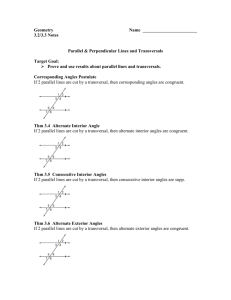
m || n Parallel Lines and Transversals
advertisement

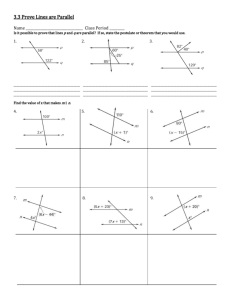
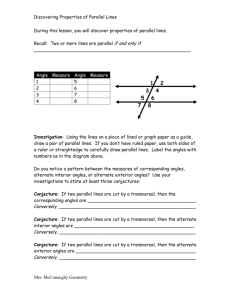
Color one pair of alternate exterior angles purple and the other orange. Color one pair of alternate interior angles red and the other yellow. Sign for parallel: m || n In the diagram on the right, parallel lines m and n have been “cut” (intersected) by a transversal, t. When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, certain angle relationships are formed. Parallel Lines and Transversals Color one pair of vertical angles blue and the other green. Exterior angles that lie on __________ sides of the transversal and on ________ parallel lines. If the lines are parallel, then they are ________. The angles that are alternate exterior in the figure below are: Interior angles that lie on __________ sides of the transversal and on ________ parallel lines. If the lines are parallel, then they are ________. The angles that are alternate interior in the figure below are: Congruent angles formed by two intersecting lines. The angles that are vertical in the figure below are: Alternate Alternate Vertical Interior Exterior Angles Angles Angles Color each pair of corresponding angles a different color. Angles that lie on the ________ side of the transversal and in ___________ positions. The angles that are corresponding in the figure below are: Parallel Lines and Transversals – Guided Practice Example 1: Use the diagram to answer the following questions. A || B and T is a transversal. Are angles 1 and 3 congruent? How do you know? Are angles 4 and 6 congruent? How do you know? If angle 2 is 145°, determine the measurements of all the angles. Justify your answers using angle relationships. -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Example 2: Given: p || q and w is a transversal. Which angles are congruent? Explain. If angle 2 is 132°, what is the measure of angle 7? Justify your answer. Example 3: Use the diagram to find the measures of the angles. List the reason below a.) mÐa = _______ Reason? ___________ b.) mÐb = _______ Reason? ___________ Example 5: Lines m and n are parallel, and line t is a transversal. a.) Use the diagram to find x. What relationship did you use set up your equation? c.) mÐc = _______ Reason? ___________ d.) mÐd = _______ Reason? ___________ e.) mÐe = _______ Reason? ___________ Is there a different way to find e? b.) Determine the measures for all the angles. ________________________________________________________ f.) mÐf = _______ Reason? ___________ Is there a different way to find f? ________________________________________________________ ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Example 6: In the diagram lines j and k are parallel. a.) What is the value of x? How do you know? Example 4: Line p and q are parallel. Give three ways to reason that angle 1 and angle 7 are congruent. Reason 1: _______________________ b.) What is the value of y? How do you know? ________________________________ ________________________________ Reason 2: _______________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ Reason 3: _______________________ ________________________________ ________________________________ -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Example 7: The diagram shows lines l, m, n, p, and q all cut by transversal t. Which two lines are parallel? How do you know?