiation: theory and observation. The entropy of the universe. Primordial neutrinos. - The problems of the Big Bang model, the initial conditions problem in cosmology. Inflationary cosmological models, spontaneous symmetry breaking. - The dark matter problem – observational status and theory. The accelerated cosmological expansion and dark energy. Thermodynamical aspects of gravitation, entropic gravity, the holographic universe, implications of quantum gravity and string theory, brane-world scenarios, ekpyrotic and cyclic models: alternatives to the Standard Big Bang. b) Theoretical astrophysics - Structure formation: Jeans instability, the formation of stars, fundamental models. - Stellar evolution and dynamics: brown dwarfs, the main sequence, giant stars, novae and supernovae, the formation of “heavy” chemical elements, white dwarfs, the Chandrasekhar limit, neutron stars, quark stars, pulsars, binary and multiple systems. - Elements of black hole physics, black hole thermodynamics, the basis of the holographic principle. READING LIST J.N.ISLAM, An Introduction to Mathematical Cosmology, Cambridge University Press, 1992. J.V. MUKHANOV, PHYSICAL FOUNDATIONS OF COSMOLOGY, Cambridge University Press, 2005. J.D.BARROW-P. DAVIES-C.HARPER, Science and Ultimate Reality, Cambridge University Press, 2004. G.W.GIBBONS-E.P SHELLARD-S.J.RANKIN, The Future of Theoretical Cosmology, Cambridge University Press, 2003. LEONARD SUSSKIND AND JAMES LINDESAY, An introduction to black holes, information, and the string theory revolution: the holographic universe - World Scientific - 2004 BLACK HOLES, White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars, Stuart L. Shapiro, Saul A. Teukolsky, Ed. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 2004 ROGER PENROSE, La strada che porta alla realtà, 2005, ed. BUR NOTES Further information can be found on the lecturer's webpage http://www2.unicatt.it/unicattolica/docenti/index.html or on the Faculty notice board. at