PlantsvsPollutants Dataset 1
advertisement

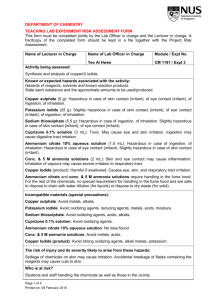
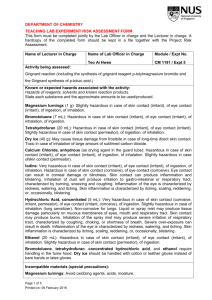
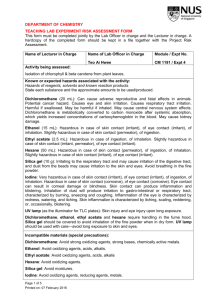
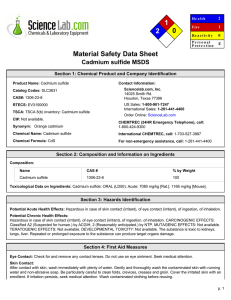
Provided Materials Project Notes Research Advisors may suggest up to three plants to be studied at each laboratory Any plant may be studied at any site Deliverables Research Advisors are responsible for the following deliverables: A list of plant(s) and associated metal(s) to be studied at each laboratory (fill out the Research Advisor Reporting Guide) A formal response letter (use the Letter Template if needed) that must contain the following: o A list of plant species you think would be most useful to our research at each of the sites o A step-wise description of the procedure you used to select these plants o Please be sure that your response letter is written in a formal style, with cohesive structure, transitions, precise language, concrete details and information, a formal style and tone, and a concluding statement Mathematical and/or graphical evidence demonstrating each plant's effectiveness at phytoremediation after 1 growing/harvest cycle, 1 year, 5 years, and 10 years for a contaminated plot of approximately 7 hectares. This can be included in your letter or as a separate attachment. Data Provided for you are data related to what we know already about certain plant species and their ability to accumulate particular metals from contaminated soil (Dataset: Metal Concentrations in Herbaceous Crops). You will need to use these data to inform your decisions. You may wish to consult additional sources as this may improve your ability to make informed decisions. 0 Industrial Site Contamination Profiles Table 1. Contamination by Industrial Site Site Associated Laboratory Contaminant(s) and Percentage of Contamination1 A 1 Arsenic (60%), Cadmium (73%), Copper (100%) B 2 Cadmium (30%), Lead (90%), Zinc (50%) C 3 Cadmium (40%), Copper (100%) D 4 Arsenic (50%), Lead (80%), Zinc (60%) 1Soil at each site was tested with random selection of multiple samples across the suspected contaminated area. Percentage values represent the fraction of samples that tested positive for toxic levels of that particular contaminant. Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) Information: Health Hazard Ratings Health Hazard Data includes information on acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) health effects, signs and symptoms. This section may be less relevant for residential settings where long-term exposures to low doses and complex chemical mixes are more common. Also, since most of the information was developed in relation to adult male exposures, it may be less relevant in residential settings where at-risk populations such as children, the infirm and the elderly live. *Retrieved online from: www.cmhc-schl.gc.ca/en/co/maho/gemare/gemare_012.cfm Table 2. MSDS Health Hazard Codes and Meanings Rating Code 0 1 2 3 4 Meaning No unusual hazard May be irritating May be harmful if inhaled or absorbed Corrosive or toxic. Avoid skin contact or inhalation May be fatal on short exposure. Specialized protective equipment required * MSDS information retrieved online from: www.ehs.neu.edu/laboratory_safety/general_information/nfpa_hazard_rating/ Table 3. Health Hazard Ratings Contaminant Arsenic Cadmium Copper Lead Zinc * MSDS information retrieved online from: www.sciencelab.com Rating 3 3 2 1 1 Material Safety Data Sheet: Exposure Effects Arsenic (As) Short term/acute exposure: Very hazardous in case of ingestion, of inhalation. Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant). Long term/chronic exposure: The substance is toxic to kidneys, lungs, the nervous system, mucous membranes. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Cadmium (Cd) Short term/acute exposure: Hazardous in case of ingestion, of inhalation. Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant, sensitizer), of eye contact (irritant). Severe over-exposure can result in death. Long term/chronic exposure: The substance is toxic to kidneys, lungs, liver. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Repeated exposure to an highly toxic material may produce general deterioration of health by an accumulation in one or many human organs. Copper (Cu) Short term/acute exposure: Very hazardous in case of ingestion. Hazardous in case of eye contact (irritant), of inhalation. Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant). Long term/chronic exposure: The substance is toxic to lungs, mucous membranes. Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Lead (Pb) Short term/acute exposure: Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Long term/chronic exposure: The substance may be toxic to blood, kidneys, central nervous system (CNS). Repeated or prolonged exposure to the substance can produce target organs damage. Zinc (Zn) Short term/acute exposure: Slightly hazardous in case of skin contact (irritant), of eye contact (irritant), of ingestion, of inhalation. Long term/chronic exposure: Repeated or prolonged exposure is not known to aggravate medical condition. * MSDS information retrieved online from: www.sciencelab.com Dataset: Metal Concentrations in Herbaceous Crops* Latin Name Common Name As Cd Cu Pb Zn Plants/ hectare (ha) Metric tons /ha (Dry) Brassica carinata A. Braun1 12 12 37 50 1650 1250000 30 10 71 55 2029 Hordeum vulgare L. 1 Ethiopian mustard Mustard greens Barley 20 16 27 Oryza sativa L. 1 Rice ND 0.4 4 ND 34 Radish ND 9.4 Triticale 21 1.9 Osier (tree), leaves only ND 4.3 Brassica juncea (L.) Czern.1 Raphanus sativus L. 1 Triticosecale, cv. ‘Trujillo’ Salix viminalis 'Orm'2 1 Root Type 5.50 Root Depth (m) <1 Fibrous Days or Years to maturity 160d 200000 9.53 <1 Fibrous 60d 334 3000000 2.24 <1 Fibrous 90d 6 90 220000 20.18 <1 Fibrous 150d 34 28 1450 300000 13.45 <1 Taproot 28d 27. 5 7.6 37 588 4000000 7.85 <2 Fibrous 110d 2.9 362.5 14000 13.61 <2 Fibrous 4y Notes cultivated under flooded conditions extensive roots extensive roots *metal concentrations are expressed as mg of metal per kg of plant material Note. All data values are to be considered reasonable and approximate. ND=no data available 1 Vamerali, T., Bandiera, M., & Mosca, G. (2010). Field crops for phytoremediation of metal-contaminated land. A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 8, 1-17. 2 Vervaeke, P., Luyssaert, S., Mertens, J., Meers, E., Tack, F.M.G., & Lust, N. (2003). Phytoremediation prospects of willow stands on contaminated sediment: a field trial. Environmental Pollution, 126, 275-282. 4 Research Advisor Reporting Guide Laboratory 1 (Industrial Site A) Plant(s) Associated Metal(s) Laboratory 2 (Industrial Site B) Plant(s) Associated Metal(s) Laboratory 3 (Industrial Site C) Plant(s) Associated Metal(s) Laboratory 4 (Industrial Site D) Plant(s) Associated Metal(s)