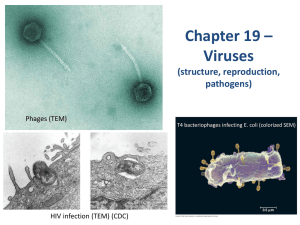
CHAPTER 19: VIRUSES OVERVIEW Viruses called infect and set in
advertisement

CHAPTER 19: VIRUSES OVERVIEW Viruses called _________________________can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead “a kind of __________________________ life” between life-forms and chemicals The origins of molecular biology lie in early studies of __________________ that infect bacteria I. Concept 19.1: Structure of a Virus Most viral research has been done with the __________________________ virus (TMV). A. Discovery of Viruses 1. _______________ (1883) Demonstrated that TMD (tobacco mosaic disease) was _______________________ Proposed that the infectious agent was a small __________________ 2. D. ___________________ (1890’s) Proposed that TMV was caused by a __________________ too small to be trapped by a filter or it produced a filterable toxin 3. M. _______________________(1897) Proposed that TMD was caused by a reproducing particle much smaller and ________________ than a bacterium Noted that the pathogen: a. reproduced only within a ________________cell b. could not be cultured on media c. could not be killed by ________________ 4. _________________________ (1935) _________________ the TMV Viruses were first observed in 1950’s with ___________________ microscope. B. Structure of Viruses A virus is not a cell but a very small infectious particle consisting of ___________________ surrounded by a _______________________ and, in some cases, a membranous ____________________ 1.Viral Genomes Viral genomes may consist of either • Double- or single-stranded ____________, orDouble- or single-stranded ________________ • Depending on its type of ___________________, a virus is called a DNA virus or an RNA virus 2. Capsids and Envelopes A __________________ is the protein shell that encloses the viral genome Capsids are built from protein subunits called ________________________ A capsid can have various structures Some viruses have membranous envelopes that help them infect ______________ These viral envelopes surround the capsids of _____________ viruses and many other viruses found in animals Viral envelopes, which are derived from the host cell’s membrane, contain a combination of __________ (protein and glycoproteins) and ___________ (phospholipids and membrane proteins ) cell molecules ___________________, also called phages, are viruses that infect bacteria They have the most ___________________ capsids found among viruses Phages have an elongated capsid head that encloses their __________________ A protein _________________ piece attaches the phage to the host and ______________the phage DNA inside II. Concept 19.2 Viral Reproduction Viruses are _________________ intracellular parasites, which means they can reproduce only within a ________________ cell Each virus has a ________________________, a limited number of host cells that it can infect A. General Features of Viral Reproductive Cycles 1. Once a viral genome has entered a cell, the cell begins to manufacture ________________________ 2. The virus makes use of host _________________, ribosomes, tRNAs, _______________, _________, and other molecules 3. Viral nucleic acid molecules and capsomeres spontaneously _____________________ into new viruses B. Viral Reproductive Cycles ________________ are the best understood of all viruses Phages have two reproductive mechanisms: the ___________ cycle and the _________________cycle 1. The Lytic Cycle The lytic cycle is a phage reproductive cycle that culminates in the ________________ of the host cell The lytic cycle produces new ________________ and digests the host’s _______________, releasing the progeny viruses A phage that reproduces only by the lytic cycle is called a _______________phage Bacteria have _________________ against phages, including restriction enzymes that recognize and ____________ up certain phage DNA Stages of Lytic Cycle: a. _____________________ b. _______________of phage DNA and _____________________ of host DNA c. __________________ of viral genomes and proteins d. ___________________ e. _________________ (ruptures) and __________________ phage particles 2. The Lysogenic Cycle The lysogenic cycle replicates the phage genome _____________________________ the host The viral DNA molecule is incorporated into the host cell’s ____________________ This integrated viral DNA is known as a ______________________ Every time the host divides, it copies the phage DNA and passes the copies to ________________cells An environmental signal can trigger the virus genome to exit the bacterial chromosome and switch to the ________________ mode Phages that use both the lytic and lysogenic cycles are called ______________________phages C. Reproductive Cycles of Animal Viruses Two key variables in classifying viruses that infect animals: _________________? Presence or absence of membranous ________________ derived from host cell membrane 1. Viral Envelopes Many viruses that infect animals have a membranous ___________________ Viral ______________________ on the envelope bind to specific ______________________ molecules on the surface of a host cell Some viral envelopes are formed from the host cell’s _______________________ as the viral capsids exit Other viral membranes form from the host’s _____________________ envelope and are then replaced by an envelope made from Golgi apparatus membrane 2. RNA as Viral Genetic Material The broadest variety of RNA genomes is found in viruses that infect _____________________ Retroviruses use ________________________ to copy their RNA genome into DNA _____________ (human immunodeficiency virus) is the retrovirus that causes _____________ (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome) The viral DNA that is integrated into the host genome is called a _________________ Unlike a prophage, a provirus remains a _________________resident of the host cell The host’s ____________________________ transcribes the proviral DNA into RNA molecules The RNA molecules function both as mRNA for synthesis of viral proteins and as genomes for new virus particles released from the cell D. Evolution of Viruses Viruses do not fit our definition of _____________________ organisms Since viruses can reproduce only _________________ cells, they probably evolved as bits of cellular nucleic acid Candidates for the _________________ of viral genomes are plasmids, circular DNA in bacteria and yeasts, and transposons, small mobile DNA segments Plasmids, transposons, and viruses are all ____________________ genetic elements III. Concept 19.3: Viruses, Viroids, and Prions ________________ caused by viral infections affect humans, agricultural crops, and livestock worldwide Smaller, less complex entities called _____________ and ____________ also cause disease in plants and animals, respectively A. Viral Diseases in Animals Viruses may damage or kill cells by causing the release of ___________________________ from lysosomes Some viruses cause infected cells to produce ___________________ that lead to disease symptoms Others have envelope __________________ that are toxic _______________________ are harmless derivatives of pathogenic microbes that stimulate the immune system to mount defenses against the actual pathogen Vaccines can __________________ certain viral illnesses Viral infections cannot be treated by _____________________ Antiviral drugs can help to _____________, though not cure, viral infections B. Emerging Viruses ___________________ of “new” viral diseases in humans are usually caused by existing viruses that expand their host territory _________________________ are caused by new strains of influenza virus to which people have little immunity Viral diseases in a small isolated population can emerge and become __________________ New viral diseases can emerge when viruses spread from ______________ to __________________ Viral strains that jump _______________________ can exchange genetic information with other viruses to which humans have no immunity These strains can cause ______________________, global epidemics C. Viral Disease in Plants Most plant viruses have an _________________ genome Plant viruses spread disease in two major modes: Horizontal transmission-entering through ___________________________ Vertical transmission-inheriting the virus from a ______________________