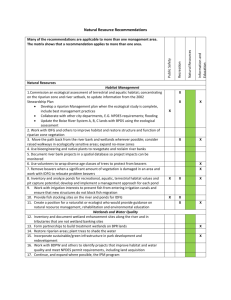
S2. Relationships between hydrological alterations, components of
advertisement

S2. Relationships between hydrological alterations, components of nature and benefits Table S2.1 Relationships between hydrological alterations and elements of the river ecosystem Hydrological alterations Sign of Affected components of Interviewees that originating an impact the effect the river ecosystem identified such link Reduction of the current flow Status of native fishes I-03, I-09, I-13 magnitude Reduction of the current flow Status of native eels I-20 magnitude Reduction of the current flow Water quality I-09, I-14, I-20, I-17 magnitude Reduction of the current flow Aesthetics of the I-13, I-14, I-16, I-01, magnitude landscape I-02 Reduction of the annual flow Biodiversity in terms of I-14 magnitude species and habitats Reduction of the annual flow Structure and quality of I-03 magnitude riparian vegetation Reduction of the annual flow + Sea water invasion I-20 magnitude Reduction of the annual flow Aquifer level I-12 magnitude Higher flows in summer Structure and quality of I-11 riparian vegetation Higher flows in summer Status of native fishes I-13 Higher flows in summer + Spread of exotic species I-11, I-13 Flow stabilization Structure and quality of I-13 riparian vegetation Flow stabilization Status of native fishes I-11, I-03 References used for cross-checking (Jowett and Richardson 1995; Næsje et al. 1995; Whiting 2002; Benejam et al. 2010) (Jowett and Richardson 1995) (Poff et al. 1997) (Brown and Daniel 1991; Pflüger et al. 2010) (Whiting 2002) (Johnson et al. 1976; Whiting 2002; Richardson et al. 2007) (Glover 1959) (Glover 1959; Whiting 2002) (Poff et al. 1997; Richardson et al. 2007) (Næsje et al. 1995; Whiting 2002) (Aparicio et al. 2000) (Poff et al. 1997; Richardson et al. 2007) I-02, I-01 (Næsje et al. 1995; Whiting 2002; Bunn and Arthington 2002) (Aparicio et al. 2000; Lake 2003; Prats et al. 2009; Boix et al. 2010) (Poff et al. 1997) (Busch and Smith 1995; Poff et al. 1997; Richardson et al. 2007) (Ballinger and Lake 2006) I-01 (Cushman 1985; Poff et al. 1997) I-11, I-10, I-03 (Cushman 1985; Næsje et al. 1995; Poff et al. 1997; Whiting 2002; Lake 2003; Benejam et al. 2010; Boix et al. 2010) (Closs and Lake 1996; Scott and Helfman 2001; Boix et al. 2010) (Glover 1959; Lake 2003) (Closs and Lake 1996; Scott and Helfman 2001; Boix et al. 2010) (Pflüger et al. 2010) Flow stabilization + Spread of exotic species I-09, I-11, I-13, I-03 Flow stabilization Prolonged low flows - I-13 I-02 Prolonged low flows - Prolonged low flows - Prolonged low flows - Water quality Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Status of native terrestrial fauna Status of native aquatic birds Status of native fishes Prolonged low flows - Spread of exotic species I-11, I-03 Prolonged low flows Prolonged low flows +/- I-12 I-10, I-04, I-01 Prolonged low flows - Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency - Aquifer level Biodiversity in terms of species and habitats Aesthetics of the landscape Diversity of river morphology Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency Lower flow velocity of water upstream Lower flow velocity of water upstream Lower flow velocity of water upstream Lower flow velocity of water upstream Capture sediment moving downstream - Aquifer level I-12, I-04 - I-13 - Biodiversity in terms of species and habitats Status of native fishes I-03 (Kingsford and Thomas 1995; Kondolf and Wilcock 1996; Bunn and Arthington 2002) (Jowett and Richardson 1995) + Spread of exotic species I-14, I-15, I-03 (Janes et al. 1996; Geiger et al. 2005; Boix et al. 2010) - Water quality I-15, I-03 (Friedl and Wüest 2002) - Aesthetics of the landscape Diversity of river morphology I-06 (Pflüger et al. 2010) I-11, I-08, I-12 (Ligon et al. 1995; Poff et al. 1997; Kondolf 1997) - - I-13, I-02 I-11, I-13 I-13 (Jackson and Beschta 1992; Ligon et al. 1995; Kondolf and Wilcock 1996; Whiting 2002) (McBride and Strahan 1984; Kondolf and Wilcock 1996; Poff et al. 1997; Whiting 2002; Richardson et al. 2007) (Glover 1959; Whiting 2002) 1 Table S2.2 Relationship between hydrological alterations and benefits for the human well-being Hydrological alterations originating an impact Effect Affected benefits Interviewees that identified such link* Reduction of the current flow magnitude Preservation of historical canals I-16, I-19, I-15 Reduction of the current flow magnitude Hydropower I-09, I-07 Reduction of the annual flow magnitude Preservation of wetlands I-14 Reduction of