Foods Final Review Answer Key
advertisement

Name___________________KEY____________________ Period__________ Date___________ Score _____________
Food and Nutrition Review
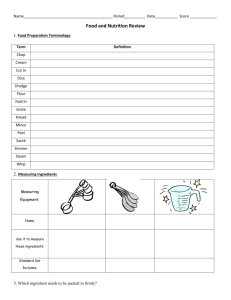
1. Food Preparation Terminology:
Term
Definition
Chop
To cut food into small pieces
Cream
To mix sugar and fat together until soft and creamy
Cut In
To cut fat into flour with a pastry blender or two knives
Dice
To cut into small cubes
Dredge
Flour
To coat food with flour or sugar
To sprinkle or coat with a powdered substance, often with crumbs or seasoning
Fold In
To combine two mixtures by gently cutting down through the mixture, across the bottom, and turning over near the surface
Grate
To rub food on a surface with sharp projections
Knead
To work dough by pressing and folding until it becomes elastic and smooth
Mince
To cut food into the smallest possible pieces
Peel
To remove or strip the skin or rind of some fruits and vegetables
Sauté
To brown or cook food in a small amount of fat over low or medium heat
Simmer
To cook food just below the boiling point
Steam
To cook by the vapor produced when water is heating to the boiling point
Whip
To beat rapidly to incorporate air and to increase volume
2. Measuring Ingredients
Measuring
Equipment:
Name
Dry Measuring Cups
Measuring Spoons
Liquid Measuring Cup
Dry ingredients ¼ cup or larger
Liquid or dry ingredients
Liquid ingredients ¼ cup or larger
Use it to measure
these ingredients:
less than ¼ cup
Flour, sugar, brown sugar, etc.
Vanilla, salt, baking soda,
Oil, milk, water, etc.
baking powder, etc.
Standard Set
Includes:
¼ cup, 1/3 cup, ½ cup, 1 cup
¼ tsp, ½ tsp, 1 tsp, 1 tbsp
Spout to pour, handle, extra room
at the top to prevent spills, easy
to read measurements.
3. Which ingredient needs to be packed in firmly? Brown sugar
4. List the following abbreviations:
Tbsp., tbsp., or T. ___Tablespoon_____
tsp. or t. ___teaspoon_______
min.
___minute________________
hr. _______hour___________
oz. _______ounce_________________
qt. _____quart_____________
pt. _________pint_________________
gal. ________gallon________
c. ______cup_____________________
lb. or # ____pound__________
doz. ______dozen_________________
pkg. ____package___________
5. List the following equivalents:
1 Tbsp. = _____3_________ tsp.
1/4 c. = ____4_________ Tbsp.
1 c. = _______16______ Tbsp.
1 c. = ____8__________ fluid oz.
1 pt. = ________2_______ c.
1 qt. = _____2_________ pt.
1 gal. = _____4__________ qt.
3/4 c. = ______12______ Tbsp.
1 qt. = ____4___________ c.
1 gal. = ______16______ c.
1/2 Tbsp. = ____1 1/2_____ tsp.
1/2 c. = ______8_______ Tbsp.
1/3 c. = _____5 1/3______ Tbsp.
1 stick of margarine= ___1/2_______ c.
