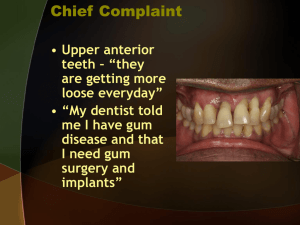
Perio Patient Case 2 The pronounced, raised ridges evident on the
advertisement

Perio Patient Case 2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. The pronounced, raised ridges evident on the anterior region of the hard palate is indicative of a. Torus palantinus b. Rugae c. Salivary duct openings d. Blisterform lesions e. Trauma The appearance of the maxillary anterior teeth indicates a. Erosion b. Abrasion c. Attrition d. Caries e. Abfraction What is the potential is associated with the mandibular right second and third molars? a. Extrusion b. Ankylosis c. Impaction d. Hypercementosis e. Fusion What is the most likely reason for food impaction between the mandibular right first and second molars? a. Mobility b. Blunted papillae c. Recession d. Caries e. Diastema Which of the following teeth has been restored with a composite restoration? a. Max RT 1st molar b. Max RT central incisor c. Mand LF 1st molar d. Mand LF lateral incisor e. Mand RT 1st molar Caries is evident radiographically on which of the following teeth? a. Max RT central incisor b. Max LF 2nd molar c. Mand LF 1st molar d. Mand RT canine e. Mand RT 2nd molar What radiographic technique was used to image the maxillary LF third molar? a. Water’s b. Posterior-anterior 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. c. Occlusal d. Localization e. Disto-oblique The most likely interpretation of the radiolucency at the apices of the mandibular anterior teeth (arrow) is a. The lingual foramen b. The mental fossa c. Periapical cemental dysplasia d. Signs of osteoporosis e. A periapical abscess What is the reason that this patient must be premedicated before periodontal probing and subgingival debridement procedures? a. History of infective endocarditis b. Thyroid condition c. Sinus infection d. Foreign born e. Blood pressure What is the recommended antibiotic premedication for this patient? a. 2g Amoxicillin orally 1 hour before treatment b. 2g Ampicillin IM 30min before treatment c. 600mg Clindamycin orally 1 hour before treatment d. 1g Cefazolin IV 30min before treatment Which of the following would be the most appropriate treatment plan for scaling and root planning for this patient? a. One quad each week b. One quad every 2 weeks c. Half mouth each week d. Half mouth every 2 weeks e. Complete mouth at one appointment Which of the following pain control choices is required for debridement of the maxillary left quadrant? a. Nitrous oxide-oxygen analgesia b. Topical anesthetic benzocaine 20% c. Infiltration anesthesia prilocaine 4% d. Noninjectable anesthetic lidocaine 2.5% and prilocaine 2.5% gel e. Block anesthesia bupivacaine 0.5% with epi Which of the following is a risk factor for this patient’s periodontal disease? a. Endocrine b. Stress c. Hormones d. Age e. Race 14. What is the AAP classification of this patient’s periodontal status? a. Chronic periodontitis b. Aggressive periodontitis c. Drug-induced gingival disease d. Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic diseases e. Necrotizing periodontitis 15. Each of the following teeth appears to be at risk for mucogingival involvement EXCEPT one. a. Max LF canine b. Max LF 2nd molar c. Mand LF central incoisor d. Mand RT canine e. Mand RT 2nd molar 16. At the reevaluation appointment, which of the following areas should be treated and monitored closely for signs of further attachment loss? a. All 4 posterior quads b. Entire mand arch c. Max RT and LF post regions d. Max and Mand Ant sextants e. Max RT posterior, Max LF post, Mand LF central, Lateral incisor regions 17. Which of the following is the most likely reason that this patient has chosen to use plastic picks to remove food from between her teeth? a. Too busy to floss b. Furcation involvement c. Gingival recession d. Blunted papillae e. Cultural influence 18. The extended and enlarged, bulbous area located on the attached gingiva apical to the maxillary left second and third molars (arrow) is most likely the result of a. A periodontal abscess b. Trauma from plastic picks c. Bone exostoses d. Occlusal disharmonies e. An impacted tooth 19. Based on probe readings at the reevaluation appointment, which of the following is the most accurate assessment of this patient’s periodontal condition? a. Classified as recurrent periodontal disease and should reenter initial nonsurgical therapy b. Considered refractory periodontal disease and should reenter initial nonsurgical therapy c. Determined to be a potential candidate for periodontal surgery and should be referred to a Periodontist d. Categorized as necrotizing ulcerative periodontitis and should be referred to a Periodontist e. Suspected drug-influenced gingival enlargement and should be referred to a physician 20. Which of the following would require contacting this patient’s physician before recommending for at-home use? a. Rinsing with essential oils b. Oral irrigation with CHX c. Brushing with NaF d. Applying a whitening product e. Use of disclosing tablets 21. Each of the following is a reason that the antibiotic this patient is currently taking for her sinus infection has failed to improve her periodontal abscess and generalized periodontal condition EXCEPT one. a. Too low a concentration reaching the oral site b. Unfavorable local risk factors present c. Microorganisms are not susceptible to the antibiotic d. Inadequate or incorrect dose being taken e. Patient noncompliance 22. If painful symptoms do not subside after vigorous debridement of the maxillary left molar region, when should the patient be referred for emergency periodontal sugery to access the furcation area? a. Immediately following the scaling apt b. When the anesthesia wears off c. After 24 hours d. Within 1-2 weeks e. At the next reevaluation appt 23. Each of the following is a potential contraindication of professional tooth whitening for this patient EXCEPT one. a. Active pathological condition b. Periodontal status c. Anterior composite restoration d. Age e. Current shade of her teeth 24. Prior to proceeding with the dental hygiene care plan, this patient’s signature must be obtained to a. Verify her vital signs b. Give consent for treatment c. Show legal status in the USA d. Validate her commitment to self-care e. Document when her last dental apt was ANSWERS 1. B 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. C A D B C E B A C D E B A A E D A C B E C D B