Organic Reactions Note – Student.DOC
advertisement

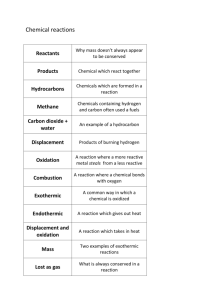
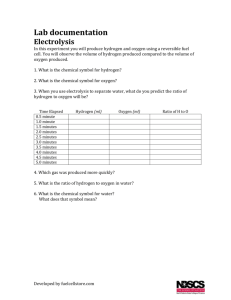
Organic Reactions Complete combustion reactions: Hydrocarbon or Alcohol + O2 CO2 + H2O Substitution reaction: alkane + halogen → haloalkane +hydrogen halide CH4+ Cl2 →CH3Cl + HCl CH3Cl + Cl2 → CH2Cl2+ HCl Addition Reactions A) Halogenation (adding halides) alkene + halogen haloalkane B) Hydrogenation (adding hydrogen) alkene + hydrogen alkane C) Hydrohalogenation (adding hydrogen halides) alkene + hydrogen halide haloalkane D) Hydration (adding water) alkene + water alcohol Hydrohalogenation and hydration follow Marknovnikov’s Rule which states that the hydrogen is added to the carbon with the most hydrogen atoms originally bonded to it. Elimination Reactions * not included in summary table / not in textbook Alkyl halides can become alkenes by elimination of a hydrogen and a halide ion from adjacent carbon atoms and in presence of OH- ion (basic solution) Dehydration Reactions The removal of a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group (ROH) producing a smaller molecule and water Alcohols can be dehydrated to alkenes using sulfuric acid Condensation Reactions The combination of two molecules to form a larger molecule by the removal of water Alcohols can be condensed to ethers using sulfuric acid A carboxylic acid and an amine can condense to from an amide Esterification This is also a type of condensation reaction carboxylic acid + alcohol ester + water Oxidation Reactions Oxidizing agents and oxidation reactions will be discussed in more detail later in this course In inorganic chemistry an oxidizing agent accepts electrons during a chemical reaction In organic chemistry an oxidizing agent increases the number of carbon to oxygen bonds in an organic molecule The symbol (O) represents oxidizing agents. Common oxidizing agents include: o Potassium dichromate K2Cr2O4 o Hydrogen peroxide H2O2 o Potassium permanganate K2MnO4 Oxidation of a primary (1°) alcohol produces an aldehyde Further oxidation of an aldehyde produces a carboxylic acid Oxidation of a secondary (2°) alcohol produces a ketone Tertiary (3°) alcohols cannot be readily oxidized due to a lack of hydrogen on the adjacent carbon. This prevents the formation of water Hydrolysis Reactions The splitting of a molecule by the addition of water or its elements (oxygen and hydrogen) As an example, a hydrolysis reaction is used to reverse an esterification O H3C C O O CH2 CH2 CH3 + Na OH H3C C - O + HO CH2 CH2 Reactions with Amines Alkyl halides will react can react with ammonia (NH3), to produce amines Reacting a 1° amine with an alkyl halide will result in the formation of a 2° amine Reacting a 2° amine with an alkyl halide will result in the formation of a 3° amine CH3