CHE 203 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I (3-0-3)
advertisement
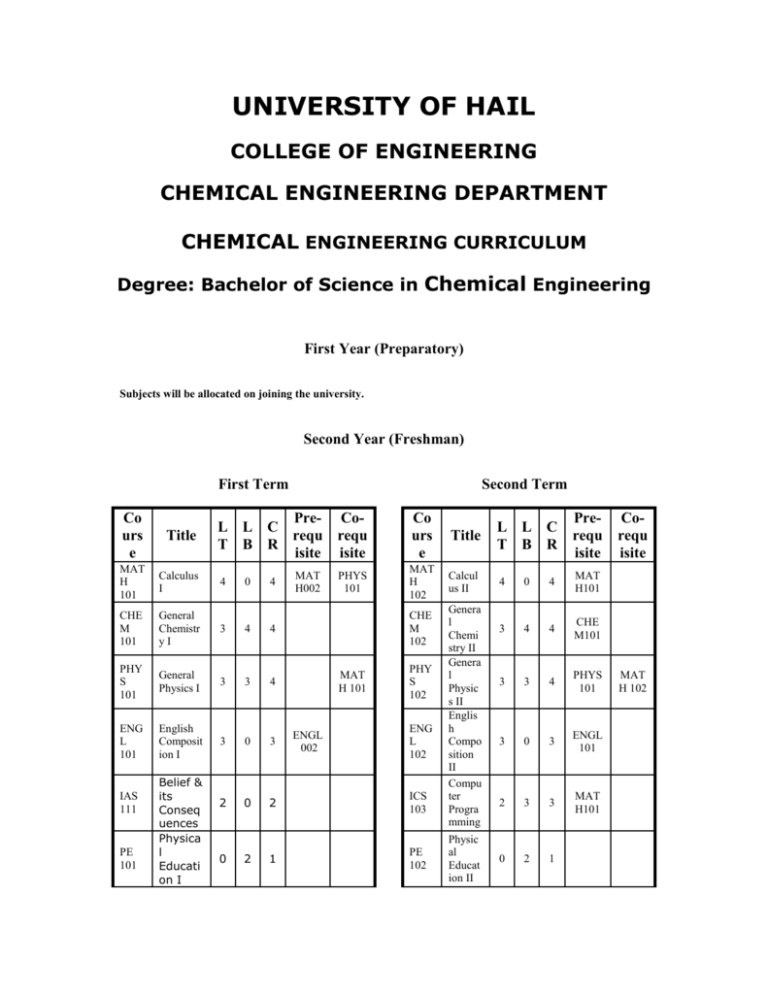
UNIVERSITY OF HAIL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT CHEMICAL ENGINEERING CURRICULUM Degree: Bachelor of Science in Chemical Engineering First Year (Preparatory) Subjects will be allocated on joining the university. Second Year (Freshman) First Term Second Term Co urs e Title MAT H 101 Calculus I CHE M 101 General Chemistr yI 3 4 4 PHY S 101 General Physics I 3 3 4 ENG L 101 English Composit ion I 3 0 3 2 0 2 ICS 103 1 PE 102 IAS 111 PE 101 Belief & its Conseq uences Physica l Educati on I Pre- CoL L C requ requ T B R isite isite 4 0 0 2 4 MAT H002 PHYS 101 Co urs e Title L L C T B R Prerequ isite MAT H 102 Calcul us II 4 0 4 MAT H101 3 4 4 CHE M101 3 3 4 PHYS 101 3 0 3 ENGL 101 2 3 3 MAT H101 0 2 1 CHE M 102 MAT H 101 ENGL 002 PHY S 102 ENG L 102 Genera l Chemi stry II Genera l Physic s II Englis h Compo sition II Compu ter Progra mming Physic al Educat ion II Corequ isite MAT H 102 TOT AL 1 5 9 TOT AL 18 1 5 1 2 19 Third Year (Sophomore) First Term Co urs e CHE 201 Title Intro. to Chem. Eng. MAT H 201 Calculus III CHE M 201 Organic Chemistr yI Second Term Pre- CoL L C requ requ T B R isite isite 3 3 3 0 0 3 3 CHE M 102, and PHYS 102 Co urs e Title CHE 203 Chem. Eng. Therm o. I 0 3 3 3 0 3 4 CHE M 102 MAT H 202 Elem. Diff. Equati ons 3 0 3 MAT H 201 3 CHE M 102, MAT H 102 CHE M 202 Organi c Chemi stry II 3 3 4 CHE M 201 MAT H 102, PHYS 102 3 0 3 ENGL 102 2 0 2 IAS 111 1 7 3 18 EE 202 2 3 3 IAS 101 Practical Grammar 2 0 2 IAS 211 1 5 9 18 TOT AL MAT H 202 + CHE M 212 ENG L 214 Techni cal Report Writin g Ethics in Islam Corequ isite MAT H 202, and CHE 203 or ME 205 or ICS 103 Transp ort Pheno mena I Fund. Electric Circuits TOT AL 3 CHE 201, MAT H 201, o r ICS 103 CHE 204 Material Science 3 Prerequ isite MAT H 102 ME 205 2 L L C T B R Fourth Year (Junior) First Term Co urs e Title CHE 300 Transport Phenome na II Second Term Pre- CoL L C requ requ T B R isite isite 3 0 3 CHE 204 Co urs e Title L L C T B R CHE 306 Stagewise Operati ons 3 0 3 Prerequ isite CHE 303 CHE 304 Corequ isite CHE 303 Chem. Eng. Thermo II CHE 304 Transport Phenome na III 3 STA T 319 Statistics for Engineer s 2 3 3 MAT H 202, CHE 203 0 3 CHE 204 3 3 MAT H 201 CHE M 326 CHE M 102, MAT H 102, PHYS 102 SE 301 0 CHE M 311 Physical Chemistr y II 3 3 4 IAS 201 Objective Writing 2 0 2 CHE 309 CHE 300 CHE 325 IAS 311 IAS 4xx TOT AL 1 6 Co urs e Title Summer Semester Pre- CoL L C requ requ T B R isite isite CHE 350 Coopera tive Work Program 0 6 0 Chem. Eng. Lab I Chem. Eng. Compu ter Lab Analyti cal Chemi stry Numer ical Metho ds Islamic Sharea h IAS Electiv e TOT AL 18 CHE 300 ENGL 214 0 6 2 1 3 2 2 3 3 CHE M 202 ICS 103, MAT H 201 3 0 3 2 0 2 2 0 2 1 3 1 2 17 CHE 304 CHE 306 0 Fifth Year (Senior) First Term Co urs e CHE 351 Title Cont. of Coop Work Second Term Pre- CoL L C requ requ T B R isite isite 0 0 9 CHE 309, ENGL 214, and 85 credit hours CHE 351 Co urs e Title L L C T B R Prerequ isite CHE 401 Proces s Dyn. & Ctrl 3 3 CHE 306, SE301 CHE 402 Kinetic s & Reacto r Design 3 CHE 303 CHE M 311 3 0 0 Corequ isite CHE 425 Eng. Econ. & Design CHE 409 Chem. Eng. Lab II CHE 495 