the annual flow magnitude Preservation of coastal ecosystems I-17, I-11, I-16 Reduction of the annual flow magnitude Drinking water supply I-10 Reduction of the annual flow magnitude Irrigation I-19 Reduction of the annual flow magnitude Inter-basin water transfer I-13, I-15 Higher flows in summer + Irrigation I-11, I-15 Flow stabilization + Hydropower I-11 Prolonged low flows + Preservation of historical canals I-16, I-19, I-15 Prolonged low flows Swimming I-01 Prolonged low flows Grazing I-04, I-01 Prolonged low flows Hydropower I-07 Prolonged low flows Industry water supply I-05 Prolonged low flows Intensive farming I-08 Prolonged low flows Irrigation I-16, I-15 Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency Preservation of wetlands I-17, I-11, I-12 Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency Preservation of coastal ecosystems I-17 Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency + Hydropower I-11, I-07 Reduced high flows in terms of magnitude and frequency + Security against floods I-13, I-02, I-05 Rapid changes in river stage Riverbank activities I-13 Rapid changes in river stage Swimming I-13 Rapid changes in river stage Washing clothes I-13 Rapid changes in river stage Angling I-13 Rapid changes in river stage Boating I-13 Rapid changes in river stage Hydropower I-09 Lower flow velocity of water upstream Boating I-11 Lower flow velocity of water upstream Relaxing sound of the flowing stream I-06, I-07 Lower flow velocity of water upstream Dumping debris I-06 Capture sediment moving downstream Preservation of coastal ecosystems I-11, I-16, I-12 *As we rely on the stakeholders’ opinion on how the ecosystem generates benefits for the human well-being, we didn’t need to cross-check with the literature. 2 Table S2.3 Relationship among components of the river ecosystem Components of the rivers whose Sign of Affected components of maintenance has an effect the effect the river ecosystem Aquifer level + Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Aquifer level Sea water invasion Aquifer level + Water quality of aquifers Biodiversity in terms of species + Aesthetics of the and habitats landscape Diversity of river morphology + Biodiversity in terms of species and habitats Diversity of river morphology + Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Diversity of river morphology + Status of native fishes Diversity of river morphology Spread of exotic species Spread of exotic species + - Status of native amphibians + Status of native fishes Status of native fishes + + Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Structure and quality of riparian vegetation Water quality + Water quality Water quality Water quality + + Interviewees that identified such link I-11 I-12, I-04 I-12 I-01 References used for cross-checking (Johnson et al. 1976; Whiting 2002; Richardson et al. 2007) (Glover 1959) (Glover 1959) (Montgomery 2002) I-13 (Aparicio et al. 2000) I-13 (Richardson et al. 2007) I-09 I-02 (Meffe and Sheldon 1988; Pusey et al. 1993; Aparicio et al. 2000; Bunn and Arthington 2002) (Kondolf 1997) (Roberts et al. 1995) (Stanford et al. 1996; Poff et al. 1997; Aparicio et al. 2000; Bunn and Arthington 2002) * I-01 I-02 (Ruiz-Olmo et al. 2001) (Lake 2003) I-13, I-03 (Whiting 2002) I-02 (Ballinger and Lake 2006) I-11, I-08, I-12 I-14 I-13 + Aquifer level Water quality Biodiversity in terms of species and habitats Status of native aquatic birds Status of native otters Status of native aquatic birds Biodiversity in terms of species and habitats Status of native terrestrial fauna Status of native fishes I-03 (Baltz and Moyle 1984; Whiting 2002) + Water quality I-08, I-03 + Aesthetics of the landscape Status of native fishes I-13, I-01, I-02 (Baltz and Moyle 1984; Knight and Bottorff 1984; Whiting 2002; Richardson et al. 2007) (Pflüger et al. 2010) + + Status of native crayfish Spread of exotic species Aesthetics of the landscape * Too specific relationship to find suitable references for cross-checking I-09, I-13, I-10, I-18, I20, I-15 I-06 I-09 I-13, I-14, I-01 (Aparicio et al. 2000) * * (Pflüger et al. 2010) 3 Table S2.4 Relationship between natural elements of the river ecosystem and benefits for the human well-being Components of the rivers whose maintenance has an Sign of the Interviewees that identified such effect effect Affected benefits link* Aesthetics of the landscape + Appreciation of the natural I-10, I-08 environment Aesthetics of the landscape + Riverbank activities I-11, I-10 Aesthetics of the landscape + Angling I-03 Aesthetics of the landscape + Walking, jogging and cycling I-09, I-10, I-16, I-01 Aquifer level + Preservation of wetlands I-11, I-12 Aquifer level + Intensive farming I-10 Aquifer level + Drinking water supply I-10, I-12 Aquifer level + Irrigation I-11 Biodiversity in terms of species and habitats + Appreciation of the natural I-08 environment Diversity of river morphology + Swimming I-01 Diversity of river morphology + Security against floods I-08 Sea water invasion Irrigation I-12 Sea water invasion Preservation of wetlands I-20 Sea water invasion Drinking water supply I-20, I-12 Spread of exotic species Preservation of historical canals I-13 Spread of exotic species Swimming I-09 Spread of exotic species +/Angling I-09, I-17, I-10, I-16 Spread of exotic species +/Appreciation of the natural I-13, I-20 environment Status of native amphibians + Appreciation of the natural I-02 environment Status of native aquatic birds + Appreciation of the natural I-09, I-13, I-02 environment Status of native crayfish + Appreciation of the natural I-02 environment Status of native eels + Angling I-09 Status of native fishes + Angling I-10, I-03, I-01 Status of native fishes + Appreciation of the natural I-13 environment Status of native otters + Appreciation of the natural I-01 environment Status of native otters + Game I-11, I-01 Status of native terrestrial fauna + Appreciation of the natural I-02 environment Structure and quality of riparian vegetation +/Appreciation of the natural I-02 environment Structure and quality of riparian vegetation + Riverbank activities I-10 Structure and quality of riparian vegetation + Swimming I-10 Structure and quality of riparian vegetation + Angling I-03 Structure and quality of riparian vegetation + Walking, jogging and cycling I-13, I-16 Structure and quality of riparian vegetation + Timber extraction I-11, I-10, I-08 Structure and quality of riparian vegetation + Security against floods I-08 Water quality + Swimming I-09, I-10, I-20, I-01, I-07 Water quality + Drinking water supply I-10, I-20 Water quality of aquifers + Drinking water supply I-10 *As we rely on the stakeholders’ opinion on how the ecosystem generates benefits for the human well-being, we didn’t need to cross-check with the literature. 4 References Aparicio E, Vargas MJ, Olmo JM, de Sostoa A (2000) Decline of native freshwater fishes in a Mediterranean watershed on the Iberian Peninsula: a quantitative assessment. Environ Biol Fishes 59:11–19. Baltz DM, Moyle PB (1984) The influence of riparian vegetation on stream fish communities of California. In: Warner RE, Hendrix KM (eds) Calif. Riparian Syst. Ecol. Conserv. Product. Manag. University of California Press, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London, pp 183–189 Ballinger A, Lake PS (2006) Energy and nutrient fluxes from rivers and streams into terrestrial food webs. Mar Freshw Res 57:15. doi: 10.1071/MF05154 Benejam L, Angermeier PL, Munné A, García-Berthou E (2010) Assessing effects of water abstraction on fish assemblages in Mediterranean streams. Freshw Biol 55:628–642. doi: 10.1111/j.13652427.2009.02299.x Boix D, García-Berthou E, Gascón S, et al. (2010) Response of community structure to sustained drought in Mediterranean rivers. J Hydrol 383:135–146. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.01.014 Brown TC, Daniel TC (1991) Landscape Aesthetics of Riparian Environments: Relationship of Flow Quantity to Scenic Quality Along a Wild and Scenir River. Water Resour Res 27:1787–1795. Bunn SE, Arthington AH (2002) Basic Principles and Ecological Consequences of Altered Flow Regimes for Aquatic Biodiversity. Environ Manage 30:492–507. doi: 10.1007/s00267-002-2737-0 Busch DE, Smith SD (1995) Mechanisms associated with decline of woody species in riparian ecosystems of the southwestern US. Ecol Monogr 65:347–370. doi: 10.2307/2937064 Closs GE, Lake PS (1996) Drought, differential mortality and the coexistence of a native and an introduced fish species in a south east Australian intermittent stream. Environ Biol Fishes 47:17–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00002376 Cushman RM (1985) Review of Ecological Effects of Rapidly Varying Flows Downstream from Hydroelectric Facilities. North Am J Fish Manag 5:330–339. doi: 10.1577/15488659(1985)5<330:ROEEOR>2.0.CO;2 Friedl G, Wüest A (2002) Disrupting biogeochemical cycles – Consequences of damming. Aquat Sci 64:55– 65. Geiger W, Alcorlo P, Baltanás A, Montes C (2005) Impact of an introduced Crustacean on the trophic webs of Mediterranean wetlands. Biol Invasions 7:49–73. doi: 10.1007/s10530-004-9635-8 Glover RE (1959) The pattern of fresh-water flow in a coastal aquifer. J Geophys Res 64:457–459. doi: 10.1029/JZ064i004p00457 Jackson WL, Beschta RL (1992) Instream flows for rivers: maintaining stream form and function as a basis for protecting dependent uses. In: Jones ME, Laeanen A (eds) Interdiscip. Approaches Hydrol. Hydrogeol. American Institute of Hydrology, St. Paul, MN, pp 524–535 Janes RA, Eaton JW, Hardwick K (1996) The effects of floating mats of Azolla filiculoides Lam. and Lemna minuta Kunth on the ground of submerged macrophytes. Hydrobiologia 340:23–26. 