File
advertisement

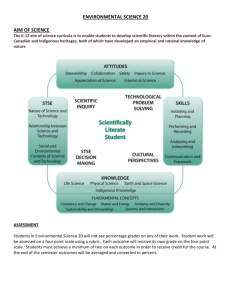
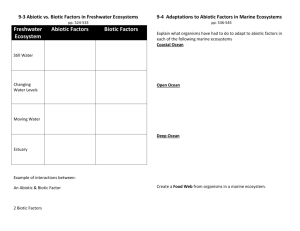
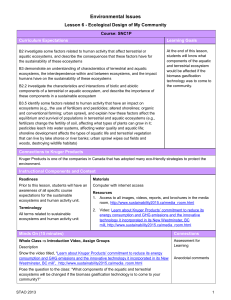
Desired Results – Ecosystems & Population Change Established Goals Unit B GLO: 1. explain that the biosphere is composed of ecosystems, each with distinctive biotic and abiotic characteristics. 2. explain the mechanisms involved in the change of populations over time. Understandings: In this unit, students become familiar with a Essential Questions: What are the major biotic and abiotic characteristics that distinguish aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems? What data would one need to collect in a field study to illustrate the major abiotic characteristics and diversity of organisms? What mechanisms are involved in the change of populations over time? Students will know: Students will be able to: B1.1STS explain how science and technology have both intended and unintended consequences for humans and the environment B1.2STS explain how conventions of mathematics, nomenclature and notation provide a basis for organizing and communicating scientific theory, relationships and concepts B2.1STS explain that scientific knowledge and theories develop through hypotheses, the collection of evidence, investigation and the ability to provide explanations range of ecosystems by studying their distinctive biotic and abiotic characteristics. Students are introduced to the concept of populations as a basic component of ecosystem structure and complete the unit by examining population change through the process of natural selection. B1.1 define species, population, community and ecosystem and explain the interrelationships among them B1.2 explain how terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems support a diversity of organisms through a variety of habitats and niches B1.3 identify biotic and abiotic characteristics and explain their influence in an aquatic and a terrestrial ecosystem in the local region B1.4 explain how limiting factors influence organism distribution and range B1.5 explain the fundamental principles of taxonomy and binomial nomenclature, using modes of nutrition at the kingdom level and morphological characteristics at the genus species level. B2.1 explain that variability in a species results from heritable mutations and that some mutations may have a selective advantage B2.2 discuss the significance of sexual reproduction to individual variation in populations and to the process of evolution B2.3 compare Lamarckian and Darwinian explanations of evolutionary change B2.4 summarize and describe lines of evidence to support the evolution of modern species from ancestral forms; i.e., the fossil record, Earth’s history, biogeography, homologous and analogous structures, embryology, biochemistry B2.5 explain speciation and the conditions required for this process B2.6 describe modern evolutionary theories; i.e., punctuated equilibrium, gradualism Sequence Outcomes Day One B1.2k, 1.3 Day Two Day Three B1.2k, 1.3 B1.2k, 1.3, 1.4 Day Four B1.2k, 1.3, 1.1sts B1.2k, 1.3 Day Five Day Six Day Ten Day Eleven A&B Concepts A&B Concepts A&B Concepts A&B Concepts B1.1-1.3 B1.5k Day Twelve B2.4k, 2.3 Day Thirteen B2.1k, 2.2, 2.5, 2.6 Day Seven Day Eight Day Nine Lesson Description Assessment Ecosystem Notes 4.1 Terrestrial Ecosystem Notes 4.2 Biomes Brochure Aquatic Ecosystem Notes 4.2 Population Limitation Notes 4.3 Changes in Ecosystems Worksheet 4.4 Quiz – Topic 4.1-4.3 Study Guide Worksheets Terrestrial Ecosystem Field Study Aquatic Ecosystem Field Study Field Study Lab Work Exit Slip (F) Topic Questions (F) Vocab (S) Biome Brochure (S) Exit Slip (F) Topic Questions (F) Vocab (S) Worksheet pg. 113120 (S) Quiz Topic 4.1-4.3 (S) Field Study Lab Work/Report Work Unit Exam Organism Classification Notes 5.1 Classification of Contents Evidence of Changing Earth Biological Inheritance Lamarck’s Theory 5.4 Mutations 5.5 Resources & Materials https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jZKIH e2LDP8&list=PL8dPuuaLjXtNdTKZkV_GiIYXp V9w4WxbX&index=6 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5eTC Z9L834s&index=10&list=PL8dPuuaLjXtNdTKZ kV_GiIYXpV9w4WxbX pg. 123-129 Field Study Extension Lab Report (S) Unit Exam (S) Vocab (S) Classification Worksheet (F) Vocab (S) Exit Slip (F) Vocab (S) Study Guide Worksheet (F) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F38B mgPcZ_I&list=PL3EED4C1D684D3ADF&inde x=19 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P3G agfbA2vo&list=PL3EED4C1D684D3ADF&ind ex=20 Day Fourteen Day Fifteen B2.1k, 2.2, 2.5, 2.6 If Time Day Sixteen B1.4-1.5, 2.12.6 Quiz 5.1-5.4 Speciation & Evolution 5.6 Sixth Extinction Performance Task Unit Exam Quiz (S) Text pg. 167 Exam (S) ASSESSEMENT Learning Outcomes Title Type (Formative/ Summative) Weighting B1.1 define species, population, community and ecosystem and explain the interrelationships among them Exit Slips Lab Reports Quiz S Of 5% F S Of 5% S 5% Vocabulary B1.2 explain how terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems support a diversity of organisms through a variety of habitats and niches B1.3 identify biotic and abiotic characteristics and explain their influence in an aquatic and a terrestrial ecosystem in the local region B1.4 explain how limiting factors influence organism distribution and range B1.5 explain the fundamental principles of taxonomy and binomial nomenclature, using modes of nutrition at the kingdom level and morphological characteristics at the genus species level. B2.1 explain that variability in a species results from heritable mutations and that some mutations may have a selective advantage B2.5 explain speciation and the conditions required for this process Unit Exam Topic Questions Worksheets, Drawings S 7.5% F S Of 5% B2.2 discuss the significance of sexual reproduction to individual variation in populations and to the process of evolution B2.3 compare Lamarckian and Darwinian explanations of evolutionary change B2.4 summarize and describe lines of evidence to support the evolution of modern species from ancestral forms; i.e., the fossil record, Earth’s history, biogeography, homologous and analogous structures, embryology, biochemistry Student Popsicle Sticks F B2.6 describe modern evolutionary theories; i.e., punctuated equilibrium, gradualism