momentum/impulse pg. 20-21
advertisement

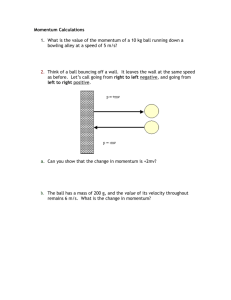
Momentum and Impulse Answer Key Pages 20 – 21 1. a) Two cars crashing b) Sliding curling rock c) Train or boat speeding up or slowing down d) Moving pen or pencil while writing 2. a) Large impulse obtained by swinging harder to increase force, or using proper technique to increase time of contact (i.e., follow-through). Both provide a large momentum to the ball. For putting the ball, a small impulse obtained by exerting a small force would be better. This decreases the momentum change the ball undergoes. Follow through for direction. b) Before dismount, a gymnast swings around the bar. As she falls, the force of gravity applies an impulse to her. Increasing her speed and momentum, especially in the legs. Gymnast rises upwards on the other side. Once her hands release from the bar, the momentum is in the gymnast’s body as she flies through the air. c) Setter must apply a force to the ball for a given length of time. Lengthen time of contact with the ball, force applied to ball can be reduced (more control). The ball will have a momentum that will carry it in the correct direction and to the correct spot to be spiked. Cushion ball and guide with right force in right direction. d) Swing bat with a large force. Accelerates bat to high velocity. Requires strength. During swing, follow through to lengthen time of contact between bat and ball. Large force and long contact time increase impulse applied and creates larger change in momentum. Ball propelled with larger velocity and travels farther out of the park. e) Car must slow down and stop, decrease momentum to zero. Braking force can be small if time to stop is large. If braking time is small, braking force is large. Abrupt stop. f) Ball must undergo a change in momentum to bring to zero. Catcher should attempt to catch the ball in the webbing of the catcher’s mitt. If the ball is caught in the palm of the hand, the ball stops in a short time. To achieve change in momentum, need a large force to stop the ball. Reaction force of ball on hand can damage the catcher’s hand. If the ball is caught in the webbing, the length of time to stop the ball increases in turn decreasing the stopping force on the ball. Damage to hand is avoided. Catcher can lengthen the time of the catch by allowing her glove to move in the direction of motion of the ball as the catch is made. This also decreases the stopping force and reduces changes of injury. 3. The opposing lineman has greater momentum, so it would be more difficult to stop him. The lineman pushes the halfback backwards. 4. Both would be equally difficult to bring to rest. The boulder has a larger mass, but the boy runs faster than the boulder. Boy cannot run any faster. However, the force of gravity applies an impulse to the boulder. AS time goes on, boulder gains momentum and rolls more quickly. Boulder will roll faster than the boy and will catch up. Boy would be crushed. Or The boy could stop to the side out of the boulder’s path. 5. Object Mass (kg) Transit bus 8 000 Velocity (km/h) 50 Momentum (kg-km/h) 400 000 Football pass 0.5 35 17.5 Sprinter 75 35 2700 Golden Boy statue 1 650 0 0 NASCAR Stock car 1 545 300 463 500 Marathon runner 65 12 780 Slapshot 0.15 150 22.5 Building 1 000 000 0 0 Skateboarder 68 20 1360 Comments Large mass, small velocity Large velocity, little mass Same mass as runner, but large velocity Mass but no velocity (no momentum) Small mass, large velocity Has mass and velocity, velocity is smaller Puck has mass and larger velocity than the football; moves faster than the football Not moving therefore no momentum Same mass as runner larger velocity