Current, Voltage, Resistance Exam Questions
advertisement

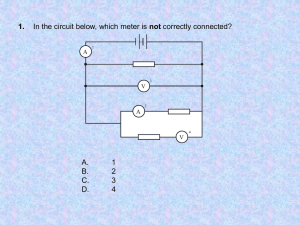
P5 Current, Voltage and Resistance exam questions (markscheme at end) Q1. A set of Christmas tree lights is made from twenty identical lamps connected in series. (a) Each lamp is designed to take a current of 0.25 A. The set plugs directly into the 230 V mains electricity supply. (i) Write down the equation that links current, potential difference and resistance. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the resistance of one of the lamps. Show clearly how you work out your final answer and give the unit. .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... Resistance = ...................................................................... (4) (iii) What is the total resistance of the set of lights? .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... Total resistance = ........................................................ (1) Page 1 (b) How does the resistance of a filament lamp change as the temperature of the filament changes? ............................................................................................................................. ........ ............................................................................................................................. ........ ............................................................................................................................. ........ ............................................................................................................................. ........ (1) (Total 7 marks) Q2. The drawing shows the circuit used to investigate how the current through a 5 ohm (Ω) resistor changes as the potential difference (voltage) across the resistor changes. (a) Draw, in the space below, a circuit diagram of this circuit. Use the correct symbols for each part of the circuit. Page 2 (2) (b) (i) Write down the equation that links current, potential difference and resistance. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the potential difference across the 5 ohm (Ω) resistor when the current through the resistor equals 0.4 A. Show clearly how you work out your final answer. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... potential difference = .............................................. volts (2) (iii) Complete the graph to show how the current through the resistor changes as the potential difference across the resistor increases from 0 V to 3 V. Assume the resistor stays at a constant temperature. Page 3 (2) (c) The resistor is replaced by a 3 V filament lamp. The resistance of the lamp increases as the potential difference across it increases. Why? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 8 marks) Q3. (a) Add the missing labels to the diagram. (3) Page 4 (b) Some students use the circuit shown above. They want to find out how the current through component X changes as they change the voltage. The graph shows their results. Describe, as fully as you can, what happens to the current through component X as the students increase the voltage. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 7 marks) Q4. The circuit shown has four identical ammeters. Page 5 (a) The table gives the current through two of the ammeters. (i) Ammeter Complete the table to show the current through the other two ammeters. Reading on ammeter in amps A1 A2 0.2 A3 0.3 A4 (2) (ii) Which one of the following statements is correct. Tick ( ) the box next to your choice. The resistance of P is more than 20 Ω. The resistance of P is equal to 20 Ω. The resistance of P is less than 20 Ω. Give a reason for your choice. Page 6 ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (b) (i) Write down the equation that links current, potential difference and resistance. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the reading on the voltmeter. Show clearly how you work out your answer. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Voltmeter reading = ……………………………. volts. (2) (iii) State the potential difference of the power supply. ........................................................................................................................... (1) (c) A second circuit contains an unknown component labelled X. As component X is heated, the reading on the ammeter goes up. What is component X? ..................................................................................................................................... Give a reason for your answer. Page 7 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Q5. A student investigates how the current flowing through a filament lamp changes with the voltage across it. She is given a filament lamp and connecting wires. She decides to use a 15V power supply, a variable resistor, an ammeter, a voltmeter and a switch. (a) Complete the circuit diagram to show how she should set up the circuit. (4) (b) The student obtains the following results. VOLTAGE (V) 0.0 3.0 5.0 7.0 9.0 11.0 CURRENT (A) 0.0 1.0 1.4 1.7 1.9 2.1 (i) Plot a graph of current against voltage. Page 8 (3) (ii) Use your graph to find the current when the voltage is 10V. Current .................... A (1) (iii) Use your answer to (ii) to calculate the resistance of the lamp when the voltage is 10V. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... Resistance .................... Ω (2) (c) (i) What happens to the resistance of the lamp as the current through it increases? ........................................................................................................................... Page 9 (ii) Explain your answer. