Nine – Wave Motion
advertisement
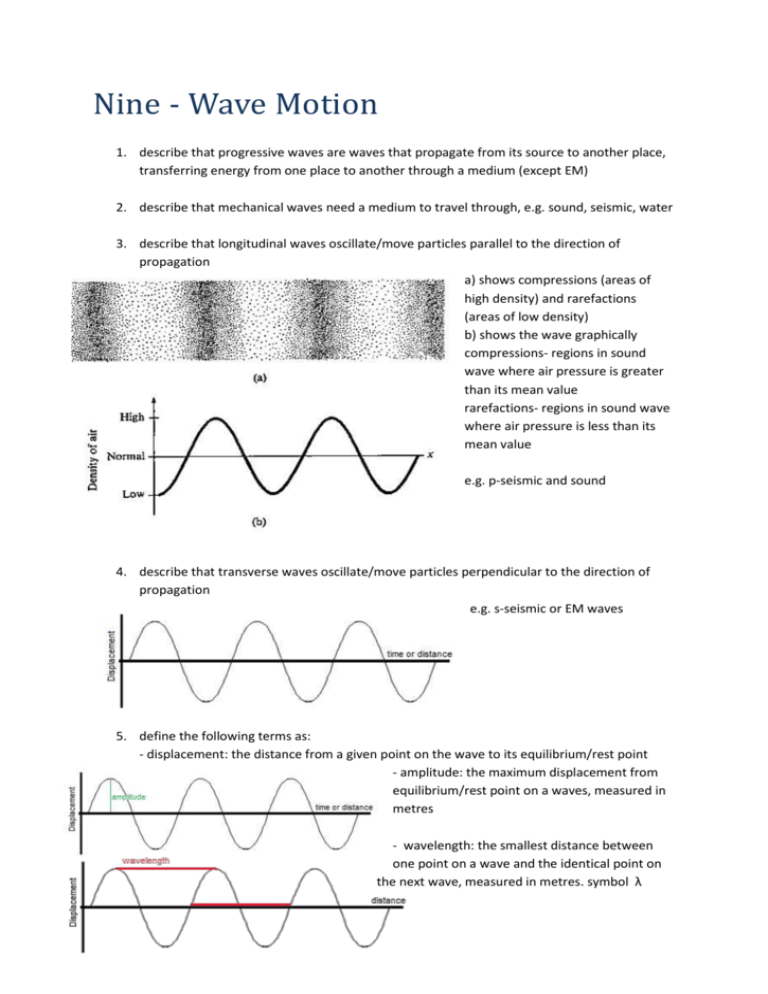
Nine - Wave Motion 1. describe that progressive waves are waves that propagate from its source to another place, transferring energy from one place to another through a medium (except EM) 2. describe that mechanical waves need a medium to travel through, e.g. sound, seismic, water 3. describe that longitudinal waves oscillate/move particles parallel to the direction of propagation a) shows compressions (areas of high density) and rarefactions (areas of low density) b) shows the wave graphically compressions- regions in sound wave where air pressure is greater than its mean value rarefactions- regions in sound wave where air pressure is less than its mean value e.g. p-seismic and sound 4. describe that transverse waves oscillate/move particles perpendicular to the direction of propagation e.g. s-seismic or EM waves 5. define the following terms as: - displacement: the distance from a given point on the wave to its equilibrium/rest point - amplitude: the maximum displacement from equilibrium/rest point on a waves, measured in metres - wavelength: the smallest distance between one point on a wave and the identical point on the next wave, measured in metres. symbol λ - period: time taken to complete one full wavelength/cycle. measured in seconds. symbol T. - frequency: the number of oscillations passing a point per second, measured in Hertz. symbol f. 1 calculated using 𝑓𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑐𝑦 = 𝑝𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑 -speed of a wave: the distance travelled by a point on a wave per unit time 6. derive from the definition of speed, frequency and wavelength, the wave equation v = fλ a) in one second, f waves are produced, each of one wavelength λ, distance travelled by first wave in one second v= fλ. b) speed = distance / time so the speed of the wave is given by wavelength/time it takes for 1 wavelength (period). so v = wavelength/period and period = 1/frequency so v = wavelength / 1/frequency = wavelength * frequency v = wavelength * frequency 7. explain that reflection is when waves rebound from a barrier/surface, changing direction but remaining in the same medium 8. explain that refraction is the change in direction of a wave when it travels from one medium to another, caused by a change in speed. -more dense -> slower speed -> shorter wavelength as v ∝λ - frequency cannot change, because it is predetermined by the source 9. explain that diffraction is the spreading of a wave when it passes through a gap (aperture) or around a corner/ edge of an object. - aperture must be comparable to the wavelength of wave for diffraction -when aperture >> λ, small diffraction -when aperture > λ, medium diffraction -when aperture = λ, most diffraction






