Some useful Java syntax
advertisement

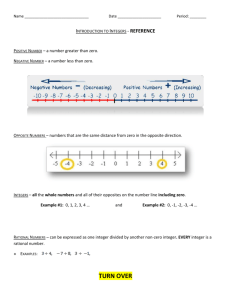
Some useful Java syntax
Adjacency List: (also refer to the sample code at the end of this document)
ArrayList of ArrayLists
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> mylist = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
ArrayList<Integer> temp = mylist.get(i);
Temp.push(x);
Mylist.set(i, temp);
Or an array of Stacks
Stack<Integer>[] mystack = new Stack[n];
Mystack[i].push(x);
Useful data structure for BFS
ArrayDeque
ArrayDeque<Point> queue = new ArrayDeque<Point>();
Point p = queue.poll() ; //returns and removes the first object of the queue
Queue.add(p); //adds to the end;
Queue.push(p); //adds to the front of the queue – without shifting all the elements, so takes O(1)
Reading input:
Don’t use Scanner – it’s slow!
BufferedReader is much faster
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = in.readLine();
Also, you’ll have to add “throws IOException” for the main method
Sample Code of building an adjacency list:
import java.util.*;
public class AdjacencyList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); //yes, I should have used BufferedReader
String in = sc.nextLine();
int edges = Integer.parseInt(in.split(" ")[0]);
int vertices = Integer.parseInt(in.split(" ")[1]);
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adjacency1 = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>();
//Option 1: Use an ArrayList of ArrayLists
Stack<Integer>[] adjacency2 = new Stack[vertices]; //Option 2: Use an Array of Stacks
in = sc.nextLine();
int start = Integer.parseInt(in.split(" ")[0]);
int end = Integer.parseInt(in.split(" ")[1]);
//Note that there are 7 edges and 8 vertices (7 roads and 8 cities)
//All the edges are inputted as A B, add B to A's adjacency list and A to B's adjacency list
//Remember to initialize the array of stacks and the arraylists in the arraylist
for(int i = 0; i<vertices; i++){
adjacency1.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
adjacency2[i] = new Stack<Integer>();
}
for(int i = 0; i<edges; i++){
in = sc.nextLine();
int a = Integer.parseInt(in.split(" ")[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(in.split(" ")[1]);
//Option 1 code:
ArrayList<Integer> temp = adjacency1.get(a); //Adding B to A's adjacency list
temp.add(b);
adjacency1.set(a,temp);
//Remember that this is an undirected graph –
//an edge from A to B also goes from B to A
temp = adjacency1.get(b); //Adding A to B's adjacency list
temp.add(a);
adjacency1.set(b,temp);
//Option 2 code:
adjacency2[a].push(b);
adjacency2[b].push(a);
}
//Print the output
for(int i = 0; i<vertices; i++){
System.out.println("City " + i + ":");
for(int j:adjacency1.get(i))
System.out.print(j + " ");
System.out.println(" ");
}
}
}