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 12 marks) Q6. (a) The diagram shows a simple circuit. Add an ammeter and a voltmeter to the circuit to show how to measure the current through the fixed resistor and the voltage across it. (2) (b) An experiment using a circuit like the one above was set up. The following results were obtained when the resistance of the variable resistor was decreased. (i) Draw a graph of the results below. Voltage across fixed resistor in volts Current in amps 0.50 0.75 1.00 1.25 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 Page 10 (2) (ii) Use the graph to find the voltage when the current is 0.05 A. Voltage =....................................... V (1) (Total 5 marks) Q7. (a) The diagram shows the voltage-current graphs for three different electrical components. Page 11 Which one of the components A, B or C could be a 3 volt filament lamp? Explain the reason for your choice. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Using the correct symbols draw a circuit diagram to show how a battery, ammeter and voltmeter can be used to find the resistance of the wire shown. (3) (c) When correctly connected to a 9 volt battery the wire has a current of 0.30 amperes flowing through it. (i) Give the equation that links current, resistance and voltage. .......................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Calculate the resistance of the wire. Show clearly how you work out your answer and give the unit. .......................................................................................................................... Page 12 .......................................................................................................................... Resistance = ......................................................... (3) (iii) When the wire is heated, the current goes down to 0.26 amperes. State how the resistance of the wire has changed. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 11 marks) Q8. A circuit was set up as shown in the diagram. (a) The table gives the current through three of the ammeters. Complete the table to show the current through the other two ammeters. Page 13 Ammeter Reading on ammeter in amps Al 0.2 A2 0.6 A3 0.3 A4 A5 (2) (b) The reading on the voltmeter is 12 V. What is the resistance of R2? Show your working and include the correct unit. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Resistance = ....................................... (3) (c) In the circuit above, the resistor R2 burned out and current stopped flowing in it. There was no other change to the circuit. Complete the table below to show the readings on the ammeters after this took place. Ammeter Reading on ammeter in amps Al 0.2 A2 0.0 A3 A4 A5 (3) (Total 8 marks) Page 14 Q9. When a mains lamp is switched on it takes 0.5 seconds for the filament to reach its normal operating temperature. The way in which the current changes during the first second after switching on is shown in the sketch graph below. Mains voltage is 240 V. (a) Calculate the resistance of the filament whilst the lamp is drawing the maximum current. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (b) Describe how the resistance of the lamp changes after the current has reached its maximum value. .................................................................................................................................... Page 15 .................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) Calculate the maximum power taken by the lamp. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (d) Calculate the power of the lamp in normal use. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (e) Calculate the energy used by the lamp in six hours of normal use. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 12 marks) Q10. A computer is set up to produce a graph of the current through an electric lamp during the first few milliseconds after it is switched on. Page 16 The lamp is modified then tested in the same way. (a) Describe three differences in the way the lamp behaves after it has been modified. 1. .......................................................................................................................... 2. .......................................................................................................................... 3. .......................................................................................................................... (3) (b) The current through the modified lamp depends on the total resistance of the filament and component X. The smaller this total resistance is, the greater the current. Page 17 The following graphs show how the resistance of the lamp filament and component X change as the lamp heats up to its operating temperature. Use the information shown on the graphs to explain the behaviour of the modified lamp. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 7 marks) Q11. The circuit contains three identical lamps. Page 18 (a) Complete each of the sentences about the circuit, using one of the phrases in the box. more than (i) less than the same as The current at A is ........................................................... .the current at B. (1) (ii) The current at A is ........................................................... .the current at D. (1) (iii) The current at F is ............................................................. .the current at E. (1) (iv) The current at F is ............................................................ .the current at D. (1) (b) In the circuit, which lamp is brightest?............................. Give a reason for your answer. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Page 19 Q12. The diagrams show a hair-dryer and the circuit inside the hair-dryer. (a) Switches S1, S2 and S3 are all shown in the OFF position. Which switch or switches have to be ON to make: (i) only the fan work? ............................................................................................ (ii) both heaters work? ............................................................................................ (2) (b) (i) What happens to the current in the circuit when the heaters are switched on? ........................................................................................................................... (ii) Suggest why it is important to have the fan working when the heaters are switched on. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (3) Page 20 (c) This hair-dryer has a plastic case. It is connected to a mains socket by a 3-pin plug. The cable connecting the hair-dryer to the plug contains only two wires. (i) Write down the colour of the insulation on the wires. Wire 1 ............................................................................................................... Wire 2 ............................................................................................................... (ii) Which of the usual three wires is not needed? ........................................................................................................................... (iii) This hair-dryer is safe to use without the third wire. Explain why. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (5) (d) The following information is stamped on the hair-dryer. (i) Which number tells us how fast the hair-dryer uses energy? ........................................................................................................................... (ii) On what else does the energy used by the hair-dryer depend? ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 12 marks) Page 21 Q13. The circuit contains two cells, an ammeter and a lamp. The reading on the ammeter is 0.2 A. (a) What will be the reading on the ammeters in each of the circuits below? (i) Current is ................... A (ii) Current is ................... A (2) (b) An ammeter was in a series circuit with two cells and a variable resistor. The ammeter showed a reading of 0.3 A. (i) Draw a circuit diagram for the circuit. (2) Page 22 (ii) What will happen to the reading on the ammeter if the resistance of the variable resistor is increased? .......................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 5 marks) Page 23 M1. (a) (i) potential difference = current × resistance accept voltage or pd for potential difference accept V = I × R accept correct transformation do not accept V = C × R do not accept V = A × R accept provided subsequent use of Δ correct do not accept an equation expressed in units 1 (ii) 46 credit correct transformation for 1 mark allow 1 mark for use of 11.5 V or division of final resistance by 20 a final answer of 920 gains 2 marks only 3 ohm(s) accept symbol Ω do not accept Ω s unit / symbol mark can be awarded in (iii) provided unit / symbol is omitted in (ii) 1 (iii) 920 (ohms) or their (a)(ii) × 20 1 (b) as temperature increases, resistance increases accept hotter for temperature increase do not accept a reference to resistance only i.e. it / resistance goes up 1 [7] Page 24 M2. (a) all symbols correct accept push switch symbol switch may be open or closed any lines through symbols = 0 marks 1 correct circuit drawn polarity of cells not relevant provided they are joined correctly 1 voltmeter must be across resistor only two cells are required in the diagram ignore the order of the components allow small gaps in circuit omission of any component = 0 marks 1 (b) (i) potential difference = current × resistance accept voltage or p.d. for potential difference accept V= I × R accept provided I R subsequent use correct do not accept C for current 1 (ii) 2 allow 1 mark for correct substitution wrong working loses both marks 2 (iii) straight line drawn through the origin judge by eye straight line passes through I = 0.4, V = their (b)(ii) / 2 and 0.0 this mark may be awarded if all points shown including these Page 25 points are correct even if no line is drawn N.B. a curve scores 0 marks 1 (c) temperature increases accept filament lamp / it gets hotter allow heat for temperature 1 [8] M3. (a) • diode • voltmeter • ammeter for 1 mark each 3 (b) idea that • current increases or goes up (with voltage) gains 1 mark • ‘It’ refers to current but current increases steadily (with voltage) gains 2 marks • (allow in proportion) – but not simply a description of the shape of the graph gains 1 mark • no current at first but no current until voltage is more than 0.3 (volts) gains 2 marks 4 [7] Page 26 M4. (a) (i) A1 = 0.5 ignore any units 1 A = 0.5 allow 1 mark for A1 = A4 ≠ 0.5 1 (ii) the resistance of P is more than 20 Ω 1 a smaller current goes through P / A2 (than 20 Ω) dependent on getting 1st mark correct accept converse 1 (b) (i) potential difference = current resistance accept pd / voltage for potential difference accept V = I R, correct symbols and correct case only accept volts = amps ohms accept provided subsequent method is correct allow combination of physical quantities and named units allow voltage = I R 1 (ii) 6 allow 1 mark for correct