The Indian CKD Registry workgroup was
advertisement

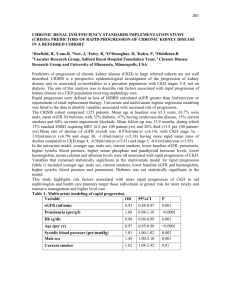
Appendix I DEFINITIONS Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 1. Kidney damage ≥ 3 months with eGFR (estimated by any method) < 60 ml/min and / OR 2. Structural or functional abnormalities as indicated by abnormalities in Pathology Imaging Urinalysis Blood composition indicating abnormal kidney function Diabetic Nephropathy (DN) 1. Histological lesions of DN OR 2. Established Diabetes Mellitus for preferably > 5 years with fixed proteinuria of > 0.5 gm or with hypertension and abnormal eGFR OR 3. Established Diabetes Mellitus for preferably > 5 years / with fixed proteinuria of > 0.5 gm OR 4. Abnormal plasma glucose with proven diabetic retinopathy / with hypertension and abnormal eGFR OR 5. Established diabetes mellitus with albumin create ratio of > 20 mg/gm with normal or abnormal eGFR Hypertensive Nephrosclerosis 1. Histological evidence of hypertensive nephrosclerosis OR 2. Sys. Hypertension of > 10 years of non renal parenchymal or renovascular etiology with LVH / Hypertensive retinopathy OR 3. Accelerated / malignant HT with Neuroretinopathy / LV dysfunction with proteinuria and altered eGFR Renovascular Disease 1. Radiologically (angiographic / doppler) demonstrable significant bilateral renal artery stenosis or significant disease in artery supplying solitary functioning kidney with no other identifiable cause of CKD OR 2. Recently detected severe hypertension and peripheral occlusive vascular disease (POVD), risk factors for POVD, h/o flash pulmonary edema, h/o >20% deterioration in eGFR with ACEI / ARB use, renal and other vascular bruit, asymmetry in renal size Chronic Glomerulonephritis (CGN) 1. Biopsy proven glomerular disease (must show evidence of dominant glomerular involvement) OR 2. Significant proteinuria > 3 months duration with edema and/or hypertension and/or gross or microscopic hematuria OR 3. History of nephritic or nephrotic illness in past OR 4. Biopsy proved glomerular disease 1 Note: Do not include Idiopathic nephrotic syndrome or minimal change disease that shows primary steroid response within three months Chronic Tubulo-interstitial Disease (TID) 1. Biopsy evidence of predominant involvement of tubulo-interstitial compartment OR 2. Presence of at least 2 of the following: a) Absence of edema / hypertension until the stage of dialysis dependency b) Evidence of marked rickets or osteomalacia c) Radiological evidence of abnormalities of urinary tract d) Proteinuria <1 gm/day e) History of recurrent urinary tract infections f) Identification of factor known to cause (e.g. drugs, toxins) g) Urinary stone disease h) Demonstrated vesico-ureteric reflux i) Disproportionate metabolic acidosis j) Longstanding polyuria and nocturia Congenital Disease 1. Presence of renal disease at birth or infancy, nephrotic state, stones, obstructive symptoms etc. 2. Specify type of renal disease Heredofamilial Heredofamilial diseases with family history suggestive genetic inheritance. Cystic Disease 1. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) OR 2. