CESR TA Machine Studies Topic Experimental Description
advertisement
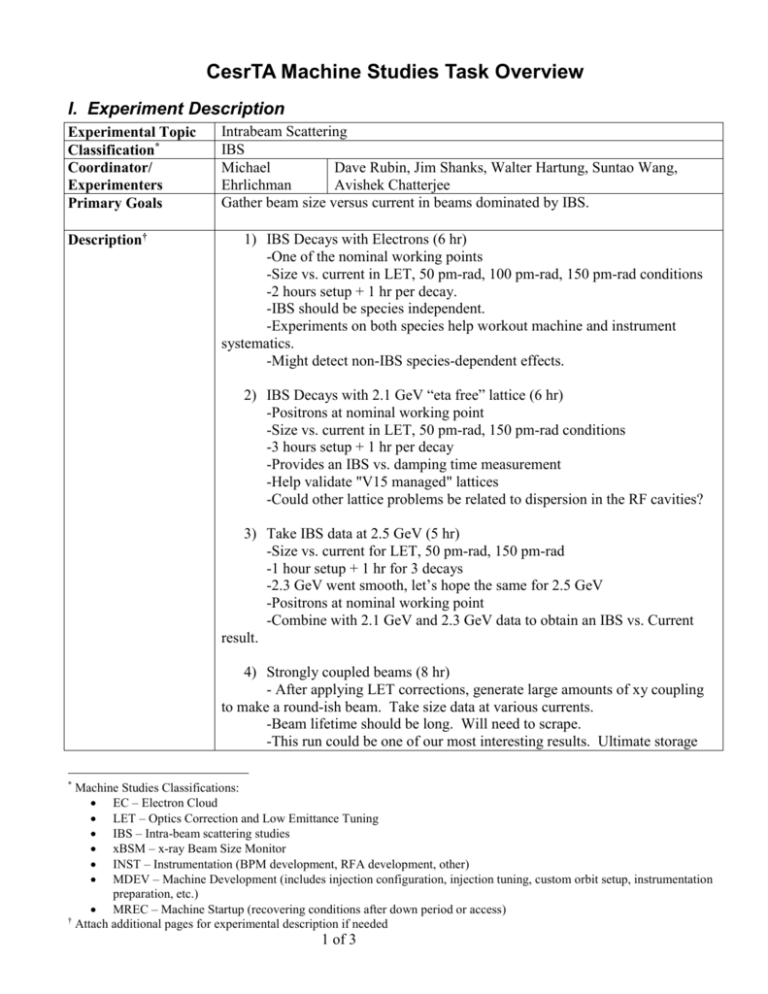
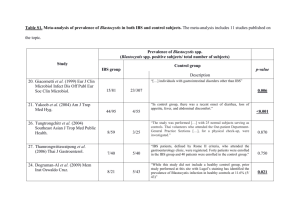
CesrTA Machine Studies Task Overview I. Experiment Description Experimental Topic Classification* Coordinator/ Experimenters Primary Goals Intrabeam Scattering IBS Michael Dave Rubin, Jim Shanks, Walter Hartung, Suntao Wang, Ehrlichman Avishek Chatterjee Gather beam size versus current in beams dominated by IBS. Description† 1) IBS Decays with Electrons (6 hr) -One of the nominal working points -Size vs. current in LET, 50 pm-rad, 100 pm-rad, 150 pm-rad conditions -2 hours setup + 1 hr per decay. -IBS should be species independent. -Experiments on both species help workout machine and instrument systematics. -Might detect non-IBS species-dependent effects. 2) IBS Decays with 2.1 GeV “eta free” lattice (6 hr) -Positrons at nominal working point -Size vs. current in LET, 50 pm-rad, 150 pm-rad conditions -3 hours setup + 1 hr per decay -Provides an IBS vs. damping time measurement -Help validate "V15 managed" lattices -Could other lattice problems be related to dispersion in the RF cavities? 3) Take IBS data at 2.5 GeV (5 hr) -Size vs. current for LET, 50 pm-rad, 150 pm-rad -1 hour setup + 1 hr for 3 decays -2.3 GeV went smooth, let’s hope the same for 2.5 GeV -Positrons at nominal working point -Combine with 2.1 GeV and 2.3 GeV data to obtain an IBS vs. Current result. 4) Strongly coupled beams (8 hr) - After applying LET corrections, generate large amounts of xy coupling to make a round-ish beam. Take size data at various currents. -Beam lifetime should be long. Will need to scrape. -This run could be one of our most interesting results. Ultimate storage * Machine Studies Classifications: EC – Electron Cloud LET – Optics Correction and Low Emittance Tuning IBS – Intra-beam scattering studies xBSM – x-ray Beam Size Monitor INST – Instrumentation (BPM development, RFA development, other) MDEV – Machine Development (includes injection configuration, injection tuning, custom orbit setup, instrumentation preparation, etc.) MREC – Machine Startup (recovering conditions after down period or access) † Attach additional pages for experimental description if needed 1 of 3 ring designs use coupling to mitigate IBS. Our data could prove valuable to those designs. -Long shift requested because we will need the vBSM for the vertical measurements, and we should allow for instrumentation work during the shift. -Positrons at 2.1 GeV -Maybe additional energies or with electrons if it goes well. -Test whether Kubo method gives right result in the presence of strong coupling. Special Needs/Requests Prerequisites‡ Root fitter front-end 2.5 GeV V15 Lattice Work out difficulties with “eta free” lattice Develop method for creating coupled beam For coupled beam measurements: vBSM needs to be ready Time Requested§ 25 hours ‡ § 1) Validate injection at 2.3 GeV and 2.5 GeV prior to IBS shifts 2) Obtain reasonable injection at the “exotic” space charge working points prior to shift 3) Obtain reasonable injection for the “eta free” lattice Personnel Description Michael ~30 line bash script that calls the root fitter, extracts the result, Ehrlichman populates MPM. Dave Rubin Nominal Qx>Qy or Qy>Qx working point Jim Shanks Dave Rubin, Michael Ehrlichman Suntao Wang No. Shifts 6 hr, 6 hr, 5 hr, 8 hr Create coupled beam by using sextupoles or moving near coupling resonance. Sextupole method is preferred, as changing working point has lots of baggage. A slit pattern was prepared for the December which would allow large vertical beams to be measured with the vBSM. This should be available for the April run. Principal Tasks 1) Decays with electrons 2) Decays with “eta free” 3) Decays at 2.5 GeV 4) Strongly Coupled Beams Indicate other machine work that is required in preparation for this machine studies experiment. Indicate the principal shift topics and estimated number of shifts required 2 of 3 II. Machine Studies Assignments Reserved for Project Management Team Use Topic ID Priority** Shift Assignments Date ** Shift Priority Scale: 1. Critical – results are necessary for preparation for subsequent down/run periods 2. Very high – results are strongly desired for achieving program milestones or in preparation for subsequent down/run periods 3. High – results are of immediate interest but not require 4. Moderate – results should be pursued at the first convenient opportunity 5. Low – results are not presently a high priority for either project milestones or planning 3 of 3