A categorical data
advertisement

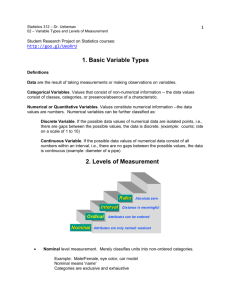
Chapter 9E Types of data It is vital that we understand the various types of data that we are able to gather (shown below) Nominal Categorical (qualitative) Ordinal DATA Numerical (quantitative) Discrete Continuous Categorical data are observations that fit some qualitative category. Data of this type do not involve numbers or measurements Numerical data, on the other hand, involve quantitative amounts. Contrasting categorical, numerical data engages with numbers and measurements, such as, number of pets, school pencils and handbags or how high can a plane fly, the daily temperature etc ** Here is a worked example to help you with the process of finding particular data assigned to specific questions WORKED EXAMPLE (1) page 327 State whether the following pieces of data are categorical or numerical a) The value of sales recorded at each branch of a fast – food outlet b) The breeds of dog that appear at a dog show THINK WRITE a) The value of sales at each branch can be measured a) The breeds of dog at a show cannot be measured The value of sales are numerical data The breeds of dog are categorical data Both data’s, numerical and categorical, have two categories attached The numerical data that we use falls into two categories 1. Discrete 2. Continuous Discrete data are responses, observations or records that can take only a certain, set values. Examples of discrete data would include, for example: the number of children in a family, the number of marks obtained in a test or the number of students in a class (you cannot have half a student) Continuous data may take any value within the range of the data. For example: a person’s height (within the range of human heights) not certain fixed heights, time in a race (measure it to fractions of a second), a dog’s weight or the length of a leaf However, the categorical data is divided into 1. Nominal 2. Ordinal data Keep in mind, that if there is no order associated with the categories formed by the data, then there are termed nominal data For example: answers to questions about a student’s hair colour or method of transport used to travel to school When the data categories are aligned or some qualitative scale, they are termed ordinal data A response to a question on a scale, for example: strongly disagree to strongly agree, would constitute ordinal data (that is, some order is implied) **Worked example 2 clearly identifies between what is discrete or continuous data WORKED EXAMPLE (2) page 328 State whether each of the following records of numerical data is discrete or continuous a) The number of people in each car that passes through a tollgate b) The mass of a baby at birth THINK WRITE a) 1. The number of people in the car must be a whole number (you cannot count half a person) 2. Give a written answer b) 1. A baby’s mass can be measured to various degrees of accuracy 2. Give a written answer The data are numerical and discrete because the answer to this observation is a set value (number of people in the car) The data are numerical and continuous because the mass of the baby is within the range of data (how much the baby weighs, in kilograms) Now that I hope you have a fair understanding of what chapter 9E is about, test yourself Question 1 (similar to worked example 1) State whether the data collected in each of the following situations would be categorical or numerical a) The number of matches in each box is counted for a large sample of boxes b) The sex of respondents to a questionnaire is recorded as either M or F c) A fisheries inspector records the lengths of 40 cod d) The occurrence of hot, warm, mild and cool weather for each day in January is recorded Question 2 For each of the following, state if the data are categorical or numerical. If numerical, state if the data are discrete or continuous a) b) c) d) The number of students in each of your multiple dance classes The teams people support at a soccer match The brands of chocolate sold at your Woolies The heights of people in your mini golf club Question 3 – multiple choice The number of people who are using a particular bus service are counted over a 2 – week period. The data formed by this survey would best be described as: A categorical data B numerical and discrete data C numerical and continuous data D quantitative data Question 4 The graph at right shows a boy’s shoe size each year for 10 years. Describe the data in this example Answers!!! 1. a) Numerical b) Categorical c) Numerical d) Categorical 2. a) Numerical and discrete b) Categorical c) Categorical d) Numerical and continuous 3. B 4.