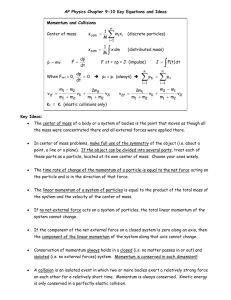
Momentum Study Questions
advertisement

K Name: ________________________ EY Momentum Study Questions 1. In terms of impulse, momentum, force, and collision time, why are airbags and seat belts a good idea? The impulse and total momentum change will be determined by the crash but the impact force on the passenger can be lessened by the use of airbags and seat belts which increase the time of the collision making the force less. 2. Which undergoes more momentum change, a ball batted from a tee at a speed of 30 m/s or a ball pitched and hit at speeds of 30 m/s? Explain. The pitched ball undergoes a velocity change of 60 m/sec and the Tee ball undergoes a velocity change of 30 m/s. Thus the pitched ball undergoes more momentum change and receives a greater impulse. 3. Is momentum conserved in an “explosion”? – If yes, how is the momentum conserved in the following? Yes! Shooting a cannon? Cannon and ball carry equal momentum Jumping off a boat or cart? Jumper and cart or boat carry equal momentum Tossing a large ball in space? The astronaut and ball carry equal momentum 4. Is the impulse delivered by an elastic ball more or less or the same as that delivered by an inelastic ball when dropped from the same height? The elastic ball imparts a greater impulse and undergoes more momentum change. The elastic ball has a double velocity change (e.g. +10 m/s to -10 m/s) 5. When a bullet is shot from a gun, the recoil momentum is equal to the bullet’s momentum. Which has more kinetic energy? Since the bullet and the gun have the same momentum the lighter bullet carries more kinetic energy. As a simple example: Take a gun and bullet both having momentum of 100. The gun mass is 100 and the bullet mass is 1. The bullet velocity is 100 with KE = ½(1)(100)2 = 5000J and the gun velocity of 1 carries KE = ½(100)(1)2 = 50J. 6. Is momentum a vector or a scalar? In a 2-dimensional collision, are both the x and y momentum components conserved? Momentum is a vector. Yes both components are conserved. Like projectile motion, the 2D problem becomes two 1D problems linked with KE. 7. Is KE conserved in collisions? Is KE a scalar or a vector? 8. Comparing mass and momentum and KE: Is the mass of a normal bowling ball always more than a baseball? Y Is the momentum of a bowling ball always more than that of a baseball? N Is the KE of a bowling ball always more than that of a baseball? N If they have the same momentum, is the KE of a baseball always more than a bowling ball? Y Many people confuse mass and momentum and kinetic energy. The most confusing may be the relationship between momentum and kinetic energy. It is possible to show that KE = p 2/2m indicating that for the same momentum, less massive objects carry more KE. See question 5. 9. Is it the impulse or the force that hurts in collisions? Force In a collision, does an air bag change the impulse or the force on the passenger? Force Why does the sheet keep the egg from breaking? This refers to the video where an egg is thrown into the sheet. The sheet takes the impulse and spreads it out over a longer time thus the force on the egg is reduced. 10. Why do cars have crumple zones instead of springy bumpers? Are automobile collisions mostly elastic or inelastic? Automobile collisions are mostly inelastic by design. Elastic collisions will have a greater impulse since the velocity change will be greater. See questions 2 & 4. 11. Why do football helmets have padding on the inside? Once again, to lengthen the time of the collision reducing the force. 12. In elastic collisions the coefficient of restitution is equal to 1. What does that mean? This means that the relative speed of approach and departure are the same between objects colliding. This is an important factoid because if you know one of the speeds after the collision, it is easy to determine the other without detailed calculations and you know that KEtotal is conserved in the collision. Two object approaching at 10 will depart at 10 regardless of the relative masses. 13. In the early days of rockets, it was stated that they could not operate in space because there was nothing to push against. What is wrong with this thought? What do rockets push against? Yes, some people believed this to be the case, but the rocket doesn’t push against the launch pad, it uses its gas to push against it. Part of the rocket throws the other part. The rocket pushes gas out the back which pushes the rocket forward. 14. Two students on roller skates stand face to face and push each other away. One student (A) has a mass of 90 kg and the other (B) has a mass of 60 kg. Which student will have the greater momentum and which will have the greater kinetic energy following the shove? a. b. c. d. A has greater momentum and kinetic energy A has greater momentum and less kinetic energy Each has the same momentum and kinetic energy Each has the same momentum but B has the greater kinetic energy 15. In testing football helmet padding materials it was found that for average head size the padding material labeled type A would spread an average direct hit “collision time” over a time interval of 0.11 seconds. Type B material would spread the time interval over a “collision time” interval of 0.14 seconds. Compare the average force for these materials for an impulse of 10 kg m/sec. J = FΔt 10 = FA(0.11) 10 = FB(0.14) FA = 90.9 N FB = 71.4 N Type B has less average force and is better. 16. A hockey player makes a slap shot, exerting a constant force of 30.0 N on the hockey puck for 0.16 sec. What is the magnitude of the impulse given to the hockey puck? J = FΔt = (30.0N)(0.16s) = 4.8 kg∙m/s