Brain Research Methods
advertisement

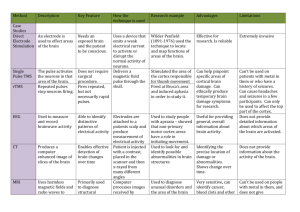
Brain Research Methods: List of Invasive methods: The only truly invasive method of brain research is: Direct Electrode Stimulation Other methods involve either drinking or injecting a contrast substance to help with imaging, these are: CT, PET and SPECT List of Radioactive methods: CT: Xrays from the machine. PET and SPECT: The tracer substance ingested. List of Types: Functional: Direct Electrode Stimulation, EEG, TMS Structural: CT, MRI Both Function AND Structure: PET, SPECT and fMRI Direct Electrode Stimulation: -Invasive: YES -Radioactive: NO -Type: Functional -Description: Measures a direct cause effect relationship between electrically stimulating part of the brain by touching it with an electrode, and a psychological response. No longer used because it is extremely invasive and not necessary due to the innovation of TMS. TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation): -Invasive: NO -Radioactive: NO -Type: Functional -Description: Similar to Direct Electrode Stimulation, but uses an electro magnetic coil to induce brain neurons to fire rather than touching it with an electrode. Has an advantage over Direct Electrode Stimulation because it is very noninvasive and works through the scalp and skull. rTMS -Identical to TMS but uses repeated magnetic pulse, rather than a single pulse. This causes disruption of brain activity in the effected area, temporarily impairing a persons ability to perform a certain task. EEG (Electroencephalograph): -Invasive: NO -Radioactive: NO -Type: Functional -Description: Detects the firing of neurons under electrodes placed upon the scalp of the patient. Helps to locate areas of brain activity while certain tasks are performed. CT (Computed Tomography) (CAT) -Invasive: Non Radioactive Contrast substance injected into blood steam. -Radioactive: Yes, Contrast substance is not radioactive, but xrays from CT machine are. -Type: Structural -Description: Uses a series of xray images to compile a computer generated 3D image of a patients brain. The injected Contrast substance highlights blood vessels in the brain, which helps to interpret the CT images. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) -Invasive: NO -Radioactive: NO (magnetic instead) -Type: Structural -Description: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to detect vibrations of atoms, and create a 3D image. Higher resolution images than a CT Scan. Main disadvantage is that it cannot be used on patients with metallic implants, as the high powered magnets would cause damage to them. PET (Positron Emission Tomography) -Invasive: Injected radioactive tracer. -Radioactive: YES (Tracer) -Type: Functional AND Structural -Description: Machine monitors the amount of glucose being used within the brain to determine areas of higher activity. Does so by detecting radioactive tracer injected into the patients blood steam. SPECT (Single-photon emission computed tomography) -Invasive: Injected radioactive tracer. -Radioactive: YES (Tracer) -Type: Functional AND Structural -Description: Very similar to a PET, main difference being the SPECT tracer lasts longer the PET tracer, which helps when monitoring tasks that take a lot longer. SPECT images are also of a lower resolution to that of PET images, but this can be overcome by combining SPECT images with a CT scan (SPECT-CT). fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) -Invasive: NO -Radioactive: NO -Type: Functional AND Structural -Description: Uses MRI technology but further enhanced with the detection of oxygen usage in the brain, which relates to brain activity. No radioactivity or invasive procedures, however no metallic objects can be inside the patient.