IAS 301 Integra ted Design Course Literat ure Style TOT AL 3 0 3 CHE 306 CHE 402 CHE 306 CHE 309 CHE 401 CHE 402 0 6 2 1 6 3 2 0 2 1 2 1 2 16 CHE 425 Total credit hours required in Degree Program: 133 + (Preparatory Year) COURSES DESCRIPTION CHE 201 Introduction to Chemical Engineering (3-0-3): Prerequisites: CHEM 102, PHYS 102 The basic principles and techniques used for calculations of material balances in chemical engineering processes are introduced. The material covered involves fundamental engineering concepts, formulation and solution of increasingly complex chemical engineering process problems and familiarization with physical properties and behavior of ideal and real gases. Problem solving session. CHE 203 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I (3-0-3): Prerequisites: CHE 201, MATH 201, or ICS 103 The first and second laws of thermodynamics are studied in detail. Material covered includes concepts of energy, enthalpy, heat effects, conservation of energy, interaction between heat transfer, mechanical work, and chemical energy liberation, equations of state, behavior of gases and liquids, standard heats of reaction, formation and combustion and entropy. Study of combined mass and energy balances. CHE 204 Transport Phenomena I (3-0-3): Co-requisites: MATH 202; CHE 203 or ME 205, or ICS 103 An introductory treatment of practical fluid dynamics covering both laminar and turbulent flow is given. Mass, energy, and momentum balances are derived, and the techniques of dimensional analysis are introduced. The principles and operation of fluid meters are developed and their characteristics are described, together with flow analysis of typical piping systems. Flow of particulates is also covered. CHE 300 Transport Phenomena II (3-0-3): Prerequisite: CHE 204 Modes of heat transfer. Differential equations of energy transport. Steady and transient heat conduction. Free and forced convection in laminar and turbulent flows. Momentum and heat transfer analogies. Boiling and condensation. Radiation heat transfer. Application to the design of process heat transfer equipment. CHE 303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics II (3-0-3): Prerequisites: MATH 202, CHE 203 Review of 1st and 2nd laws. Thermodynamic relations. PVT properties. Thermodynamic diagrams. Properties of mixtures. Ideal and real mixtures. Phase equilibria, calculation concepts. The concept of fugacity and activity in liquid phase models. Chemical reaction equilibria concepts and criteria. The steam power plant. CHE 304 Transport Phenomena III (3-0-3): Prerequisite: CHE 204 and Co-requisite: CHE 300 Fundamentals of mass transfer. Differential equations of mass transfer. Steady-state and unsteadystate molecular diffusion. Convective mass transfer. Interface mass transfer. Mass transfer theories. Mass transfer equipment. Absorption and humidification operations. CHE 306 Stage-wise Operations (3-0-3): Prerequisites: CHE 303, CHE 304 Review of vapor-liquid equilibria. Differential and flash distillation. Binary distillation. McCabe-Thiele and Ponchon-Savarit methods. Introduction to multicomponent distillation. Liquid-liquid and solidliquid extraction. CHE 309 Chemical Engineering Laboratory I (0-6-2): Prerequisites: CHE 300, ENGL 214 and Co-requisite: CHE 304 This laboratory emphasizes concepts presented in the transport phenomena courses. A safety session is given at the commencement of the course. Safe practices are strictly adhered to throughout the course. Students carry out selected experiments in fluid mechanics, heat transfer, thermodynamics and diffusional mass transfer. Data collected are analyzed and compared to applicable theories. CHE 325 Chemical Engineering Computing Laboratory (1-3-2): Co-requisite: CHE 306 Programming chemical engineering calculations and problem solving. Data acquisition and processing, computer assisted design and simulation of chemical engineering problems using appropriate commercial software packages. CHE 351 Applied Chemical Engineering Cooperative Work (0-0-9): Prerequisites: CHE 309, ENGL 214, Approval of the Department (130 Cr. Hr.). (Registration in this course is limited to students in the College of Applied Engineering) In this course the student will spend a period of 28 weeks of industrial employment in industry. Students are required to write a detailed formal report on their experience. Evaluation by the employer will be counted towards the grade given for this course. CHE 401 Process Dynamics and Control (3-0-3): Prerequisites: CHE 306, SE 301 (May not be taken for credit if credit already awarded for SE 302 or EE 380) Dynamics and simulation of linear systems. Transfer functions for 1st and 2nd order. General Transfer functions. Linearization. Modes of control; Block diagram representation, open and closed loop transfer functions, stability studies, parameter tuning, frequency response analysis, Nyquist and Bode diagrams. Case studies. CHE 402 Kinetics and Reactor Design (3-0-3): Prerequisites: CHE 303, CHEM 311, Senior Standing Theory of chemical kinetic mechanisms and derivation of overall rate expressions. Interpretation of constant volume, variable volume batch reactor data and its application to the design of ideal backmix and plug flow reactors. Comparison of reactor performance including series, parallel, and multiple reactions. Nonisothermal reactor operation. Basic heterogeneous reactions and nonideal reactors performance. CHE 409 Chemical Engineering Laboratory II (0-6-2): Prerequisites: CHE 306, CHE 309 and Co-requisites: CHE 401, CHE 402 A laboratory to complement the theoretical derivations in stagewise operations, process dynamics and control, and kinetics and reactor design. A safety session is given at the commencement of the course. Safe practices are strictly adhered to throughout the course. Two environmental engineering reaction experiments are included. Students carry out selected experiments, analyze data collected referring to applicable theories and present their findings in formal reports. CHE 425 Engineering Economics and Design Principles (3-0-3): Prerequisite: CHE 306 and Co-requisite: CHE 402 Process economic analysis of chemical plants with particular emphasis on cost estimation, interest calculations, depreciation, profitability, methods for decision-making among alternatives and capital budgeting. Process flow diagram analysis, design of flow systems, design and integration of process