10.9 Notes (Completed)
advertisement

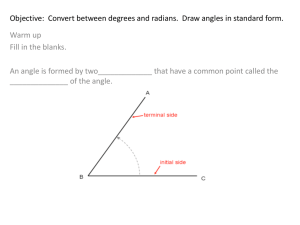
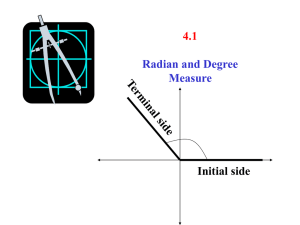
P.o.D. – Solve each triangle using the Law of Cosines/Sines. 1.) a=7, b=4, C=102 degrees. Find c. 2.) C=59 degrees, a=13, b=12. Find c. 3.) a=13, b=6, c=15. Find A. 4.) a=7, b=7, C=85 degrees. Find c. 5.) a=18, b=24.5, C=20 degrees. Find c. 1.) 8.8 2.) 12.3 3.) 59.3 degrees 4.) 9.5 5.) 9.8 10-9: Radian Measure Learning Target(s): I can approximate values of trigonometric functions using a calculator; convert angle measures from radians to degrees or vice versa. Angles have two sides: 1. An initial side 2. A terminal side Terminal Side Initial Side - The endpoint of the two rays is known as the vertex. - An angle centered at the origin is said to be in Standard Position. - Positive angles are measured counterclockwise. - Negative angles are measure clockwise. - If two angles have the same position, then they are said to be co-terminal. Radian vs. Degree: - Just as distance may be measured in feet and centimeters, angles can be measured in both radians and degrees. Definition of a Radian: 𝑠 𝜃 = , where s is the arc length 𝑟 and r is the radius. Conversion Factors: 2𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 = 360° 𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 = 180° 1 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛 ≈ 57.3° Some Other Common Radian Measures: 𝜋 45° = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 4 𝜋 60° = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 3 𝜋 30° = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 6 𝜋 90° = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 2 Acute Angles are between 0 and 𝜋 radians. 2 𝜋 Obtuse Angles are between and 2 𝜋 radians. EX: For the positive angle 9𝜋 subtract 2𝜋 to obtain a coterminal angle. 9𝜋 9𝜋 8𝜋 𝜋 − 2𝜋 = − = 4 4 4 4 4 EX: For the positive angle 5𝜋 6 subtract 2𝜋 to obtain a coterminal angle. 5𝜋 5𝜋 12𝜋 7𝜋 − 2𝜋 = − =− 6 6 6 6 EX: For the negative angle − 3𝜋 add 2𝜋 to find a coterminal angle. 3𝜋 −3𝜋 8𝜋 5𝜋 − + 2𝜋 = + = 4 4 4 4 Recall your Quadrants for Geometry: In Q1 0 < 𝜃 < In Q2 𝜋 2 𝜋 2 <𝜃<𝜋 4 , In Q3 𝜋 < 𝜃 < In Q4 3𝜋 2 3𝜋 2 < 𝜃 < 2𝜋 Complementary – two angles 𝜋 whose sum is radians or 90 2 degrees. Supplementary – two angles whose sum is 𝜋 radians or 180 degrees. EX: Find the complement and 𝜋 supplement of . 6 Complement: 𝜋 𝜋 3𝜋 𝜋 2𝜋 𝜋 − = − = = 2 6 6 6 6 3 Supplement: 𝜋 6𝜋 𝜋 5𝜋 𝜋− = − = 6 6 6 6 EX: Find the complement and supplement of 5𝜋 6 . Complement: 𝜋 5𝜋 3𝜋 5𝜋 −2𝜋 −𝜋 − = − = = 2 6 6 6 6 3 Since the angle is negative, no complement exists. Supplement: 5𝜋 6𝜋 5𝜋 𝜋 𝜋− = − = 6 6 6 6 *There are 360 degrees or 2𝜋 radians in a circle. Conversions Between Degrees and Radians: 1. To convert degrees to radians, multiply degrees by 𝜋 . 180 2. To convert radians to degrees, multiply radians by 180 𝜋 . EX: Convert 60 degrees to radians in terms of pi. 60° 𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 60𝜋 𝜋 × = = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 1 180° 180 3 EX: Convert 320 degrees to radians in terms of pi. 320 𝜋 320𝜋 16𝜋 × = = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 1 180 180 9 EX: Convert -30 degrees to radians in terms of pi. −30 𝜋 −30𝜋 −𝜋 × = = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 1 180 180 6 *We could write this as a positive angle. −𝜋 −𝜋 12𝜋 11𝜋 + 2𝜋 = + = 𝑟𝑎𝑑𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑠 6 6 6 6 𝜋 EX: Express as a degree 6 measure. 