Microwave Cooking
6. What are the 3 things microwaves are attracted to? Fat, sugar, liquid
7. List at least 3 microwave safe containers? Plastic, glass, ceramic
8. What is cooking time? the amount of time the microwaves are on
9. What is standing time? the time after the microwaves are shut off, the food continues to cook
10. Why is standing time so important? the food needs to cook entirely
11. What type of dish would be better for microwave cooking: tall or shallow? Why? Shallow, even cooking
12. Which food would cook faster: a whole potato, or thin potato slices? Thin potato slices
13. Why is it important to cover the food when cooking? Prevent splatters, steam to cook the food
14. What does it mean to “vent” the cover? Allow room in the cover for steam to escape
15. What can happen if you don’t “vent” the cover? “exploding” in the microwave
Kitchen Safety
16. What are four ways you can put out a grease fire? Fire extinguisher, baking soda, lid, wet towel
17. How should you care for a severely bleeding cut? Apply pressure
18. What should you use when trying to reach items on a high shelf? A step stool
19. What is the minimum amount of time you should wash your hands before cooking? 20 seconds
20. What should you do FIRST if someone is being shocked (besides not touching them) Turn off the power
21. How should you lift the lid off a pan that is full of hot, steamy food? Away from your face
22. When cooking on the stovetop, what direction should all of the pan handles be facing? Toward the center
23. Which one is safer, dull or sharp knives? Why? Sharp, you may push too hard on a dull knife, resulting in injury
24. Why should you never mix chlorine bleach and ammonia? Toxic gas
Food-borne Illness and Danger Zone
25. Finish this phrase: When in doubt, ___throw ____ __it__ __out__!
26. If a can is bulging, it likely contains ___botulism______.
27. What is the most common food source for the food-borne illness E-coli? Undercooked ground beef
28. What is the most common food source for the food-borne illness salmonella? Eggs and poultry
29. A worker who uses the bathroom and doesn’t wash their hands can spread this food-borne illness. Hepatitis
30. How is staphylococci spread? Bodily fluids, mucous, cuts, scrapes, etc.
31. Define cross contamination. Using the same surface or utensil on raw meat and then raw vegetables/fruit, etc.
32. How can cross contamination be prevented? Wash all cutting boards, utensils, etc.
33. The temperature of the danger zone is between __41°F_____ and __135°F____.
34. What happens to bacteria left in the danger zone? Bacteria grows rapidly
35. How long should food be left in the danger zone? 2 hours
36. What happens to bacteria below 41°F? The growth is slowed
37. What happens to bacteria above 135°F? They begin to die
38. What are two ways to safely thaw meat? Refrigerator, microwave
39. How can you safely thaw a whole turkey? Sink of cold water, change water every 3 minutes
40. What are two methods you should NOT use to thaw meat? Counter top, sink of hot water
41. MyPlate- Fill out the chart based on the MyPlate Logo:
Name
Color
MyPlate Recommendation
Fruits
Red
Make half your plate fruits and vegetables
Vegetables
Green
Eat more dark green and orange vegetables
Grains
Orange
Make half your grains whole grains
Protein
Purple
Go lean with protein
Dairy
Blue
Eat low fat or reduced fat dairy
42. Dietary Guidelines- Fill in the blank.
Eat nutrient _dense_ foods.
Balance ___calories__ to manage weight.
Reduce __sodium__, fats, and added __sugars__, refined grains, and alcohol.
Increase vegetables, fruits, whole grains, milk, seafood, and use __oils__ in place of solid fats.
Build healthy _eating_ patterns that meet nutritional needs over time at an appropriate calorie level.
Include physical _exercise_ as part of healthy eating patterns.
43. Ten Tips To A Great Plate- Fill in the blank.
Balance Calories
Enjoy your food, but eat __less__.
Avoid oversized __portions__.
Foods to increase:
Make _half_ your plate fruits and vegetables.
Switch to __fat-free_____ or low-fat (1%) milk.
Make at least __half____ your grains whole grains.
Foods to reduce:
Compare __sodium__ in foods like soup, bread, and frozen meals and choose the foods with lower numbers.
Drink _water__ instead of sugary drinks.
44. What are empty calories?
Food which is high in calories, and low in nutrients
45. What are three factors affecting caloric needs?
Age, gender, activity level
46. What are the 6 basic nutrients, how many calories per gram do they contain, and what is the MAIN function of each?
Nutrient
Calories per
Main Function
Gram
1.Fat
9
To provide reserve store of energy, carries fat soluble
vitamins, cushion, heat regulator
2. Carbohydrates
4
To provide energy
3.Protein
4
To build and repair body tissue
4.Vitamins
0
To regulate body functions
5.Minerals
0
To regulate body functions
6. Water
0
Carries water soluble vitamins, regulates body
temperature, carries waste products out
Carbohydrates
47. What type of carbohydrate is simple? __sugars_______
48. What type of carbohydrate is complex? __starch______
49. Which type of carbohydrate (simple or complex) is the best energy source? ___complex___________
Quick Breads
50. What are 4 examples of quick breads? Pancakes, waffles, muffins, biscuits
51. Identify the role of each ingredient in quick breads.
Ingredient
Purpose
Flour
Structure
Liquid
Moisture, helps ingredients react with each other
Leavening Agents
Makes rise
Fat
Flavor/tender/browning
Salt
Enhance flavor
Sugar
Flavor/tender/browning
52. What two types of leavening agent do quick breads use? A. __baking soda_ B. ____baking powder____
53. When making quick breads, why should you not over mix them? __Prevent gluten formation, tunnels, and peaks__
54. If your recipe calls for baking powder, can you substitute and use baking soda? Why or why not? No, baking soda
reacts with an acid, baking powder reacts with heat and moisture
55. Which mixing method has you make a well in the middle of the dry ingredients and then add all the liquid
ingredients at once? Muffin Method or Biscuit Method? (Circle One)
56. Which mixing method has you cut-in the fat and then knead the dough? Muffin Method or Biscuit Method?
(Circle One)
57. What tool would you use to cut fat into flour? Pastry blender
Rice and Pasta
58. Explain how to cook pasta (how much water, with or without lid, what do you add to the water, when do you put the
pasta in the water, etc.)