substitution 2 (iii) 6 accept their (b)(ii) 1 (c) thermistor or Page 27 accept correct circuit symbol allow phonetic spelling 1 resistance goes down (as temperature of thermistor goes up) do not accept changes for goes down do not accept an answer in terms of current only answers in terms of other components are incorrect 1 [10] M5. (a) 4 symbols correct accept (accept for bulb; lose 1 mark if line through symbols, lose 1 mark if circuit incorrect, switch may be open or closed) (allow or ) gains 1 mark 4 but all correct gains 2 marks ammeter in series with lamp for one mark voltmeter in parallel with lamp / lamp and switch / lamp, switch and ammeter for one mark (b) (i) 5 points correctly plotted allow (0, 0) correct if graph goes through the origin even if no × or O gains 1 mark but 6 points correctly plotted gains 2 marks smooth curve through points – not straight line / curve + straight line for one mark 3 Page 28 (ii) 2 (A) allow 0.05 (½ square) from candidates’ graph for one mark 1 (iii) R = V / I or R = 10 / 2 gains 1 mark but R = 5 (Ohms) ecf gains 2 marks 2 (c) (i) resistance increases for one mark (ii) temperature (of filament) has increased / filament gets hot for one mark 2 [12] M6. (a) ammeter anywhere in series in the circuit accept just letter A or box with A voltmeter across or in parallel with the fixed resistor only accept just letter V or box with V 2 (b) (i) four correct plots deduct one for any incorrect plot a straight line through the points no requirement to extrapolate through origin do not credit bar charts unless correct line drawn or correct points 2 (ii) 0.25 ecf rule applies if graph is wrongly plotted Page 29 1 [5] M7. (a) C award mark if A and B identified as not filament lamp 1 resistance increases negated by wrong statement e.g. current goes down 1 as the lamp gets hot accept as current (through lamp) or voltage (across lamp) increases do not accept non-ohmic reason independent of choice of component 1 (b) ammeter wire and battery only in series non standard symbols acceptable if correctly identified (labelled) for ammeter, voltmeter and battery 1 voltmeter only in parallel with wire or battery all in series or ammeter in parallel neither of these two marks awarded 1 all symbols correct ignore lines drawn through centres of symbols 1 (c) (i) voltage = current × resistance accept V = I × R accept volts = amps × ohms do not accept V = C × R Page 30 accept if subsequent method correct 1 (ii) 30 accept correct substitution for 1 mark (9/0.3) 2 ohms accept correct symbol Ω 1 (iii) goes up must be a comparison accept calculation if answer is larger than c (ii) 1 [11] M8. (a) 0.9 1 1.1 accept the value of A4 + 0.2 1 (b) V = I R or 12 = 0.6 R or accept V = A R V = I × ohm’s sign do not credit Ohm’s law triangle 2 R = 20 correct numerical answer earns both marks Page 31 ohms 1 (c) A3 = 0.3 A4 = 0.3 accept the same numeric value as A3 A5 = 0.5 accept the value of A4 + 0.2 3 [8] M9. (a) Current = 0.4A (1) R = V/I or 240/0.4 (1) R = 600 ohm (1) 3 (b) Doubles gets 2 marks OR gets bigger gets 1 mark 2 (c) P = V.I or 240 × 0.4 P = 96W for 1 mark each 2 (d) 1 = 0.2A P = 48W for 1 mark each BUT may get equation mark here if not in (c) 2 Page 32 (e) P = V.I.t (1) P = 240 × 0.2 × 6 × 3600 OR P = 48 × 6 × 3600 gets 1 mark P = 1036800 W gets 1 mark 3 [12] M10. (a) current rises/starts lower/starts from zero for 1 mark ideas that: * smaller/only 0.45 (A) change in current quicker/only 2 (ms) for current to settle slightly lower/0.45 (A) final current maximum only 0.45 (A) rather than 1.5 (A) (*must compare e.g. “only...” or state figure from first graph) any 2 for 1 further mark each 3 (b) resistance of filament rises as temperature rises/higher at operating temperature resistance of X falls as temperature rises/low(er) at operating temperature total resistance stays roughly the same as temperature rises so current stays roughly the same as temperature rises (must be related to previous point) resistance of X falls faster at first than resistance of filament rises so current rises (must be related to previous point) operating resistance slightly increased so operating current slightly reduced (must be related to previous point) resistance of X high at start so current zero/low each gains 1 mark (must be related to previous point) (to a maximum of 4) 4 [7] Page 33 M11. (a) (i) the same as 1 (ii) less than 1 (iii) the same as 1 (iv) more than 1 (b) 3 accept D because there is more or twice the current in this part of the circuit or the resistance is less accept only one lamp to go through, (not two) or on its own not sharing the voltage or energy with another do not credit one lamp to go through or sharing current 2 [6] M12. (a) (i) S3 for 1 mark 1 (ii) S1, S2 and S3 for 1 mark 1 (b) (i) increases/current passes through heaters/current unaffected in fan for 1 mark 1 (ii) (fan) blows/air moving prevents dryer overheating for 1 mark each Page 34 2 (c) (i) brown blue any order for 1 mark each 2 (ii) earth/green and yellow for 1 mark 1 (iii) (case is) plastic plastic does not conduct (electricity) for 1 mark each 2 (d) (i) 1300/power for 1 mark 1 (ii) time/units of time for 1 mark 1 [12] M13. (a) (i) 0.2 1 (ii) 0.2 1 (b) (i) a series circuit must contain two cells the correct way round and an ammeter accept the components in any order in the series circuit but there must be no obvious gaps in the wires at corners Page 35 or joins 1 the symbol for a variable resistor a rectangle with a diagonal arrow drawn through it accept a diagram for a ‘slide resistor’ 1 (ii) decrease 1 [5] Page 36