File
advertisement

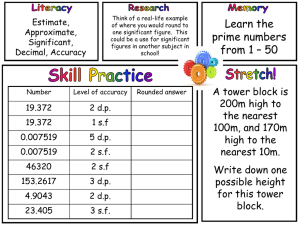
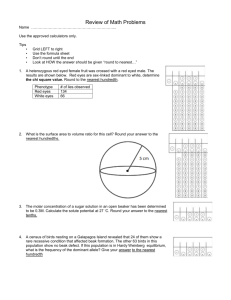
Durability of Materials PBAT - Periodic Soaking Procedure: 1. Get similar (do not need to be exactly equal) size and weight samples of Zn, Cu, Limestone, and Clay. 2. Record any initial qualitative observations (color, texture, luster, etc.) 3. Record the initial mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01 g 4. In a test tube, cover each sample with ~3 mL of acid. Record any signs of an immediate reaction. 5. Let the samples stay in the acid for 15-20 min at constant temperature and humidity. 6. Dispose of excess acid and let the samples dry for 24 hrs. 7. Record any qualitative observations and the final mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01g 8. Repeat the periodic soaking (steps 4-8, wet acid exposure then drying) cycle a total of ____ times 9. Rinse the samples with distilled (pure) water to remove any corrosion or reaction products 10. After the last drying, record the final mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01g *** For the control, repeat the experiment using distilled water instead of acid Durability of Materials PBAT - Periodic Soaking Procedure: 1. Get similar (do not need to be exactly equal) size and weight samples of Zn, Cu, Limestone, and Clay. 2. Record any initial qualitative observations (color, texture, luster, etc.) 3. Record the initial mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01 g 4. In a test tube, cover each sample with ~3 mL of acid. Record any signs of an immediate reaction. 5. Let the samples stay in the acid for 15-20 min at constant temperature and humidity. 6. Dispose of excess acid and let the samples dry for 24 hrs. 7. Record any qualitative observations and the final mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01g 8. Repeat the periodic soaking (steps 4-8, wet acid exposure then drying) cycle a total of ____ times 9. Rinse the samples with distilled (pure) water to remove any corrosion or reaction products 10. After the last drying, record the final mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01g *** For the control, repeat the experiment using distilled water instead of acid Durability of Materials PBAT - Periodic Soaking Procedure: 1. Get similar (do not need to be exactly equal) size and weight samples of Zn, Cu, Limestone, and Clay. 2. Record any initial qualitative observations (color, texture, luster, etc.) 3. Record the initial mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01 g 4. In a test tube, cover each sample with ~3 mL of acid. Record any signs of an immediate reaction. 5. Let the samples stay in the acid for 15-20 min at constant temperature and humidity. 6. Dispose of excess acid and let the samples dry for 24 hrs. 7. Record any qualitative observations and the final mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01g 8. Repeat the periodic soaking (steps 4-8, wet acid exposure then drying) cycle a total of ____ times 9. Rinse the samples with distilled (pure) water to remove any corrosion or reaction products 10. After the last drying, record the final mass of each sample to the nearest 0.01g *** For the control, repeat the experiment using distilled water instead of acid 1