8.4 waves and sound
advertisement

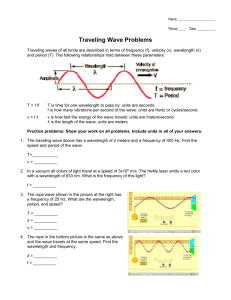
SPH3U Wave Speed and Sound A sound wave requires a __________ source to be produced - requires a _________ (wood, steel, air) to travel through (cannot travel in space due to vacuum no medium) - it is the disturbance (particles vibrating back and forth) which travels, not the ____________ themselves - in air, the local __________ of air molecules increases and decreases depending on the sound wave - areas of high density are called __________ (high air pressure, areas of low density are called ____________ low air pressure - humans are sensitive to sound frequencies in the range from ________________________ - when referring to sound, _________ is a term used to describe frequency - when you hear sound, you are listening to a combination of many different frequencies of sound at the same time The Tuning Fork - when it is struck, the tuning fork produces sound with a single frequency - the frequency of sound is dependent on the mass of the fork and independent of the speed of sound - as it is struck harder, the tines move further hence producing greater air molecule motion, greater volume Speed of Sound - In general, the speed of sound is greatest in solids, then liquids and slowest in gases (depends only on the properties of the medium) - for gases, the speed of sound is dependent on the __________ and the air pressure - speed of sound in air at atmospheric pressure is given as vsound = (332 + 0.6 T) m/s where T is temperature is in oCelsius - speed of sound is independent of the _________ or ________of the source Example 1- 3.0 s after you see a lightning bolt, you hear the thunder. If the air temperature is 25 oC, calculate the distance the storm is from your current position and the speed of sound in km/h? Example 2: A ball is dropped (initial velocity is zero) from a height of 40 m and you are standing 100 m from where the ball lands. In 3.1513 s after the ball is dropped, you hear the sound the ball makes when it hits the ground. Calculate the air temperature (no air friction). Example 3: A firecracker, 1500 m directly above your head explodes. The sound generated by the explosion travels through two layers of air at different temperatures (20 degrees Celsius and 30 degrees Celsius). It takes 2 seconds for the sound to travel through the layer with a temperature of 20 degrees Celsius. Determine the thickness of each layer and calculate the time required for the sound to travel from the explosion to your ear. Echoes, Sonar and Reflections Whenever a sound wave meets a hard surface, the sound wave reflects off of the surface and changes direction. In some cases, reflection of the sound wave leads to an ___________. Example 1: A boat (with a Sonar device) is used to track the distance between the surface of the water and the bottom of the lake. The speed of sound in water is approximately 1500 m/s. A sound wave is launched, and 2.8 seconds later a reflection is detected. Calculate the distance between the boat and the bottom of the lake. Example 2: You and your friend are in a mountain range, when you yell “Physics is FUN”. 1.5 s later, you hear the echo “Physics is FUN FUN FUN”. If the sound wave reflects off of a wall that is 263 m from your position, calculate the air temperature. The Wave Equation This equation is valid for any type of wave (sound, light, water), and relates the speed of a ____ to its _________ and its __________. v Wave Equation = v = f f - the frequency (f) of the wave is determined by the vibrating source that produces the wave - the speed of the wave (v) is determined by the characteristics of the medium (medium what the wave travels through) - the wavelength of the wave () is determined by the speed and frequency of the wave Example 1: The frequency of a tuning fork is 800 Hz and the air temperature is 10oC. A second tuning fork is struck, and has a frequency of 1200 Hz. Calculate the wavelength for each tuning fork. Example 2: A tuning fork has a frequency of 512 Hz. It is struck in a cold room (air temperature is 0 degrees Celsius) and then moved into a warmer room, where the air temperature is 34 degrees Celsius. Calculate the wavelength of the tuning fork in each room. Practice Problems: 1. If the speed of sound is 360 m/s, what is the temperature of air? (Ans: 46.67 Celsius) 2. A person shouts out “I love Physics” in a cave and hears an echo 4 seconds later “I love Physics Physics Physics”. If the temperature of the air is 28 degrees Celsius, find the distance the person is standing away from the wall that reflected the sound? (Ans: 697.6 m) What happens to a sound wave when it travels from air into water? Reflection and Transmission of Waves As a wave enters another medium, part of the wave is _________ at the medium interface (boundary) and part of the wave is _________________ at the medium interface. Example 1: A person is standing on a dock, and shouts out “BELAS ”. The temperature of the air is 30oC. The speed of sound in water is 1500 m/s. Calculate the wavelength of sound in air and the wavelength of sound in water. (in the diagram, label water, air, medium interface, reflected wave and transmitted wave) Example 2: The wavelength of sound in air is 2.0 m, while the air temperature is 36oC. Calculate the wavelength of the sound in water if the speed of sound in water is 1500 m/s. Practice Problems: 1) Sound travels from a medium with a speed of sound of 350 m/s into a medium where the temperature is 0 oC. The frequency of the sound is 1200 Hz. Calculate the wavelength of the sound in each medium. (Ans: 0.292 m, 0.277 m) 2) Sound is traveling in water at a speed of 1500 m/s. The wavelength of the sound is 1.5 m. Calculate the wavelength of sound in air if the temperature is 20 oC. (Ans: 0.344 m)