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ( ARPKD) Obstructive Uropathy 1. Objective evidence of anatomic or neurogenic obstruction to urinary tract at any level preferably bilateral or unilateral in single functioning kidney AND 2. Exclusion of other causes of CKD Graft dysfunction Renal allograft recipient having evidence of CKD as defined above. This should be entered under status Post-transplant. Others Any specific disease not covered in the above mentioned categories Undetermined CKD not fitting in any of the above categories Please note Histological diagnosis takes precedence over clinical findings Please select only one cause 2 Supplementary Table 1: Patient characteristics in different years Year 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 Age 50.0±14.7 50.5±14.5 49.6±14.7 50.6±14.5 49.9±14.7 Gender Stage of CKD ratio I II III IV V Total 2.1:1 367 660 2,346 2,950 5,539 11862 (3.1 ) (5.6 ) (19.8 ) (24.9 ) (46.7 ) 176 407 1,987 2,793 4,947 (1.7 ) (3.9 ) (19.3 ) (27.1 ) (48.0 ) 278 556 2,167 2,734 5,295 (2.5 ) (5.0 ) (19.6 ) (24.8 ) (48.0 ) 108 288 1,765 2,614 4,915 (1.1 ) (3.0 ) (18.2 ) (27.0 ) (50.7 ) 76 226 1,349 1,594 2,867 (1.2 ) (3.7 ) (22.1 ) (26.1 ) (46.9 ) 2.4:1 2.4:1 2.7:1 2.4:1 Figures in parentheses are percentages 3 10310 11030 9690 6112 Supplementary Table 2: Demographics and etiologic diagnosis in different stages of CKD Age Gender (years) CKD Stages Causes of CKD ratio Graft (M:F) I 37.411.7 2.3:1 II 43.612.8 2.4:1 III 51.013.6 2.8:1 IV 53.214.3 2.4:1 V 49.414.8 2.3:1 DN UD HT CGN CIN Obs ADPKD Others failure RVD Total 263 154 142 151 60 54 26 134 7 14 1,005 (26.2) (15.3) (14.1) (15.0) (6.0) (5.4) (2.6) (13.3) (0.7) (1.4) 647 320 273 325 153 76 49 268 10 16 (30.3) (15.0) (12.8) (15.2) (7.2) (3.6) (2.3) (12.5) (0.5) (0.7) 3,102 1,515 1,299 1,321 676 315 245 1,119 28 84 (32.3) (15.8) (13.5) (13.7) (7.0) (3.3) (2.5) (11.6) (0.3) (0.9) 4,177 2,003 1676 1625 877 445 351 1371 41 119 (32.9) (15.8) (13.2) (12.8) (6.9) (3.5) (2.8) (10.8) (0.3) (0.9) 7,257 3,932 2,912 3,311 1,700 771 605 2,788 73 164 (30.8) (16.7) (12.4) (14.1) (7.2) (3.3) (2.6) (11.8) (0.3) (0.7) 2,137 9,614 12,685 23,563 CKD: chronic kidney disease, DN: diabetic nephropathy, UD: undetermined, HT: hypertensive nephrosclerosis, CGN: chronic glomerulonephritis, CIN: chronic interstitial nephritis, RVD: renovascular disease, ADPKD : autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Figures in parentheses are percentages 4 Supplementary Table 3: Comparison of Age, gender distribution and CKD stages at the time of presentation in different income categories CKD Stages Gender Monthly family ratio income (Rs) Age (years) (M:F) I II III IV V Total <5,000 2.4:1 421 844 3,799 5,202 9,837 20,103 (2.1) (4.2) (18.9) (25.9) (48.9) 428 896 4,162 5,315 10,127 (2) (4.3) (18.9) (25.4) (48.4) 98 258 1,260 1,713 2,775 (1.6) (4.2) (20.6) (28.1) (45.5) 5-20,000 >20,000 49.9±14.7 50.0±14.6 51.0±14.4 2.3:1 2.4:1 Figures in parentheses are percentages 5 20,928 6,104 Supplementary Table 4: Etiological diagnosis in different income categories Monthly family income (Rs) <5,000 Total DN UD HT CGN CIN Obs ADPKD Others failure RVD 5,772 3,995 2,347 3,104 1,406 814 544 3,289 42 156 520,000 >20,000 (26.9) 7,497 (33.6) 2,447 (18.6) 3,443 (15.4) 665 (10.9) 3,031 (13.6) 1,070 (14.5) 3,150 (14.1) 732 (6.6) 1,633 (7.3) 509 (3.8) 762 (3.4) 133 (2.5) 627 (2.8) 142 (15.3) 1,880 (8.4) 683 (0.2) 84 (0.4) 36 (0.7) 194 (0.9) 63 Graft 21,469 22,301 6,480 (37.8) (10.3) (16.5) (11.3) (7.8) (2.1) (2.2) (10.5) (0.6) (1) CKD: chronic kidney disease, DN: diabetic nephropathy, UD: undetermined, HT: hypertensive nephrosclerosis, CGN: chronic glomerulonephritis, CIN: chronic interstitial nephritis, RVD: renovascular disease, ADPKD : autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease Figures in parentheses are percentages 6 Supplementary fig 1: Showing the locations of contributing centers 7 8