Human Geography - Clicker QuestionsJeff Lash Chapter 5 1
advertisement

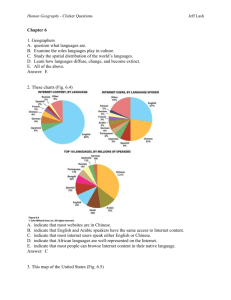
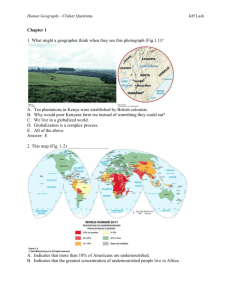
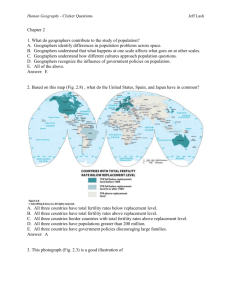
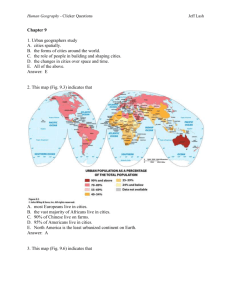
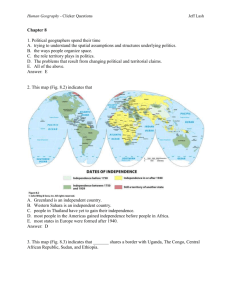
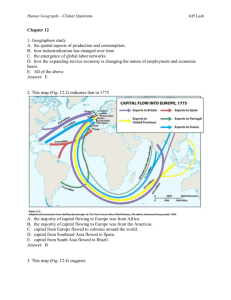
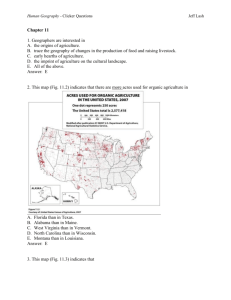
Human Geography - Clicker Questions Jeff Lash Chapter 5 1. Geographers A. examine how people and society construct identities. B. examine how place factors into identity. C. examine how geography reflects and shapes power relationships among different groups of people. D. Examine race, ethnicity, gender, and sexuality in order to understand how people construct identities. E. All of the above. Answer: E 2. In the 1990s Tiger Woods (Fig. 5.4) defined his identity as A. Black B. Caucasian C. American Indian. D. Asian. E. Cablinasian. Answer: E 3. This graph (Table 5.2) suggests Human Geography - Clicker Questions Jeff Lash A. that the U.S. Census Bureau doesn’t count American Indians. B. that in 2050 the “Asian Alone” population will decline. C. that in 2050 the “Black Alone” population will change significantly D. that in 2050 the “White, non Hispanic” population will no longer be the majority population in the United States. E. All of the above. Answer: D 4. This map of Milwaukee, Wisconsin (Fig. 5.5) indicates Human Geography - Clicker Questions Jeff Lash A. that the highest density of African Americans is in the southern part of the city. B. that some census tracts have a population of over 80% African American while other tracts have less than 6%. C. that the size of the census tract determines where African Americans live. D. that African Americans do not like to live near the water. E. that Milwaukee is not racially segregated. Answer: B 5. These photographs (Figs. 5.7 and 5.8) show A. that the idea of ethnicity as an identity stems from that notion that people are closely bounded, even related, in a certain place over time. B. that the idea of ethnicity as an identity stems from people settling in urban areas. C. that ethnicity is a foreign concept. Human Geography - Clicker Questions D. how ethnicity is used to assimilate cultures. E. None of the above. Answer: A 6. This photograph (Fig. 5.8) illustrates A. how people with power construct illegal monuments. B. how people’s identity is shaped by power. C. how power relationships are reflected in the cultural landscape. D. how governments alone control who does and does not have power. E. All of the above. Answer: C 7. This photograph taken outside a temple in South Korea (Fig. 5.13) illustrates A. how most Korean women earn a living. B. the concept of dowry deaths. C. the concept of the informal economy. Jeff Lash Human Geography - Clicker Questions Jeff Lash D. poverty in Asia. E. the power that men have over women in South Korea. Answer: C 8. This map of Gender Empowerment (Fig. 5.15) suggests A. that women in China have the same amount of decision-making power as Egyptian women. B. that women in South America have more power than women in North America. C. that women in Canada, Norway, and Australia have more decision-making power than women in Switzerland, Turkey, and China. D. that women in India have no power. E. that women around the world have less power than men. Answer: C 9. This photograph taken in Mumbai, India (Fig. 5.18) illustrates Human Geography - Clicker Questions A. India’s barrioization. B. India’s tradition of public courtship. C. India’s tradition of Hindu spirituality. D. India’s cultural shift from arranged marriages to love marriages. E. India’s cultural shift from Hindu to Christian definitions of marriage. Answer: D 10. These maps of Los Angeles (Fig. 5.19) reflect Jeff Lash Human Geography - Clicker Questions Jeff Lash A. the relationship between ethnicity and the urban riots of 1992. B. 1960s discrimination against Koreans by the white population. C. the steady influx of Korean residents and small-business owners in the rapidly changing urban area. D. the steady expansion of the Black community. E. the decline of Korean businesses in the 1970s. Answer: C