NEWTON*S LAWS STUDY GUIDE
advertisement

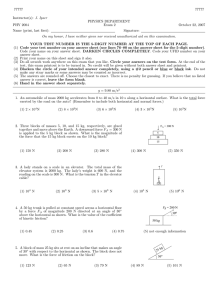
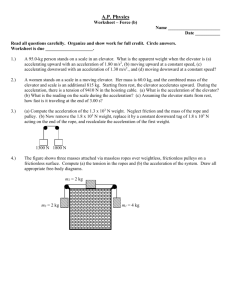
NEWTON’S LAWS STUDY GUIDE (AP 1) 1. A force of 10.0 N is applied at an angle of 30.0o above the horizontal on a 1.25-kg block initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface. a. Draw the free body diagram. b. What is the magnitude of the block’s acceleration? (6.93m/s2) c. What is the magnitude of the normal force? (7.25 N) 2. A 150 N feeder is supported by three cables as shown. Find the tension in each cable. (130N, 98N, 150N) 30o 50o 150 N 3. A 25.5 g bullet leaves the muzzle of a rifle with a speed of 335 m/s. What force (assumed constant) is exerted on the bullet while it is traveling down the 0.78m long barrel of the rifle? (1,800 N) 4. A student decides to move a box of books into her dorm room by pulling on a rope attached to the box with a force of 80N at an angle of 25o with the horizontal. The box of books has a mass of 25 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the floor is 0.30. a. Find the acceleration of the box. (0.37m/s2) b. Along the way, the student must move the box up a ramp inclined at 10 o with the horizontal. If the box starts from rest at the bottom of the incline with the same force, can it be moved up the incline? If so, what is the acceleration up the ramp? (no) 5. A student slides a 2000 N crate across a floor by pulling with a force of 750 N at an angle of 30o with the horizontal. If the crate moves at a constant speed, find the coefficient of friction between the crate and the floor. Is this the static coefficient or the kinetic coefficient? (0.4) 6. A boy drags a 125 N sled up a 25o slope at constant velocity. If the coefficient of friction between the sled and the hill is 0.25, what force must he exert at an angle of 32 o with respect to the hill? (83N) 7. The block m1 (of mass 10.0 kg) sits on a table as shown with coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the table and m1 are 0.60 and 0.40 respectively. a. The block m2 needs what mass to just barely set the system in motion?(hint: use a = 0m/s2, then any mass larger will make it move) (6.0 kg) b. After the system begins to move, what is the acceleration? (1.2m/s2) m1 m2 8. A golf ball is hit with 66 N of force giving the golf ball a velocity of 35 m/s. What is the magnitude of the force in which the golf ball pushes back on the 15 kg club? 9. A 5.0 kg object is sliding to the right at across a frictionless surface. How strong of a force is needed to keep the object sliding to the right? Without an additional pushing/pulling force, will the object slow down? Explain. 10. A 65.0 kg physics student does an experiment in an elevator with a scale. The elevator stays stationary for 2 seconds, then accelerates for 5 seconds, then goes at a constant velocity for 10 seconds and then slows down for 5 seconds until the elevator is again at rest for 2 seconds. a. What is the weight of the physics student when they are not in the elevator? b. Describe the reading of the scale (larger, small or equal to normal weight) for the 24 seconds the elevator is in motion. c. If the scale reads 850 N when t = 4 seconds, what is the acceleration of the elevator? (3.3 m/s2) d. If the scale reads 350 N when t = 20 seconds, what is the acceleration of the elevator? (-4.4 m/s2) e. Draw an acceleration vs time graph for the 24 seconds the student is in the elevator.