Motion and Forces Study Guide *ANSWER ON YOUR OWN PAPER!!!
advertisement
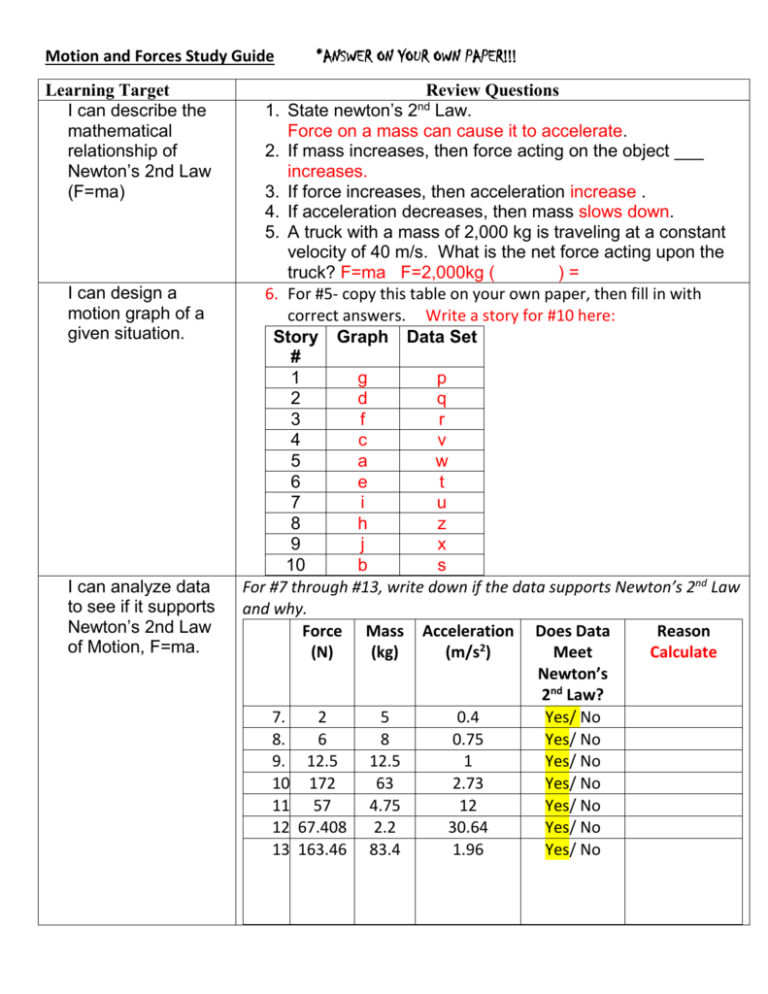
Motion and Forces Study Guide Learning Target I can describe the mathematical relationship of Newton’s 2nd Law (F=ma) I can design a motion graph of a given situation. I can analyze data to see if it supports Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion, F=ma. *ANSWER ON YOUR OWN PAPER!!! Review Questions 1. State newton’s 2 Law. Force on a mass can cause it to accelerate. 2. If mass increases, then force acting on the object ___ increases. 3. If force increases, then acceleration increase . 4. If acceleration decreases, then mass slows down. 5. A truck with a mass of 2,000 kg is traveling at a constant velocity of 40 m/s. What is the net force acting upon the truck? F=ma F=2,000kg ( )= 6. For #5- copy this table on your own paper, then fill in with correct answers. Write a story for #10 here: Story Graph Data Set # 1 g p 2 d q 3 f r 4 c v 5 a w 6 e t 7 i u 8 h z 9 j x 10 b s For #7 through #13, write down if the data supports Newton’s 2nd Law and why. Force Mass Acceleration Does Data Reason 2 (N) (kg) (m/s ) Meet Calculate Newton’s 2nd Law? 7. 2 5 0.4 Yes/ No 8. 6 8 0.75 Yes/ No 9. 12.5 12.5 1 Yes/ No 10. 172 63 2.73 Yes/ No 11. 57 4.75 12 Yes/ No 12. 67.408 2.2 30.64 Yes/ No 13. 163.46 83.4 1.96 Yes/ No nd I can calculate momentum. I can describe the mathematical relationship of Newton’s 3 Action/Reaction (momentum) p=mv. I can describe Newton’s law of Gravitation. 14. Calculate the momentum of a 65 kg skateboarder moving forward at the rate of 3 m/s. P=mv = 65kg x 3m/s = 195 kgm/s 15. Calculate the momentum of a 20 kg toddler in a car traveling west at the rate of 22 m/s. P=mv = 20 kg x 22 m/s = 440 m/s 16. Superman is often shown throwing huge objects (such as a bus), while he stays completely still. Why does this not support Newton’s 3rd Law and Conservation of Momentum? Still is V=0m/s Law of conservation says all momentum is conserved so there has to be a reaction(mv) to the action(mv) and their isn’t. p=p mv= mv rd 17. State Newton’s 3 Law. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. 18. When a long jumper jumps, Earth exerts a force that moves him/ her upward and to the east. Since there is a reaction force exerted on Earth, why doesn’t Earth move the same distance down and to the west? Earth is more massive. 19. When a bowling ball hits the pins at the end of the bowling alley, what happens to the balls momentum? The momentum is transferred into the pins. 20. What is Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation? F=G m1m2 d2 21. The force of gravity between two objects depends on what 2 factors? Mass and distance apart 22. True or False… Gravity is the pull of an object towards the center of the Earth. 23. If you went to the moon and dropped a feather and a hammer at the same time, which would land first? Neither, they would hit at the same time Why? Moon’s gravity is so much less, therefor less atmospheric pressure and less air resistance to cause friction between the objects. 24. If you drop a bullet at the same time one is fired straight outward from the same height, which bullet will hit the ground first? Since they are dropped from the same gravitational Potential energy height, they hit at the same time. Why? All objects on Earth are attracted at the same acceleration rate of 9.8m/s2 I can predict the gravitational force between two objects using Newton’s Law of Gravitation. 25. The force between a planet and a spacecraft is 1 million Newton’s. If the spacecraft moves to half of its original distance from the center of the planet, what will its force be? F=G m1m2 1,ooo,oooNewtons of Force=planet 1 (2) D2 52 (Cross multiply) F= 1,000,000N x .25 = 250,000N 26. The planet Mercury is less massive than Earth. Your mass on Mercury would be less than/ greater than/ equal to your mass on Earth. Mass stays the same 27. Your weight on Mercury would be less than/ greater than/ equal to your mass on Earth. Weight=mass x gravity Mercury’s gravity is less than Earth’s so your weight will be less.