The Theory Of Light
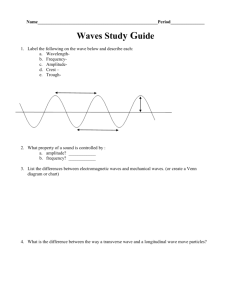
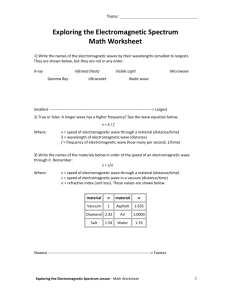
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
THE THEORY OF LIGHT: PAST AND PRESENT
EARLY THEORIES OF LIGHT
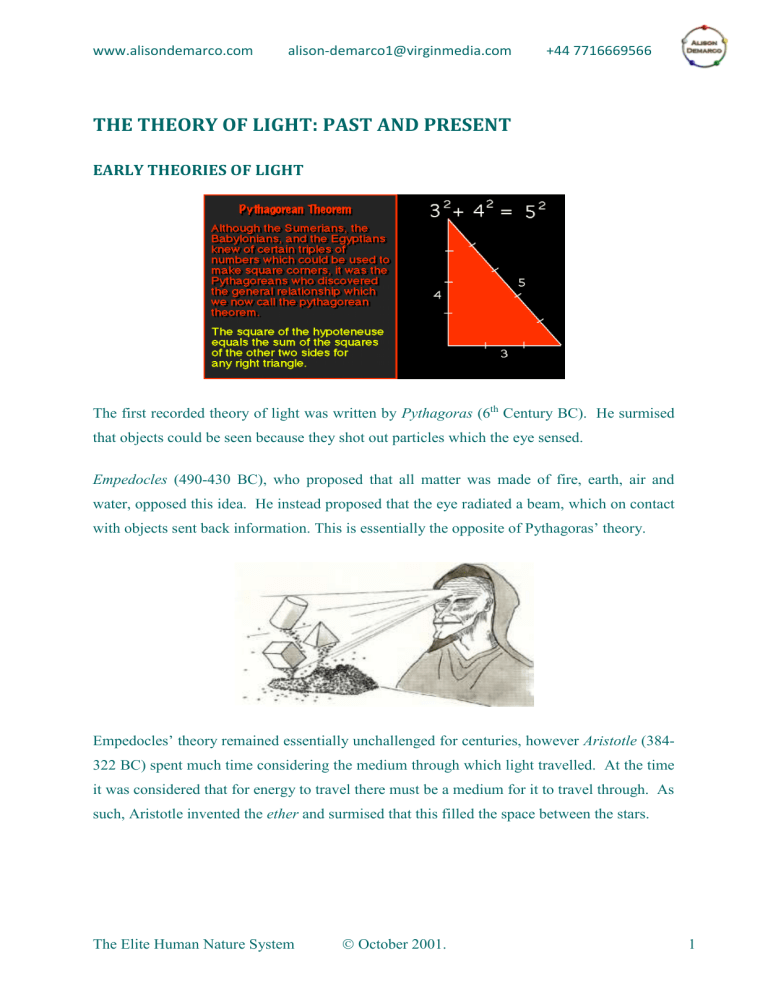
The first recorded theory of light was written by Pythagoras (6 th Century BC). He surmised that objects could be seen because they shot out particles which the eye sensed.
Empedocles (490-430 BC), who proposed that all matter was made of fire, earth, air and water, opposed this idea. He instead proposed that the eye radiated a beam, which on contact with objects sent back information. This is essentially the opposite of Pythagoras’ theory.
Empedocles’ theory remained essentially unchallenged for centuries, however
Aristotle (384-
322 BC) spent much time considering the medium through which light travelled. At the time it was considered that for energy to travel there must be a medium for it to travel through. As such, Aristotle invented the ether and surmised that this filled the space between the stars.
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 1
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
With the fall of the Greco-Roman Empire in the 5 th
Century AD, science (or philosophy as it was then called) and the advancement of science fell by the way. As a result, no credible theories appeared until the 17 th
Century.
‘MODERN’ THEORIES OF LIGHT
1704:
Isaac Newton (1642-1727) – The corpuscular theory of light
According to Newton, a luminous body (one that emits light) emits swarms of particles
(corpuscles) that travel in straight lines through the ether. Newton also discovered in 1672 that visible light could be broken down into its components or spectrum.
1690:
Christian Huygens (1629-1695) – The wave theory of light.
Huygens, a contemporary of Newton, formulated the wave theory of light. However, due to
Newton’s great reputation, Huygens’ theory was discarded.
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 2
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 3
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
1801:
Augustine Fresnel (1788-1827) and Thomas Young (1773-1829)
The wave theory of light, first proposed by Huygens, was proven, hence proving Newton wrong.
1849:
Armand Fizeau (1819-1896) – Measurement of the speed of light.
Fizeau, whilst not only measuring the speed of light, also added weight to the wave theory of light and proved that light slows down in a solid medium, such as glass.
1859:
Robert Von Bunsen (1811-1879) and Gustav Kirchoff (1824-1887)– Electromagnetic spectrum.
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 4
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
Spectographic Analysis:
Bunsen and Kirchoff discovered that each metal gives off a distinct colour when heated.
Furthermore, this light can be split using a prism and the composition of a given sample can be determined.
1873:
James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879) – Electromagnetic spectrum.
Maxwell proposed a mathematical model, whereby light travels as two separate but interlocking waves. The first wave represents an electrical field and the second represents a magnetic field. Maxwell also proposed that not all energy travelling by this route had to be visible. This gives us the name electromagnetic spectrum.
1887/8:
Heinrich Hertz (1857-1894) – The discovery of radio waves (1887/8).
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 5
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
Hertz confirmed Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetic waves. He then went on to produce another form of electromagnetic radiation (radio waves) and proved them to travel at the speed of light, thus being another member of the spectrum.
1895:
Wilhelm Rontgen ( 1845-1923) – The discovery of X-rays.
Further evidence for the existence of the electromagnetic spectrum with the discovery of its second most energetic member.
1905:
Albert Einstein (1879-1955) E = mc
2
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 6
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
Einstein showed that energy and matter are one and the same thus postulating wave/particle duality.
1923:
Arthur Compton (1829-1962) – Wave/particle duality of light.
Compton found unexpected results in experiments with X-rays, which could only be explained if X-rays behaved as a particle. This created some problems as X-ray had already been proven to be a wave. Rather than cast aside the results, Compton chose to take these results as confirmation of Einstein’s controversial theory.
1925/6:
Werner Karl Heisenberg ( 1901-1976), Erwin Shrodinger (1887-1961) – Quantum mechanics
Heisenberg and Schrodinger laid down the equations necessary for wave/particle duality to become reality. They described a system where light energy travels as small ‘packets’ or quanta, which can either be waves or particles according to E = mc 2 .
1932:
Karl Jansky (1905-1950 - Radio astronomy
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 7
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
The Bell telephone laboratories hired Jansky in 1928 to investigate the cause of interference on radio-telephone calls. Jansky noticed that the background hiss on a loudspeaker was periodic, but four minutes less than the rotation of the earth. By 1932 he concluded that the source lay in the direction of the centre of the universe.
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 8
www.alisondemarco.com
alison-demarco1@virginmedia.com
+44 7716669566
The Elite Human Nature System
October 2001. 9