File
advertisement

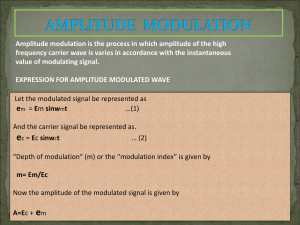
UNIT- 1 2 Marks Frequently Asked Questions: 1. Define modulation. Process by which some parameters (amplitude, frequency and phase) of a high frequency carrier is varied in accordance with the modulating signal. 2. What is the need for modulation? Reduction in antenna height Long distance communication Ease of radiation Multiplexing Improve the quality of reception Avoid mixing of signals 3. Define multiplexing. Transmission of two or more signals simultaneously over the same channel. 4. Define Bandwidth. Difference between upper and lower side band frequencies. Expressed as , BW=fUSB-fLSB 5. (i) Amplitude Modulation: Process of changing the amplitude of a high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal. (ii) Angle Modulation: Process of changing the phase or frequency of a high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal. (iii) Frequency Modulation: Process of changing the frequency of a high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal. (iv) Phase Modulation: Process of changing the phase of a high frequency carrier signal in proportion with the instantaneous value of the modulating signal. 6. What is AM envelope? The shape of the amplitude modulated wave is called as AM envelope. 7. Define Modulation index. Ratio of maximum amplitude of modulating signal to maximum amplitude of carrier signal. For amplitude modulation, m=Em/Ec 8. Define percent modulation of AM. Percentage change in the amplitude of the output wave when modulation process is done. Percentage modulation=m*100 9. Draw the frequency spectrum of AM. Amplitude Ec maEc/2 0 fc-fm maEc/2 fc fc-fm Frequency 10. State Carson’s rule? The bandwidth required to transmit an angle modulated wave as twice the sum of the peak frequency deviation and the highest modulating signal frequency. Mathematically Carson’s rule is BW=2(f +fm) Hz. 11. Define Deviation Ratio. Ratio between peak frequency deviation and the maximum modulating signal frequency. Mathematically ,the deviation ratio is DR= f (max) /fm(max) Other Questions: 12. What is communication and the classification of communication system? Process of conveying or transforming the information from one point to another point. Types: Analog communication Digital communication 13. What are advantages, disadvantages and applications of AM wave? Advantages: Used for long distance communication Inexpensive Disadvantages: More likely to be affected by noise. Complexity and Receiver cost is more. Applications: Sound or audio broadcasting Aircraft communications in VHF range Point to point link communication( mobile, ship to shore) 14. What are advantages, disadvantages of angle modulated wave? Advantages: Noise reduction Improved system fidelity Power utilization Disadvantages: Complex transmitters and receivers Manufacturing circuit is more expensive Requires wider bandwidth 15. What is phase deviation and frequency deviation? Phase Deviation: Angular displacement or shift of the carrier phase in radians with respect to reference phase. The change in carrier phase produces corresponding change in frequency. Frequency Deviation: Relative displacement or shift of the carrier frequency in hertz with respect to the modulating signal. 16. Define the following terms: i. Instantaneous phase ii. Instantaneous frequency iii. Instantaneous phase deviation iv. Instantaneous frequency deviation (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Instantaneous phase: Precise phase of the carrier at a given instant of time. Instantaneous phase= ct+(t) radians Instantaneous frequency: Precise frequency of the carrier at a given instant of time. Instantaneous phase deviation: Instantaneous change in the phase of the carrier at a given instant of time and indicates how much the phase of the carrier is changing with respect to its reference phase. Instantaneous phase deviation = (t) radians Instantaneous phase deviation: Instantaneous change in the frequency of the carrier at a given instant of time. Instantaneous frequency deviation = ’(t) rad/sec 17. What is deviation sensitivity of FM? K’= change in the output frequency change in the amplitude of the input = /v (rad/sec/V) 18. What is deviation sensitivity of PM? K= change in phase of the output frequency change in the amplitude of the input = /v (rad/V) 19. Define carrier swing. Peak to peak frequency deviation (2f) 20. Define percent modulation of FM. Ratio of frequency deviation actually produced to the maximum allowable frequency deviation in percent form. % modulation= f (actual) * 100 f (max) 16 marks Frequently Asked Questions: 1. Explain briefly about the Principles of Amplitude Modulation. AM Envelope Shape of the modulated signal Eam=Ec+Em Where,Ec is max. amplitude of carrier signal&Em is max amplitude of modulating signal Modulation index and Percentage Modulation Frequency spectrum and Bandwidth fUSB=fc+fm fLSB=fc-fm Calculation of Modulation Index from AM Waveform m=Em/Ec AM power Distribution m=√2((Ptotal/Pc)-1) Current calculation of AM signal AM by multiple sine waves. Transmission efficiency 2. Explain in detail about Angle Modulation. Process of changing the phase or frequency of the carrier signal in accordance with the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal. Expression of Angle modulated wave: S(t)=Vc cos [2πfct+ (t)] If the frequency of the carrier is varied in accordance with the modulating signal FM occurs. If the phase of the carrier is varied in accordance with the modulating signal PM occurs. Whenever the frequency is varied phase also varied and vice versa. Hence, Direct FM is indirect PM and Direct PM is indirect FM. Direct Frequency modulation- frequency of the carrier is varied in accordance with the modulating signal at a rate equal to the frequency of the modulating signal. Direct Phase modulation- Phase of the carrier is varied in accordance with the modulating signal at a rate equal to the frequency of the modulating signal. Phase deviation - displacement of carrier phase in radians with respect to the reference phase. Frequency deviation- displacement of carrier frequency in Hz with respect to the reference phase. FM and PM waveforms. 3. Compare the performance of AM and FM systems. S. No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Amplitude Modulation Amplitude of the carrier is varied in accordance with the amplitude of the modulating signal. Has poor fidelity due to narrow bandwidth. Most of the power is in carrier hence less efficient. Noise interference is more. Adjacent channel interference is present. Operates in MF and HF range. Only carrier and two side bands are present. Transmission equipment is simple. Transmitter power varies according to modulation index. Depth of modulation has limitations. Frequency Modulation Frequency of the carrier is varied in accordance with the amplitude of the modulating signal. Has better fidelity due to wider bandwidth. Most of the power is useful hence more efficient. Noise interference is less. Adjacent channel interference is avoided. Operates in VHF and UHF range. Infinite number of sidebands present. Transmission equipment is complex. Transmitter power remains constant. Depth of modulation has no limitations. Other questions: 4. Explain about the Frequency Analysis of Angle modulated waves: In FM or PM, a single modulating frequency produces an infinite number of pairs of side frequencies. Thus has an infinite bandwidth. Modulation by a single frequency sinusoid: Frequency analysis of angle modulated wave by a single frequency sinusoid produces a peak phase deviation. Angle modulated wave can be expressed as, S(t) = Vc cos[ct+mfcos(mt)] To solve this cosine signal function Bessel function identities are applied. 𝑛𝜋 Cos(α+ mfcosβ) = ∑∞ 𝑛=−∞ 𝐽𝑛(𝑚) cos[∝ +𝑛𝛽 + 2 ] A sideband set contains an upper and lower side frequency (fc±fm, fc±2fm,….fc±nfm) Find the amplitude of side frequencies Jn As the modulation index increases, the number of side frequencies also increases. Plot the graph modulation index and amplitude.