𝜋 180 180 × = = 30° 6 𝜋 6 EX: Express 5𝜋 3 as a degree measure. 5𝜋 180 900 × = = 300° 3 𝜋 3 EX: Express 3 radians as a degree measure. 3 𝑟𝑎𝑑 180° 540 × = 𝑑𝑒𝑔𝑟𝑒𝑒𝑠 1 𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑 𝜋 ≈ 171.887° *We could also have done 3(57.3) = 171.9° *Let’s write a calculator program to convert radians to degrees and vice versa. Recall: 𝜃 = 𝑠 𝑟 Arc Length: 𝑠 = 𝑟𝜃, where r is the radius and theta is the measure of the central angle. - It is important to note that theta must always be in radians when used in a formula. EX: A circle has a radius of 27 inches. Find the length of the arc intercepted by a central angle of 160 degrees. First, convert 160 degrees to radian measure. 160° 𝜋 160𝜋 8𝜋 × = = 1 180° 180 9 Next, apply the formula for arc length, 𝑠 = 𝑟𝜃. 8𝜋 𝑠 = 27 ( ) = 9 24𝜋 ≈ 75.398 𝑖𝑛𝑐ℎ𝑒𝑠 Linear Speed (v): Linear Speed v = 𝑎𝑟𝑐 𝑙𝑒𝑛𝑔𝑡ℎ 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 = 𝑠 𝑡 Angular Speed 𝜔 (omega): 𝑐ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑒 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑟𝑎𝑙 𝑎𝑛𝑔𝑙𝑒 𝜃 𝜔= = 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑡 EX: The second hand of a clock is 8 centimeters long. Find the linear speed of the tip of this second hand as it passes around the clock face. We first need to find the distance (arc length) traveled by the second hand as it makes one complete revolution. 𝑠 = 𝑟𝜃 = 8(2𝜋) = 16𝜋 Now find its linear speed. 𝑠 16𝜋 4𝜋 𝑐𝑚 ⁄𝑠 𝑣= = = 𝑡 60 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑠 15 ≈ 0.8378 𝑐𝑚/𝑠 EX: The circular blade on a saw rotates at 2400 revolutions per minute. Find the angular speed in radians per second. We can use a process known as dimensional analysis. 2400 𝑟𝑒𝑣 2𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑 1 𝑚𝑖𝑛 × × 1 𝑚𝑖𝑛 1 𝑟𝑒𝑣 60 𝑠𝑒𝑐 4800𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑 = = 80𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑/𝑠𝑒𝑐 60 𝑠𝑒𝑐 EX: Referring to the previous problem, the blade has a radius of 4 inches. Find the linear speed of a blade tip in inches per second. Linear Velocity is Angular Velocity multiplied by Radius, 𝑣 = 𝜔𝑟 𝑣 = 80𝜋(4) = 320𝜋 ≈ 1005.3096 𝑖𝑛/𝑠𝑒𝑐 Area of a Sector: 1 2 𝐴= 𝑟 𝜃 2 EX: A sprinkler on a golf course is set to spray water over a distance of 75 feet and rotates through an angle of 135 degrees. Find the area of the fairway watered by the sprinkler. Let’s first draw a picture of the situation. 135° 𝜋 𝑟𝑎𝑑 3𝜋 𝜃= × = 𝑟𝑎𝑑. 1 180° 4 1 3𝜋 2 𝐴 = (75) ( ) = 2 4 16875𝜋 ≈ 6626.797 𝑠𝑞𝑢𝑎𝑟𝑒 𝑓𝑒𝑒𝑡 8 *Let’s write a calculator program to find the area of a sector. Do the following on your own: a.) Convert 1 degree to radians. b.) Convert 60 degrees to radians. c.) Convert 5𝜋 6 radians to degrees. a.) 0.017 radians 𝜋 b.) 3 c.) 150 degrees Use a calculator to evaluate each of the following in radian mode. a.) Cos(6) b.) tan 7𝜋 6 a.) 0.9602 b.) 0.5774 Clever Uses of Trigonometry: Radians vs. Degrees Gang Sines More appropriate on Pi Day Upon completion of this lesson, you should be able to: 1. Find co-terminal angles. 2. Find the complement and supplement of angles. 3. Convert degrees to radians and vice versa. For more information, visit http://www.mathwarehouse.com/trigonome try/radians/convert-degee-to-radians.php Now get against the wall. We have a unit circle to recite!!!!!! HW Pg. 715 1-28 Quiz 10.5-10.9 tomorrow