Name: Period: ______ Date: Learning Target: I can understand
advertisement

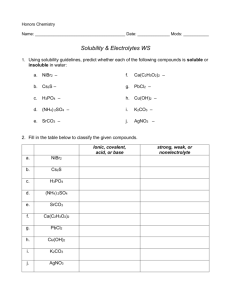
Name: ____________________________________________ Period: __________ Date: __________________ Learning Target: I can understand precipitation reactions. Criteria for Success: I can predict whether a precipitate will form when solutions of soluble ionic compounds are combined. I can write net ionic equations for precipitation reactions. Precipitation Reactions A. A _____________________ reaction is a reaction in which _______________ ions in separate solutions are mixed together to form an __________________ compound that settles out of solution as a ________________. 1. The insoluble compound that settles out is called a _____________________. 2. Use a reference chart of ___________________ rules to determine which compounds will form _______________________. Which product will form a precipitate? (NH4)2S(aq) + Cd(NO3)2(aq) → NH4NO3(?) + CdS(?) Net Ionic Equations A. A _________ ______________ ____________________ includes only those compounds and ions that undergo a ___________________ change in a reaction in an aqueous solution. 1. Ions that do __________ take part in a chemical reaction and are found in solution both before and after the reaction are ___________________ __________. Circle the spectator ions Zn(NO3)2(aq) + (NH4)2S(aq) → ZnS(s) + 2NH4NO3(aq) Zn2+(aq) + 2NO31-(aq) + 2NH41+(aq) + S2-(aq) → ZnS(s) + 2NH41+(aq) + 2NO31-(aq) B. Use the following steps to ________________ net ionic equations. 1. First, convert the chemical equation into an overall ionic equation. All _____________ ionic compounds are shown as _________________________ ions in solution. The _____________________ are shown as solids. 2. Second, _________________ the _____________________ ions on both sides of the equation. 3. Third, write final net ionic equation without _____________________ ions. Example Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction: (NH4)2S(aq) + Cd(NO3)2(aq) → 2NH4NO3(aq) + CdS(s) 1. 2. 3. Guided/Independent Practice Part 1: Using Solubility Rules Directions: Predict the products in the following double displacement reactions. Use a reference chart with the solubility rules to determine which of the products will form a precipitate. If no precipitate forms, write “none.” 1. mercury(II) chloride (aq) + potassium sulfide (aq) → 2. sodum carbonate (aq) + calcium chloride (aq) → 3. copper(II) chloride (aq) + ammonium phosphate (aq) → 4. lithium hydroxide (aq) + iron (III) nitrate (aq) → Part 2: Writing Net Ionic Equations Directions: Determine if a precipitate will form by mixing the aqueous solutions provided in each question. If so, write the net ionic equation for the reaction. If no precipitate forms, write “none.” 5. Will a precipitate form if solutions of potassium sulfate and barium nitrate are combined? If so, write the net ionic equation for the reaction. 6. Will a precipitate form if solutions of potassium nitrate and magnesium sulfate are combined? If so, write the net ionic equation for the reaction. 7. Will a precipitate form if solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulfate are combined? If so, write the net ionic equation for the reaction. 8. Will a precipitate form if solutions of strontium chloride and potassium sulfate are combined? If so, write the net ionic equation for the reaction.