Final shoulder dystocia
advertisement

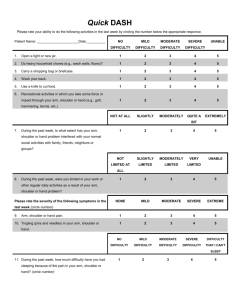
SHOULDER DYSTOCIA DEFINITION Shoulder dystocia is defined as a vaginal cephalic delivery that requires additional obstetric manoeuvres to deliver the fetus after the head has delivered and gentle traction has failed. Time delay between head and shoulder delivery > 60 seconds DO NOT Panic Give excessive traction over fetal head Apply fundal pressure Routine traction in an axial direction can be used to diagnose shoulder dystocia but any other traction should be avoided. Factors associated with shoulder dystocia Pre-labour Previous shoulder dystocia Diabetes mellitus 30kg/m2 Induction of labour ALARMER: A-Ask for assistance L-Lift up the buttocks A-Anterior disimpactation of shoulder R-Rotation of posterior arm M-Manual removal of posterior arm E- Episiotomy R-Roll over Baby should be delivered within 7 minutes Intrapartum Prolonged first stage of labour Secondary arrest Prolonged second stage of labour Oxytocin augmentation Assisted vaginal delivery First line – Mc Roberts and suprapubic pressure Second line – rotational Thirdline – symphysiotomy, cleidotomy and zavenelli McRoberts maneuver Flex and abduct the maternal hips, position the maternal thighs up on to the maternal abdomen. This position flattens the sacral promontory and results in cephalad rotation of the pubic symphysis.this straightens the lumbosacral angle and results in disimpaction of anterior shoulder Success rate -90% Rubin’s maneuver (Disimpaction of the shoulder) Suprapubic pressure Assistant places the hand suprapubically over the posterior aspect of fetal anterior shoulder, applying pressure in downward and lateral direction Continue the downward traction Do not apply fundal pressure. Initially apply the pressure continuously , but if delivery is not accomplished apply rocky motion which dislodges the shoulder from behind the pubic symphysis If this is not successful Insert two fingers of right hand vaginally behind the posterior aspect of the approachable shoulder of the fetus and rotate the shoulder towards the fetal chest (adduction) This reduces the diameter of fetal shoulder girdle Bisacromial diameter occupies the larger oblique diameter Not possible to deliver Follow one of the following 3 manouvres Manual removal of Posterior arm : Most commonly followed when Mc Robert fails Done by the obstetrician Give liberal episiotomy Place right hand in the vagina Locate the posterior fetal arm, flex the fetal elbow and deliver the forearm by sweeping it across the fetal chest WOODS CROK SCREW MANEUVER Insert two fingers of right hand vaginally , place them on the anterior aspect of fetal posterior shoulder rotate the shoulder away from the fetal chest through 180 degrees bring it under the pubic symphysis and deliver Deliver the shoulder which is in the sacral hollow. If not possible rotate it by 180 degrees bring it under pubic symphysis and deliver. COMBINATION OF RUBINS AND WOODS CORK SCREW The Rubin and Woods cork screw maneuver may be combined . Downward traction should be continued during these rotational maneuvers, stimulating the rotation of the screw being removed . ROLL OVER- ALL FOURS OR GASKIN MANOUVRE Roll the patient onto her hands and knees . Provide gentle downward traction to deliver the posterior shoulder with aid of gravity. This maneuver increases pelvic diameter – inlet AP diameter increases as much as 1 cm and the outlet AP diameter increases upto 2 cms But it is not evidence based Success rate 83% Zavanelli maneuver: For bilateral shoulder dystocia Done under GA Rotate the head to undo the restitution and flex to undo the extension and then replace in the vagina maintaining a constant firm pressure. Caeserean is performed immediately Destructive procedures -Cleidotomy -Symphysiotomy ABDOMINAL RESCUE For bilateral shoulder dystocia unresponsive to cephalic replacement LSCS is performed Elevate the anterior shoulder and rotate it to oblique position-posterior shoulder descends beneath the promontory where it can be delivered directly Then rotate the fetal body so that the impacted anterior shoulder enters the pelvis and it can be delivered There is significant maternal morbidity associated with shoulder dystocia, particularly postpartum haemorrhage (11%) and third and fourth degree perineal tears (3.8%).11 Other reported complications include vaginal lacerations,80 cervical tears, bladder rupture, uterine rupture, symphyseal separation, sacroiliac joint dislocation and lateral femoral cutaneous neuropathy