ORG Behaviour
advertisement
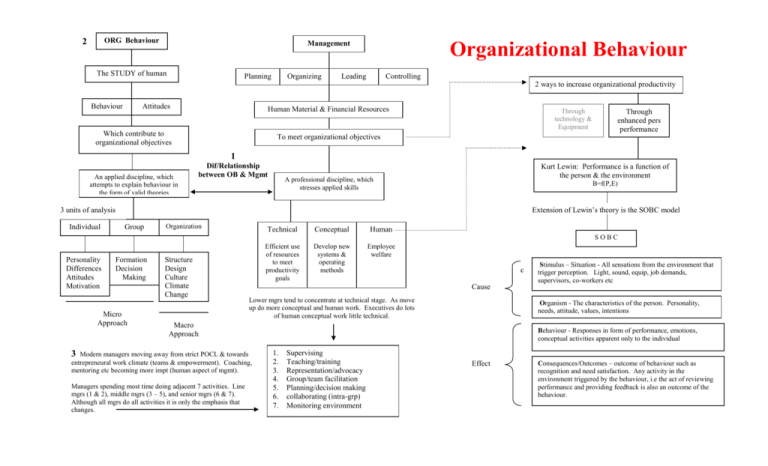
ORG Behaviour 2 Management The STUDY of human Planning Organizing Organizational Behaviour Leading Controlling 2 ways to increase organizational productivity Behaviour Attitudes Human Material & Financial Resources Which contribute to organizational objectives Through technology & Equipment Through enhanced pers performance To meet organizational objectives 1 An applied discipline, which attempts to explain behaviour in the form of valid theories Dif/Relationship between OB & Mgmt Kurt Lewin: Performance is a function of the person & the environment A professional discipline, which stresses applied skills B=f(P,E) Extension of Lewin’s theory is the SOBC model 3 units of analysis Individual Group Organization Technical Conceptual Human Efficient use of resources to meet productivity goals Develop new systems & operating methods Employee welfare SOBC Personality Differences Attitudes Motivation Formation Decision Making Micro Approach Structure Design Culture Climate Change c Cause Lower mgrs tend to concentrate at technical stage. As move up do more conceptual and human work. Executives do lots of human conceptual work little technical. Organism - The characteristics of the person. Personality, needs, attitude, values, intentions Macro Approach 3 Modern managers moving away from strict POCL & towards entrepreneural work climate (teams & empowerment). Coaching, mentoring etc becoming more impt (human aspect of mgmt). Managers spending most time doing adjacent 7 activities. Line mgrs (1 & 2), middle mgrs (3 – 5), and senior mgrs (6 & 7). Although all mgrs do all activities it is only the emphasis that changes. Stimulus – Situation - All sensations from the environment that trigger perception. Light, sound, equip, job demands, supervisors, co-workers etc Behaviour - Responses in form of performance, emotions, conceptual activities apparent only to the individual 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Supervising Teaching/training Representation/advocacy Group/team facilitation Planning/decision making collaborating (intra-grp) Monitoring environment Effect Consequences/Outcomes – outcome of behaviour such as recognition and need satisfaction. Any activity in the environment triggered by the behaviour, i.e the act of reviewing performance and providing feedback is also an outcome of the behaviour. One aspect of our personalities and individual differences with which we are concerned as managers Our Values & Effect on Personality is an individuals sense of job satisfaction as this will enhance performance. Our Values I 5&6 = 9 Job Satisfaction Measuring device to judge behaviour, they give us a sense of right and wrong (Rokeach) Our values define our self-concept. 10 Consequences: Improved mental/physical health; Improved resistance to job stress; Key Attitudes (Facets) Instrumental Values Terminal Values Acceptable means/behaviours to achieve goals. Ambition Cleanliness, Imagination, Politeness (The means to an end) The goals to be achieved, that which we seek that relfect our value system. Achievement, Wisdom, Security etc (think in terms of Maslow) Work itself Co-workers Supervision Promotions Years in Service As employees grow older they experience more job satisfaction Determinants of Job Satisfaction Organizational Expectations Supervision Job Challenge Job clarity Incentives Realistic job previews. Job must meet expectations. Participation, consultation, makes employees feel impt, selfesteem etc. Creativity Use of skills Risk taking Intrinsic rwds Accomplishment Do employees know what is expected. Feedback improves this. Extrinsic Pay, promotions, recognition, status Individual Differences Locus of Control Extroversion Seeks external stimulation Internal External Introversion Avoids external stimulation 7 8 Machiavelliasm High Machs – the ends justify the means. Main tool is manipulation of others, especially in non regulated organizations. Predominant at top of org. Observation 12 Interviews Questionnaires Job Description Index 10 Individual Since our values determine our behaviour, and our behaviour is observable, others (and ourselves will define us by our values (observed behaviour). Therefore our personality is governed by our values. We are a product of our values. Since our values are different (no two people are exactly the same) this accounts for our individual differences. Pay Measuring Job Satisfaction McClelland’s Socially Acquired Needs Intrinsic Rewards (Job design) Intrinsic Accomplishment, pride etc 11 Equity theory Given performance Achievement Affiliation Power Personalized (-) + Perception Equity theory (individual dependant) Extrinsic Rewards (Job design) = Level of Job satisfaction Both types of rewards are impt. Compare these rewards v effort and performance of others (am I being treated fairly) Socialized (+) There is not a direct relationship between performance and job sat. Perception (Equity theory) links them. I will only be satisfied if I perceive adequate rewards. My job must be interesting and challenging (intrinsic) and have extrinsic rewards in order to have perceived equity. 14 How Economic Downsizing Can Effect Work Attitudes Org commitment - waves of downsizes and mergers cause employees to question their level of org commitment (is the loyalty a one way street?) Job involvement - may not be as adversely effected. I.e employee may be involved in the job despite the uncertainty. (May even become more involved in the job as a form of refuge) Job satisfaction Previously noted Willing to defend / go the distance for the org. Desire to maintain membership in the org Identify with job Actively particpates Acceptance of org goals and values Work Attitudes Organizational Commitment 13 Job involvement Goes beyond company loyalty Actively promote the organization Defend the organization Willingness to give of oneself Different than job satisfaction (about the job only not the org) Can be committed without satisfaction Develops over time Benefits of organizational commitment Employee retention Lower absenteeism Work harder, perform better, more productive Set higher goals when participate in goal setting Personally accept org goals and values Belief that job is central part of life View work as a major source of satisfaction Physically and psychologically involved in work Job is a central part of life How Managers promote these positive work attitudes Demonstrate they care about employee welfare Help employees achieve personal goals Job design for intrinsic rewards Employee decision making Innovative and regular rewards Be available to deal with work problems Set goals with employees and ensure some are for personal development 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Organizational Behaviour compared to management Define Organizational Behaviour Characteristics of managers job in modern times Issues of Organizational productivity and employee needs Values and their relationship to personality Terminal vs. instrumental values Psychological traits that influence employee behaviour Introversion vs. Extroversion 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Nature of Job Satisfaction Determinants/consequences of JS Job satisfaction and performance Measurement of Job satisfaction Org commitment & Job Involvement Effect of economic insecurity





