question and answer paper
advertisement

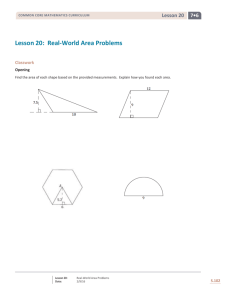
FUNCTIONAL SKILLS MATHEMATICS LEVEL 2 I.D: 501/1437/2 QUESTION AND ANSWER PAPER YOU NEED This question and answer paper A pen with black or blue ink A pencil and an eraser A ruler marked in mm and cm A protractor A calculator Do not open this paper until you are told to do so by the Exam Supervisor THERE ARE FOUR TASKS IN THIS EXAM Total marks available: 60 Try to answer ALL questions TIME ALLOWED: 1 HOUR 30 MINUTES INSTRUCTIONS Make sure that your candidate information is entered correctly on this question and answer paper Make sure that your writing is clear, and show all your working Answer each question in the space provided on this question and answer paper If you use extra paper, make sure that it has your name and candidate number on it and is securely attached to your question and answer paper At the end of the test, hand this question and answer paper and all notes to the Exam Supervisor Candidate Name: ……………………………………………….………………………… Candidate Number: ..……………………………………………………………………… Centre Code: .……………………………………………………………………………… Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Blank page 01/09/10v1 2 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Task 1 Linda is going to paint her bedroom. She will paint the walls yellow and the ceiling white. She will apply 2 layers of paint to the walls and 2 layers of paint to the ceiling. Plan of Linda’s bedroom Diagram not to scale The height of the room is 2.55 metres. Linda can buy paint from the Décor 8 shop or the Paintrite shop. The boxes below give the amounts, the prices and the coverage of the paints from each shop. Décor 8 Paintrite Matt Emulsion Paint Matt Emulsion Paint Yellow 2.5 litres £22.95 Yellow 2.5 litres £21.99 5.0 litres £39.99 White 1.0 litre £3.95 2.0 litres £6.95 White 0.5 litre £3.49 1.0 litre £5.49 2.0 litres £7.99 1 litre of this paint covers 14 square metres 1 litre of this paint covers 12 square metres 01/09/10v1 3 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 1 Calculate the amounts of paint that Linda would need from each shop to paint her bedroom. Ignore the window area in your calculation to allow for wastage of paint. Show your working clearly. Give your answers to two decimal places and state the units. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………(9 marks) 01/09/10v1 4 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Linda uses a special calculator on a DIY internet website to find out how much yellow and white paint she needs from each of the shops. The table below gives the results. Amount of paint Décor 8 (litres) Paintrite (litres) 6.0 2.5 7.0 2.5 Yellow White 2 Compare your answers to question 1 with the data from the website. State any differences between the amounts of paint. Give a possible reason for the differences. ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………… (2 marks) Linda wants to keep her costs as low as possible. 3 From which shop should Linda buy her paint? Explain why she should buy the paint from the shop you have chosen. Show calculations in your explanation. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (4 marks) 01/09/10v1 5 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Task 2 The diagram shows the area around Coniston Water. Diagram not to scale Waterhead Coniston Brantwood Torver KEY: -- - - Walk route ....... Boat route On Wednesday 5th May, Steve and Shaun are going to park their car at Brantwood then walk around the lake to Torver. They will take Steve’s dog with them. They want to spend 1½ hours in Torver where they will have lunch. Then they will catch a boat back to Brantwood. Steve and Shaun have a map with a scale of 1 : 25 000. On the map the distance from Brantwood to Torver is 28 centimetres. They walk at an average speed of 4 kilometres per hour. 01/09/10v1 6 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 This is the summer timetable for the boat. Summer 13 Mar to 31 Oct Coniston - dep 10.15 28 Mar 3 Oct 10 Jul 5 Sep 11.15 12.05 12.40* 1.05 2.05 3.05 4.05 5.05 Waterhead 10.20 11.20 12.10 12.45 1.10 2.10 3.10 4.10 5.10 Torver 10.35 11.35 12.25 1.00 1.25 2.25 3.25 4.25 5.25 Brantwood 10.50 11.50 12.40 1.15 1.40 2.40 3.40 4.40 5.40 Coniston - arr 11.05 12.05 12.55 1.30 1.55 2.55 3.55 4.55 5.55 * 12.40 sailing does not operate on Tuesdays or Wednesdays; operates from 29 Apr to 19 Sep only. 1 Work out a time plan for Steve and Shaun. Complete the table below to show the time at each stage of their day out. Show your working. Stage Time Leave Brantwood Arrive Torver Leave Torver Arrive Brantwood ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. (8 marks) 01/09/10v1 7 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Steve and Shaun go to a café in Torver for lunch. This is the menu board. Lunch menu Food Chicken and ham salad Surf ‘n’ turf salad Goats cheese salad Sandwiches filled with: £5.80 £6.40 £5.40 Drink Coffee