Biodiversity Packet (Part I)
advertisement

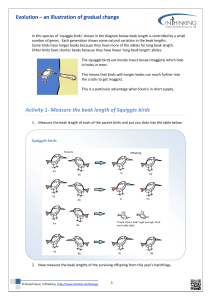
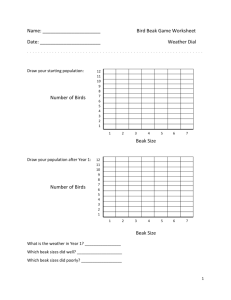
Name____________________________________________________ Biodiversity Chapter 7 Period____ Adaptations Vocab: Habitat: Predator: Prey: Adaptation: Structural Adaptation: A____________ adaptation that helps an organism survive in its environment. This includes body coverings & parts (claws, beaks, feet, armor plates, skulls, teeth) 1. Camouflage example: 2. Mimicry example: 3. Chemical example: Other examples: Behavioral Adaptation: The way an organism _______ or _____________ to its environment in order to survive. This includes escaping danger, methods of gathering & storing food, finding shelter, defending oneself, hibernating, migrating, raising young 1. Reflexive example: 2. Instinctive example: Structural or Behavioral or BOTH?!? For each adaptation listed below, decide whether it is a structural adaptation, behavioral adaptation, or if it involves both. # 1 Adaptation A cheetah can run at 60mph to catch prey. 2 A rabbit freezes when it sees a predator. 3 A human has opposable thumbs. 4 A species of toad can survive frozen solid for the entire winter. 5 A parrot can mimic human speech to ask for a cracker. 6 A falcon’s bones are hollow to reduce its weight. 7 An anaconda can unhinge its jaw to swallow prey whole. 8 An armadillo can roll up into a ball and protect itself with tough skin. 9 Canadian geese migrate south for the winter. 10 A salamander can cut off its own tail to distract predators and regrow it later. 11 A whale can hold its breath for up to 2 hours during deep ocean dives. 12 A baby seal’s white coat helps it to blend in with the snow around it. 13 Male emperor penguins incubate their egg while the females return to the sea to feed 14 A robin builds a nest out of soft grasses and other materials. 15 A sea urchin has spikes all over its body. 16 A velociraptor had feathers to help regulate body temperature. 17 A squid shoots ink to distract predators. 18 A caterpillar’s body markings make it look like a snake to fool predators. 19 A chameleon can change its color to blend in with its surroundings. 20 Structural Behavioral Both Deep Ocean Adaptations Some of the strangest adaptations on Earth are found on organisms that live in the deep ocean, far below where sunlight ever reaches. List at least one adaptation for each species. Species Adaptations Sperm Whale Phronima Jellyfish Hatchetfish Fangtooth Hairy Angler Gulper Eel What are some uses for bioluminescence? Beak Adaptation Lab Goal: To learn about the advantages and disadvantages of variations, by simulating birds with different types of beaks competing for various foods. Pre-Lab: Look at the following beaks found on different species of birds. Give a basic description of each beak, then based on the structure of the beak, predict how each species uses its beak to feed. Species Description Function Cardinal Hummingbird Eagle Warbler Pelican Toucan Procedure: 1. Give each member of your group one of the following: a pair of tweezers, binder clip, spoon, or scissors. 2. You are now a very hungry bird. The tool you have selected is your “beak”. 3. The first member of your group will have 20 seconds (timed using the clock by another group member) to use their tool to attempt to eat the various seeds, worms, etc that are on the plate. 4. The cup is your stomach. It must remain upright at all times. You must hold your beak in one hand, and your stomach in your other hand, close to your body. Only food that is placed in the cup by the beak has been “eaten”. 5. Food items will be placed in your “habitat”. When the timer partner says “go”, you will have 20 seconds to feed (or until the food runs out). Collect as much food in your stomach as possible until the timer says “stop”. 6. Empty your stomach and count the contents. Record data in your group data table below, reset the plate, and start again from Step 3 with another group member with a different beak type. Partner 1 2 3 4 Beak Type # Rice # Rubber Bands # Beans # Paper Clips Analysis: Based on your data, what was the best bird beak for each type of food? Food Type Rice Bird Beak With Highest Capture # Rubber Bands Beans Paper Clips Questions: Answer the following questions in complete sentences. a. Which beak was best adapted to each type of food? Which beak was least adapted to each type of food? b. Would you change your feeding strategy if you had another opportunity to “feed?” Explain. c. What would happen if all of the bird types in this activity flew to an island where no birds had been before and the only food available was rice? Which birds would be most successful? Which birds would be least successful? d. If you came back to this island (from c) in 50 years, what should you expect to see? (What type of birds will live on the island?) e. What does this lab tell you about how animals adapt to their environments?