Monday Homework
advertisement

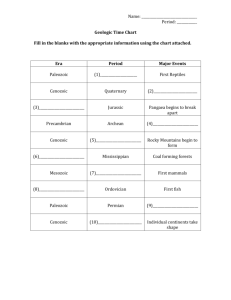
Homework/Study Guide for December 1-5, 2014 Name: _____________________________________ Period: _________ Monday Homework 8-2.1 1. What is adaptation? 2. What is natural selection? 3. What is the saying for natural selection? 4. What is evolution? 5. Natural selection favors populations with traits that help them survive and reproduce, such as each of the following except: A. camouflage B. Sterility C. Sensory abilities D. Food gathering adaptations Which animal would be better to survive if the food was limited? A. Elephant B. Worm C. Tiger D. Rhino How would the following traits benefit animals: Camouflage, Sharp Teeth, Long Neck, Heavy Coat, Good Ears, and the size of a bird’s beak? 6. 7. 8-2.2 8. Name and give a brief description of the 6 types of fossils. 9. Name the steps to how fossils form. 10. What can cause fossils of a distinct area be located in an area where you wouldn’t expect to find them? Such as a warmweathered plant fossil found in a cold environment. 8-2.3 11. Name the mass extinction for the following: Precambrian Time, Paleozoic Era, Mesozoic Era, and Cenozoic Era. 8-2.4 12. Name the divisions in the geologic time scale in order from the smallest to the largest and then from the largest to the smallest. Tuesday Homework 8-2.5 13. Complete the following Chart: Precambrian Time, Paleozoic Era, Mesozoic Era, and Cenozoic Era. Division Biological and Geological Factors that 1st appeared. Biological and Geological Factors that Became Dominated Precambrian Time Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era 14. Write down the formula that was given to help you remember the divisions in order. 15. What is the modern day eon, era, period, and epoch? 8-2.6 16. What is the difference between relative age and absolute age? Give examples. 17. Describe an index fossil 18. What are the 2 cross-cutting sections we talked about. 19. What is the law of superposition? The law of superposition deals with what type of rocks layers. 20. Look at the following layers of sedimentary rocks and place them in the order of the youngest to the oldest. Answer Intrusion Fault 8-2.7 22. Name some natural factors that can cause extinction and name some man-made factors that can cause an extinction. 21. How do you find the S-P interval? 23. Explain Water Displacement. Create an illustration? 24. What is an independent variable and dependent variable? Create a graph and label the IV and DV. Unit 8-2 Study Guide #2 Name: ____________________ 8-2.1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is adaptation? An adaptation is a trait or behavior that helps an organism survive and reproduce. What is natural selection? Natural Selection is the process that explains this survival and shows how species change over time. What is the saying for natural selection? Survival of the Fittest What is evolution? Shows have species change over time Natural selection favors populations with traits that help them survive and reproduce, such as each of the following except: A. camouflage B. Sterility C. Sensory abilities D. Food gathering adaptations 6. Which animal would be better to survive if the food was limited? A. Elephant B. Worm C. Tiger D. Rhino 7. How would the following traits benefit animals: Camouflage-to hide, Sharp Teeth-protection and to eat/tearing flesh, Long Neck-eat leaves in high places, Heavy Coat-for warmth, Good Ears-for hearing, and the size of a bird’s beak-food gathering? 8-2.2 8. Name and give a brief description of the 6 types of fossils. Mold: Cavity Cast: The filling (Fills the mold) Petrified (Permineralized): turns into rock Preserved: Prevents organisms from decaying by being trapped in rock, ice, tar, or amber Carbonized: leaves a carbon imprint by being pressed between layers of soft mud that hardens Trace: footprint, trail, or burrow of an organism was left behind 9. Name the steps to how fossils form. 1. Animal must die near bodies of water 2. 2nd Step: Sedimentation: As time passes sediments bury the exoskeleton 3. 3rd Step Permineralization: As the sediments continue to pile on, the lower layers become compacted by the weight of the layers on top. 4. 4th Step: Uplift: As the continental plates move around the earth, crashing into each other, mountains are formed. Former sea floors are lifted up and become dry land. 5. 