Environmental Systems 3
advertisement
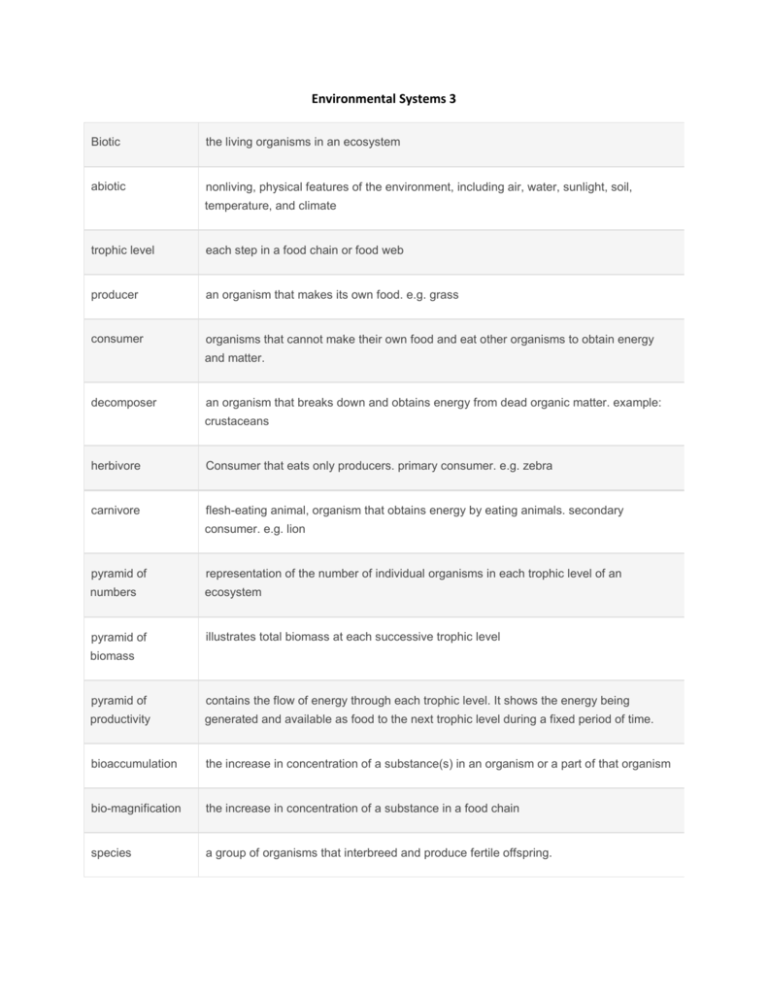
Environmental Systems 3 Biotic abiotic the living organisms in an ecosystem nonliving, physical features of the environment, including air, water, sunlight, soil, temperature, and climate trophic level each step in a food chain or food web producer an organism that makes its own food. e.g. grass consumer organisms that cannot make their own food and eat other organisms to obtain energy and matter. decomposer an organism that breaks down and obtains energy from dead organic matter. example: crustaceans herbivore Consumer that eats only producers. primary consumer. e.g. zebra carnivore flesh-eating animal, organism that obtains energy by eating animals. secondary consumer. e.g. lion pyramid of representation of the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an numbers ecosystem pyramid of illustrates total biomass at each successive trophic level biomass pyramid of contains the flow of energy through each trophic level. It shows the energy being productivity generated and available as food to the next trophic level during a fixed period of time. bioaccumulation the increase in concentration of a substance(s) in an organism or a part of that organism bio-magnification the increase in concentration of a substance in a food chain species a group of organisms that interbreed and produce fertile offspring. population a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time habitat the environment in which a species normally lives niche where and how a species lives. This includes all the information about what defines a species. community ecosystem a group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat. a community of interdependent organisms (the biotic component) and the physical environment (the abiotic component) they inhabit. intraspecific competition within a species. competition interspecific The competition between different species. competition predation the occurrence of one animal/plant eating another. e.g. snowshoe hare and lynx. parasitism the relationship where the parasite benefits at the expense of the host from which it derives food. e.g. ticks and tapeworms mutualism a symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit. e.g. coral reefs and lichens. the Lincoln index a method of estimating animal population size by collecting a sample from the population, marking them in some way, releasing them back into the wild, then resampling some time later and counting how many marked individuals you find the second capture. Also known as 'capture-mark-release-recapture' technique. The formula used in calculating population size is N = n1 x n2 / m quadrats a method of estimating animal population size by limiting the sampling area of nonmobile organisms. Sizes vary from 0.25m square-1m square and are optimal for the particular organisms. stratified random taking results from two different ha, a process or selecting individuals from a population in sampling such a way that the subgroups in the population are represented in the sample, the population is divided into subpopulations and random samples are taken of each stratum. transect A line along which one reads and records the object of study (elevation, animal/insect life, plants) systematic A method of sampling in which you determine randomly where you want to start selecting sampling in the sampling frame and then follow a rule to select every xth unit from the sampling frame list. continuous A method of sampling in which every organism along a transect is recorded sampling percentage the percentage of the area within the quadrat covered by one species. frequency biomass the mass of organic material in organisms or ecosystems, usually per unit area. diversity the number of different species and the relative numbers of individuals of each species. The Simpson's a way of calculating diversity. D = N(N-1) / sum of n(n-1). N = total number of organisms diversity index of all species found. n = number of individuals of a particular species. biome a collection of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions. rainforest a particular biome with constant high temperatures and high rainfall throughout the year. they lie in a band around the equator within the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn and accumulate high light levels. Their position enables high levels of photosynthesis and high rates of NPP. A very high biodiversity










