Chapter 1 Challenge Presentation Guide What are Following
advertisement

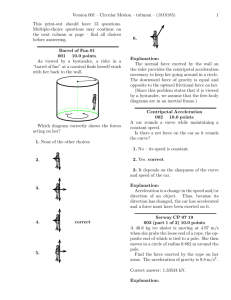
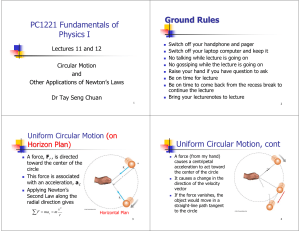
Chapter 1 Challenge Presentation Guide 1) What are Following distance, braking distance, and the total stopping distance? a. Define the following i. Following distance ii. Braking distance iii. Thinking/reaction distance iv. Total stopping distance b. What are the relationships among them? c. What are the factors that affect each? 2) How do you decide what to do when the light turns yellow as you approach an intersection? a. When the light turns yellow, one must determine if one is in the GO Zone or the STOP Zone: b. Define the Following i. GO Zone ii. STOP Zone iii. Variables in Equation: 1. Speed (v) a. Constant Speed b. Instantaneous Speed i. Error 1. Systematic error a. Accuracy 2. Random error a. Precision c. Average Speed d. Velocity 2. Acceleration (a) a. Positive acceleration b. Negative acceleration 3. Yellow Light Time (ty) 4. Response/Reaction Time (tr) 5. Width of Intersection (w) c. Although one can’t always get an exact measurement of the GO Zone and the STOP Zone, one can estimate by considering the factors that affect each zone. i. If one increases speed and/or yellow light time, then the GO Zone _______; if one increases the width, then the GO Zone _______. ii. If one increases the speed and/or reaction time, then the STOP Zone _______; if one increases the negative acceleration (slow down at a faster rate), then the STOP Zone _______. iii. In most intersections, there is an Overlap Zone. In poorly designed intersections, a Dilemma Zone. 3) What is the connection among speed, friction, and radius of the curve when one is turning? a. When one is on a curve, there is a centripetal force and there is centripetal acceleration. A force is _______. The _______ between the tires on the road provides the Centripetal Force. If there is not enough friction, then the car would _______. i. If a car moves too fast (high speed) along a curve, then _______. If the car approaches a curve at a high speed, it requires _______ centripetal force. ii. As the radius of the curve decreases, making the curve tighter, the speed required to safely make the curve _______. As the radius of the curve decreases, the centripetal force needed to make the curve _______.