equipment such as chemical reactors, separators, pumps, compressors, heat exchangers, absorbers, etc., into a chemical process. Development of the general principles of process design including materials selection, transfer and handling, plant location, plant layout, waste disposal, safety considerations, etc. Application of software packages such as Aspen Plus and Chemshare. CHE 495 Integrated Design Course (1-6-3): Co-requisite: CHE 425 Development of general engineering skills and judgment needed in the solution of open-ended problems from a technical-economic viewpoint are the major goals of this course. The design of a project from conception to implementation including preliminary feasibility study, preparation of process, flow diagram, process design, pre-construction cost estimate, equipment sizing (design), selection of materials of construction, and analysis of project. Applications will be in areas such as petroleum, petrochemicals, emerging chemical industries and water desalination. Design topics will be assigned to teams of students. ADVANCED CHEMISTRY COURSES CHEM 201 Organic Chemistry I (3-3-4): Pre-requisite: CHEM 102 Structure, stereochemistry and the properties of organic compounds, synthesis and reactions of alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, dienes, alicyclic, alcohols, ethers, mechanism of radical substitution, radical, electrophilic addition and electrophilic aromatic substitution. Laboratory: Laboratory techniques of organic chemicals and laboratory synthesis of organic chemicals. CHEM 202 Organic Chemistry II (3-3-4): Pre-requisite: CHEM 201 Identification of organic compounds by spectroscopic methods. Synthesis and properties of carboxylic acids and derivatives, aldehydes, ketones, amines, polycyclic and hetereocyclic aromatics, carbohydrates, amino acids and nucleic acids. Laboratory: Basic spectroscopic techniques, laboratory synthesis of organic chemicals and multistep synthesis. CHEM 311 Physical Chemsitry II (3-3-4): Prerequisite: CHE 203 Laws of thermodynamics, phases, and phase equilibria. The application of thermodynamics to electrochemical cells, chemical kinetics, transport properties, surface chemistry. Laboratory: Error analysis and statistics, Techniques of physical measurements, Experiments involving conductivity, electrochemistry, chemical kinetics, and transport properties of gases and liquids. Determination of the enthalpy of neutralization; Determination of the melting enthalpy of a pure substance; The conductivity measurement; Reaction rate and activation energy; Gas viscosity (Estimation of molecular diameter); & The viscosity measurement (Falling ball viscometer). CHEM 326 Analytical Chemistry (2-3-3): Prerequisite: CHEM 202 Sampling and sample preparation, volumetric analysis, gravimetric methods of analysis, and instrumental analysis techniques such as ultra-violet spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, chromatography, and thermal analysis. Statistical data treatment and evaluation. Laboratory: Experiments on basic analytical methods, including gravimetric and volumetric techniques and experiments related to qualitative and quantitative analysis using various instrumental techniques.