5th Step: Erosion at work: Fossil formation is revealed by erosion 10. What can cause fossils of a distinct area be located in an area where you wouldn’t expect to find them? Such as a warmweathered plant fossil found in a cold environment. Erosion, Climatic Changes, Movement of tectonic plates (Pangaea forming and splitting), and geological features changing 8-2.3 11. Name catastrophes that caused the mass extinction for the following: Precambrian Time, Paleozoic Era, Mesozoic Era, and Cenozoic Era. Mass extinctions cause the eras to end. Precambrian Time Paleozoic Era Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Mass Extinction Glaciation or glacier events Volcanic Activity Climatic Changes Lowering of sea levels Asteroids and Comets Early Cenozoic (Ice Ages) None/we are still living 8-2.4 12. Name the divisions in the geologic time scale in order from the smallest to the largest and then from the largest to the smallest. Smallest to Largest: Epochs, Periods, Eras, and Eons Largest to Smallest: Eons, Eras, Periods, and Epochs 8-2.5 13. Give a brief description for the following: Precambrian Time, Paleozoic Era, Mesozoic Era, and Cenozoic Era. Division Biological and Geological Factors that 1st appeared. Precambrian Time Invertebrates, soft bodied animals/ cyanobacteria and stromatolites/algae and fungi Paleozoic Era Trilobites, Vertebrates, Arachnids (spiders), insects, amphibians, reptiles, seed plants, fish, brachiopods, ammonites, forests, gymnosperms (seeded plants), and mountains Dinosaurs, angiosperms (flowering plants), small mammals and birds Trilobites, fish, and invertebrates Humans, Mountain Ranges, and Continents Mammals and flowering plants (angiosperm) Mesozoic Era Cenozoic Era Biological and Geological Factors that Became Dominated Stromatolites and Cyanobacteria Dinosaurs, reptiles, ammonites, forest, and seed plants (gymnosperms) 14. What is the formula that was given to help you remember the divisions in order? Eon = E + P = EP (Eons = Eras + Periods = Epochs) 15. What is the modern day eon, era, period, and epoch? Eon: Phanerozoic Era: Cenozoic Period: Quaternary Epoch: Holocene 8-2.6 16. What is the difference between relative age and absolute age? Relative age shows the comparison of the rock layers (young/old) Absolute age gives the exact age of the rocks (20,000 years old) 17. Describe an Index fossil. In order to be an index fossil: the organism is extinct, it only lived for a short period of time, fossils must be found in rock layers, fossils must be found over a wide area of Earth; and the organism must be unique Helps find the relative age o f a rock 18. What are the 2 cross cutting sections we talked about? Intrusions and faults (They are always the youngest when they cut through a layer of rock) 19. What is the law of superposition? The older rocks are found at the bottom and the younger rocks are found at the top. Found in the sedimentary rocks. The law of superposition deals with what type of rock layers? Sedimentary Rock Layers 20. Look at the following layers of sedimentary rocks and place them in the order of the youngest to the oldest. Answer Intrusion Fault 8-2.7 21. Name some natural factors that can cause extinction and name some man-made factors that can cause an extinction. • • Natural Factors: Organisms that could not survive changes due to volcanic eruptions and global warming, global cooling during ice ages, climatic changes, changes in oxygen levels in seawater, or a massive impact from an asteroid or comet became extinct. Man-Made Factors: cutting of the rainforest regions, removing natural habitats, over-harvesting, and pollution. 22. How do you find the S-P interval? Use the formula S-P: Subtract the Pwave arrival time from the Swave arrival time 23. Explain Water Displacement. Do an illustration? You can measure the volume of an irregular object using water displacement. Water Displacement determines the volume of an irregular shape. • Amount of H2O with object = ______ minus Amount of H2O without object = ____ Difference = Volume = ______ 24. What is an independent variable and dependent variable? Create a graph and label the IV and DV. IV: The variable that he experimenter purposefully change DV: The variable that responds to the change made from the IV (Independent variable always go on the x-axis and Dependent variables always go on the y-axis)