10th Grade Chemistry - Science at CIC with Ms. Luckasavitch
advertisement

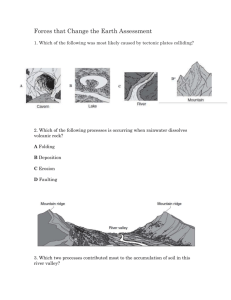
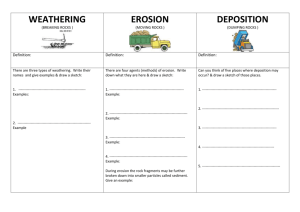
6th Grade Science Quarter 4, 2015 Ms. L. Luckasavitch Room SS7 Email: lluckasavitch@cic-valencia.org.ve Website: luckasavitch.weebly.com Course Description: The goal of Science 6 is to provide students with the foundation of knowledge to understand, construct, and reinforce scientific concepts. The topics covered will include an overview of science and the scientific method, freshwater systems, the ocean, weather and climate, plate tectonics, earthquakes, volcanoes, rocks and minerals, weathering and erosion, and geologic time. To this regard, students will actively engage in hands-on exploration of these topics. Students will learn how to think like scientists while applying the concepts of observing, measuring, communicating, classifying, predicting, inferring, hypothesizing, and experimenting. Textbook: Science Explorer: Earth’s Changing Surface. Wysession, Michael. Prentice Hall. 2007 Materials: Ringed Binder Pens, pencils, erasers Units of Study: Unit 9 – Weathering, Erosion, and Deposition Essential Question: How does nature affect the shape of Earth’s surface? Ch. 2: Weathering and Soil Formation and Ch. 3: Erosion and Deposition (5 weeks) Objectives: Students will understand how the forces of erosion and deposition reshape Earth’s surface by wearing it down and building it back up. They will understand that some forces act over a short period of time, while others take much longer. Desired outcomes: The students will be able to… 1. Describe how weathering and erosion affect Earth’s surface. 2. Discuss the causes of mechanical and chemical weathering. 3. Explain the factors affecting the rate of weathering. 4. Explain how weathering, erosion, and deposition combine forces to wear down and build up Earth’s surface. 5. Explain the cause of the different types of mass movements. 6. Describe the cause and effect of water erosion, both on Earth’s surface and underground. 7. Describe the landforms caused by water deposition. 8. Differentiate between the different types of glaciers in terms of their location, formation, and movement. 9. Explain how glaciers cause erosion and deposition. 10. Describe the landforms created by glaciers. 11. Describe how wind causes erosion and the features it forms through deposition. Unit 10 – History of Earth Essential Question: How has the Earth changed over time, what caused those changes, and how did it affect both the geology of Earth and the biology present? Ch. 4: A Trip Though Geologic Time (4 weeks) Objectives: Students will understand how fossils are used to determine Earth’s past environments and organisms. They will also understand the major events that took place within Earth’s geological time scale. Desired outcomes: The students will be able to… 1. Describe the different types of fossils and explain how they formed. 2. Explain how the fossil record is used to describe organisms and environments of the past. 3. Use the law of superposition, rock changes, and index fossils to explain how scientists determine the relative ages of rocks within a layer. 4. Explain radioactive dating and describe how scientists use it to determine the absolute age of rocks. 5. Explain how and why scientists use the geological time scale. 6. Describe the structure of the geological time scale and how the time periods are defined. 7. Describe what took place during early Earth, Precambrian time, and the 3 eras in terms of geological events and development of life. Evaluation: Tests (One per unit along with an Error Analysis of each test) Assignments (Textbook end-of-chapter questions; Labs; Project; Science Fair; etc.) Quizzes (One or two per chapter) Homework (Guided notes, Visual Dictionary, etc.) 40% 35% 20% 5% Next Generation Science Standards Performance Expectations: MS-ESS2-2. Construct an explanation based on evidence for how geoscience processes have changed Earth's surface at varying time and spatial scales. MS-ESS2-3. Analyze and interpret data on the distribution of fossils and rocks, contintental shapes, and seafloor structures to provide evidence of the past plate motions. MS-ESS3-1. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distributions of Earth's mineral, energy, and groundwater resources are the result of past and current geoscience processes. MS-ESS3-2. Analyze and interpret data on natural hazards to forecast future catastrophic events and inform the development of technologies to mitigate their effects. MS-ESS1-4. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth's 4.6-billion-year-old history. HS-ESS1-5. Evaluate evidence of the past and current movements of continental and oceanic crust and the theory of plate tectonics to explain the ages of crustal rocks. HS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to illustrate how Earth’s internal and surface processes operate at different spatial and temporal scales to form continental and ocean-floor features.