5 Johnson WC, Burgess RL, Keammerer WR (1976) Forest Overstory Vegetation and Environment on the Missouri River Floodplain in North Dakota Author. Ecol Monogr 46:59–84. Jowett IG, Richardson J (1995) Habitat preferences of common, riverine New Zealand native fishes and implications for flow management. New Zeal J Mar Freshw Res 29:13–23. doi: 10.1080/00288330.1995.9516635 Kingsford RT, Thomas RF (1995) The Macquarie Marshes in Arid Australia and their waterbirds: A 50-year history of decline. Environ Manage 19:867–878. doi: 10.1007/BF02471938 Knight AW, Bottorff RL (1984) The importance of riparian vegetation to stream ecosystems. In: Warner RE, Hendrix KM (eds) Calif. Riparian Syst. Ecol. Conserv. Product. Manag. University of California Press, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London, pp 160–167 Kondolf GM (1997) PROFILE: Hungry Water: Effects of Dams and Gravel Mining on River Channels. Environ Manage 21:533–51. Kondolf GM, Wilcock PR (1996) The Flushing Flow Problem: Defining and Evaluating Objectives. Water Resour Res 32:2589–2599. doi: 10.1029/96WR00898 Lake PS (2003) Ecological effects of perturbation by drought in flowing waters. Freshw Biol 48:1161–1172. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01086.x Ligon FK, Dietrich WE, Trush WJ (1995) Downstream ecological effects of dams. Bioscience 45:183–192. McBride JR, Strahan J (1984) Establishment and survival of woody riparian species on gravel bars of an intermittent stream. Am Midl Nat 235–245. Meffe GK, Sheldon AL (1988) The Influence of Habitat Structure on Fish Assemblage Composition in Southeastern Blackwater Streams. Am Midl Nat 120:225–240. doi: 10.2307/2425994 Montgomery C (2002) Ranking the benefits of biodiversity: an exploration of relative values. J Environ Manage 66:313–326. Næsje T, Jonssons B, Skurdal J (1995) Spring flood: a primary cue for hatching of river spawning Coregoninae. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 52:2190–2196. doi: 10.1139/f95-811 Pflüger Y, Rackham A, Larned S (2010) The aesthetic value of river flows: An assessment of flow preferences for large and small rivers. Landsc Urban Plan 95:68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2009.12.004 Poff NL, Allan JD, Bain MB, et al. (1997) The Natural Flow Regime. A paradigm for river conservation and restoration. Bioscience 47:769–784. Prats J, Dolz J, Armengol Bachero J (2009) Variabilidad temporal en el comportamiento hidráulico del curso inferior del río Ebro. Ing del agua 16:259–272. Pusey BJ, Arthington AH, Read MG (1993) Spatial and temporal variation in fish assemblage structure in the Mary River, south-eastern Queensland: the influence of habitat structure. Environ Biol Fishes 37:355– 380. doi: 10.1007/BF00005204 Richardson DM, Holmes PM, Esler KJ, et al. (2007) Riparian vegetation: degradation, alien plant invasions, and restoration prospects. Divers Distrib 13:126–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-4642.2006.00314.x 6 Roberts J, Chick A, Oswald L, Thompson P (1995) Effect of carp, Cyprinus carpio L., an exotic benthivorous fish, on aquatic plants and water quality in experimental ponds. Mar Freshw Res 46:1171–1180. doi: 10.1071/MF9951171 Ruiz-Olmo J, López-Martín JM, Palazón S (2001) The influence of fish abundance on the otter (Lutra lutra) populations in Iberian Mediterranean habitats. J Zool 254:325–336. Scott MC, Helfman GS (2001) Native Invasions, Homogenization, and the Mismeasure of Integrity of Fish Assemblages. Fisheries 26:6–15. doi: 10.1577/1548-8446(2001)026<0006:NIHATM>2.0.CO;2 Stanford JA, Ward J V, Liss WJ, et al. (1996) A General Protocol for Restoration of Regulated Rivers. Regul Rivers Res Manag 12:391–413. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1646(199607)12:4/5<391::AIDRRR436>3.0.CO;2-4 Whiting PJ (2002) Streamflow Necessary for Environmental Maintenance. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 30:181–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.30.083001.161748 7