Review Guide for Common Assessment on Geology Unit Answers
advertisement

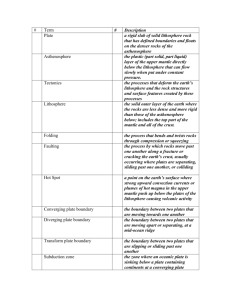
Review Guide for Common Assessment on Geology Unit Assessment Date: Jan. 28 (new date due to snow days) Answers due by Jan. 25 You will be taking your first common assessment in Science soon. The unit that you are being tested on is the Geology Unit. This common assessment will test you on the “Big Ideas” that all sixth graders should exhibit proficiency on. In other words, they are the concepts that every sixth grader should take away from the unit of study. Notice that you are not being given a typical study guide. Instead, I have listed the key concepts that you can expect to be tested on. If you have forgotten any of this information, you can use your textbook to assist you in reviewing the information. This common assessment will count for a point value of 50 points just like a regular test. You should not have to study hours and hours for this assessment. It focuses mainly on the big ideas of each unit. If you have done a good job throughout this entire unit, you should find that most answers will come easily to you. This is the only homework assignment that I will be giving you so do a good job gathering the answers to help you recall all that you have learned in this unit. Good luck! Be able to name and describe the FIVE criteria (NOT properties) that are used to classify a mineral Criteria (characteristic) Description 1. inorganic Not from living things 2. solid Definite volume and shape 3. crystal structure The particles line up in a repeating pattern over and over 4. naturally occurs Occurs in nature 5. definite chemical composition Contains certain elements in definite proportions Be familiar and able to interpret a diagram of the rock cycle p. 168 Briefly describe the rock cycle below - Earth’s constructive and destructive forces build up and wear down the crust. Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rock continuously move through a series of processes (melting, cooling and hardening, compaction and comentation, and tremendous heat and pressure) to change from one form to another. Rocks can follow many pathways. Know the difference between constructive and destructive forces and examples of each pg. 17 A constructive force is shape the surface by building up mountains and landmasses Example: volcano, delta, sand dune, etc. A destructive force is slowly wear away mountains and eventually every other feature on the surface Example: weathering, tornado, earthquakes, landslide etc. Know the basic three types of volcanoes and what kind of volcano is the Hawaiian Islands p.104 -105 Three types of Volcanoes Description Example shield Repeated lava flows during Hawaiian Islands quiet eruptions gradually build up a broad, gently sloping volcanic mountain Composite (stratovolcano) Layers of lava alternate with Mt. Hood; Mt. Fuji; Mt. St layers of ash, cinders, and Helens bombs, in a composite volcano, which has both quiet and explosive eruptions Cinder cone When cinders erupt explosively Sunset Crater in Arizona is from a volcanic vent, they pile an extinct cinder cone; up around the vent, forming a Paricutin, Mexico cone-shaped hill What force moves the Earth’s plates and where are they located? P. 42-43 The force that moves the Earth’s plates is convection currents. The plates are located in the sub-layer called the lithosphere. What are faults, types of Earth’s stress, and the evidences of continental drift theory? Pgs. 44,55,30-31 Faults are breaks in the Earth’s crust where rocks have slipped past each other and form along boundaries. Three types of Earth’s stress are shearing, tension, and compression Three evidences of continental drift theory are evidence from landforms, evidence from fossils, and evidence from climate Know these terms: geologist, seismograph, ore, alloy (such as, stainless steel), and Pangaea pgs. 17,66,138, 135, and 29 term definition geologist A scientist who studies the forces that make and shape planet Earth seismograph A device that records ground movements caused by seismic waves as they move through the Earth ore Rock that contains a metal or economically useful mineral alloy A solid mixture of two or more metals Pangaea The name of a single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today’s continents Know the three types of plate boundaries p 44-.46 Type of Plate Boundary Description transform A place where two plates slip past each other, moving in the opposite direction divergent The place where two plates move apart or diverge convergent The place where two plates come together, or converge Know what determines the size of a crystal p. 129 The size of a crystal is determined by the rate that the magma cools, the amount of gas the magma contains, and the chemical composition of the magma. What are the properties of minerals? Pgs. 121-126 Six properties of minerals are hardness, color, streak, luster, density, crystal structure, cleavage and fracture, and special properties (magnetism, fluorescence, radiation, effervescences, etc) Know the three groups of rocks, how they get their names, and how (and where) they are each formed pgs. 151, 149, 155, 162 Three Types of Rocks igneous Gets it name from How (or where) Formed Cooling of molten rock Latin word “ignis” meaning “fire” sedimentary Made from sediments metamorphic Greek word “meta” means change and “morphosis” meaning form Particles of other rocks and the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together Existing rock is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions This test is all multiple choice except for the single essay question, “Name and describe the “Big Five” criteria (NOT properties) used to classify a mineral. If you have done a good job keeping up with your class assignments, tests in this unit, and have paid attention in class, you should not have to spend a great deal of time studying for this assessment. Good Luck! Start reviewing. Mrs. B Essay Practice: “Name and describe the “Big Five” criteria (NOT properties) used to classify a mineral. Name and describe four of the characteristics or properties used to classify any mineral. (4pts) Characteristics or criteria are naturally-occuring, inorganic, solid, crystal structure and definite chemical composition Properties: color (not very good means), luster (light is reflected), hardness (ranked from soft to hard), cleavage (breaks along planes in a regular way), fracture (breaks in an irregular way), density (specific density at a certain temperature in water), fluorescence