__Use high heat, bring water to a boil, with the lid on. Cook a small amount of pasta in a large amount of
water. Add salt and oil to water. When water is boiling, add pasta. Cook with lid off. Drain pasta in a
colander immediately after cooking. ___
59. Explain how to cook rice (with or without lid, do you add anything to the water, when do you put the rice in the
water, what temperature should the stove be on, what should you do when the rice is done, etc.)
__Add rice to water. Bring to a boil.
Fluff rice with a fork.___
Reduce heat to low.
Cook for 18 minutes with lid on.
Remove from heat.
60. If you have 3 cups cooked pasta, it will be approximately _6__ cups of cooked pasta.
61. If you have 4 cups of uncooked rice, it will be approximately __12___ cups of cooked rice.
Proteins
62. What are amino acids? __the building blocks of proteins____________________________________________
63. What is a complete protein? __a protein containing all 9 essential amino acids from an animal source____________
64. What is an incomplete protein? __a protein that does NOT contain all 9 essential amino acids from a plant source___
65. The following are examples of __Complete__ proteins: Meat, Fish, Poultry, Cheese, Eggs, Yogurt, Milk
66. The following are examples of __Incomplete__ proteins: Grains, Nuts, Beans, Seeds, Peas, Corn
Milk
67. Define:
Pasteurization- __heat treatment of milk/milk products to remove or kill harmful bacteria___________
Homogenization- _the breakdown and distribution of fat particles so that the milk will not separate_______
Fortified-_Adding nutrients, in milk, vitamin A & D________________________________________________
68. True OR False You can lower the fat in recipes by using lower fat content milk or milk products.
Fats
69. Fat does the following: Carrier for vitamin _A_, _D_, _E_, and _K_; reserve supply of _energy_; adds _flavor_ in
food; satisfies _hunger_; protects _vital_ organs from shock and temperature changes; promotes healthy _skin_; makes
you feel _full_ longer.
70. Which type of cholesterol is better for you: HDL’s or LDL’s? __HDL______
71. Which one is MORE saturated: solid fats or liquid fats? ___Solid_________
72. Which one is LESS saturated: solid fats or liquid fats? _____liquid________
73. What are the four types of fat? List in order of best to worst. Also explain what happens to the HDL’s and LDL’s.
Type of Fat
HDL
LDL
Monounsaturated
May raise
Lowers
:-} Polyunsaturated
No effect
Lowers
:-{ Saturated
Blocks protective effect
Raises
Trans
Lowers
Raises
Vitamins
74. List the four fat-soluble vitamins:
1. ___A_______
2. ____D________
3. ___E__________
4. ___K_________
75. List the two water-soluble vitamins? 1. ___B_____ 2. ___C______
76. What vitamin can you get from sunlight, as well as dairy products? __D_____________
77. What vitamin will help prevent neural tube defects like spina bifida? __Folate________
Minerals
78. List the three types of minerals:
1. _Macro_________
79. List the three macro minerals:
2. _Trace___________ 3. __Electrolyte___________
1. _calcium_________
2. ___phosphorous_________ 3. ___magnesium__________
80. List the five trace minerals:
1. _iron_
2. _zinc____
3. __fluorine__ 4. _copper__
5. _iodine__
81. List the three electrolytes:
1. _sodium_________
2. __chloride_________ 3. __potassium___________
82. What disease could you get if you are deficient in calcium? ____osteoporosis_______
83. What disease could you get if you are deficient in iron? ___anemia_________
Water
84. Functions of water in the body include: Carries water soluble _vitamins_; carries _waste_ through the body,
regulates body _temperature_; prevents _dehydration_.
Fruits and Vegetables
85. List six ways to preserve nutrients when cooking fruits and vegetables?
1. _Microwave_______________________________
2. _Bake____________________________________
3. _Steam___________________________________
4. _Stir Fry___________________________________
5. _Simmer__________________________________
6. _Sauté____________________________________
86. What are some important guidelines for selecting fresh fruits and vegetables?
Firm, free from decay & bruises, good color
87. How do you prevent oxidation of fresh fruits?
Cover with a liquid containing ascorbic acid (vitamin c)
Fiber
88. T/F Fiber is only found in plant sources.
T/F Fiber in only found in animal sources.
89. The National Cancer Institute recommends eating _20___ - _35____ grams of fiber daily.
90. Whole grains are made from the __bran___, _____germ____, and ___endosperm____________. (Label each)