Cappuccino Café latté Espresso £2.00 £2.35 £2.35 £1.70 Ham and mustard Egg mayonnaise £5.25 £4.95 Hot chocolate Tea £2.20 £1.75 Cheese and tomato Beef and horseradish £4.95 £5.45 Fruit juice Lemonade/coke £1.50 £1.30 Today’s special offers: Buy two salads and get the cheapest one half price. Buy two filled sandwiches and get one fruit juice free. They want to order one item of food each and one drink each. Shaun is a senior citizen so they will get a 15% discount on the total cost of their lunch. After lunch they will go from Torver back to Brantwood on the boat. This table shows the prices for an adult ticket. Coniston £2.10 Waterhead £4.60 £2.40 £6.80 £4.50 £8.90 £6.70 Torver £2.30 £4.30 Brantwood £2.20 Coniston Senior ticket - ½ price of adult ticket Dog ticket - £1 for any journey 01/09/10v1 8 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 They need to buy 1 adult ticket, 1 senior ticket and 1 dog ticket. They can spend a maximum of £15 on boat tickets and lunch. 2 Suggest what Steve and Shaun should order for lunch. Check that the total cost of the boat tickets and lunch will not come to more than £15. Show all your calculations including the check. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ( 7 marks) 01/09/10v1 9 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Task 3 The Body Mass Index (BMI) uses height and weight to estimate how much body fat an adult has. Table A gives an estimate of BMI, from height and weight. Table B shows how adults are classified according to their BMI. Table A Body Mass Index (BMI) Table Height (m) Weight (kg) 60 62 64 66 68 70 72 74 76 78 80 82 84 86 88 90 1.50 1.54 1.58 1.62 1.66 1.70 1.74 1.78 27 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 28 26 25 24 22 21 20 20 28 27 26 24 23 22 21 20 29 28 26 25 24 23 22 21 30 29 27 26 25 24 22 21 31 30 28 27 25 24 23 22 32 30 29 27 26 25 24 23 33 31 30 28 27 26 24 23 34 32 30 29 28 26 25 24 35 33 31 30 28 27 26 25 36 34 32 30 29 28 26 25 36 35 33 31 30 28 27 26 37 35 34 32 30 29 28 27 38 36 34 33 31 30 28 27 39 37 35 34 32 30 29 28 40 38 36 34 33 31 30 28 01/09/10v1 10 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Shona is 5 feet 8 inches tall. She weighs 12 stones 5 pounds. 1 Which BMI category is Shona in? Show your calculations and explain how you used the BMI table to work out Shona’s BMI. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (5 marks) 2 Calculate how much weight Shona needs to lose in order to be in the Normal weight BMI category. Clearly explain how you worked out your answer. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (6 marks) 01/09/10v1 11 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Shona goes on a diet. She aims to eat 1 200 calories a day. She will divide her 1 200 calories in the ratio 2 : 1 : 3 for breakfast, lunch and dinner. The table below gives the number of calories per 100g and a typical portion size of different breakfast items. 3 Choose items for Shona’s breakfast. Include something to eat and a drink. The number of calories must be within her breakfast allowance. Show your calculations. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (4 marks) 01/09/10v1 12 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 Task 4 Aeroplanes emit carbon dioxide (CO2). CO2 emissions from aeroplanes are measured in kilograms per flight. Lubna sees this graph in a magazine. Average aeroplane CO2 emissions per passenger Year Lubna says ‘The graph shows that the CO2 emissions per passenger in 2000 were double what they were in 2006’. 1 Is Lubna correct? Give a reason for your answer. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) 01/09/10v1 13 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 In 1990 experts predicted that in 2010 the average CO2 emissions per passenger would be 250 kilograms. 2 Does the graph suggest that these experts will be correct? Explain your answer. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) This table gives some information about different aeroplanes. The average CO2 emissions per passenger can be calculated using this formula C where F S C is the average CO2 emissions per passenger in kg F is the average aeroplane CO2 emissions per flight in kg S is the average number of seats used per flight Lubna works for an international company. Last year she travelled four times on a Boeing 747. This year she will be travelling four times on the Airbus A320. Lubna thinks that by using the Airbus A320 she will more than halve her CO2 emissions. 01/09/10v1 14 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 3 Is Lubna correct? Show working to explain your answer and include a calculation check. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ( 5 marks) An airline company owns an old DC10 aeroplane. It wants to replace the old DC10 with a new aeroplane that will produce at least 25% less CO2 emissions per passenger. 4 Which aeroplane do you think the company should choose to replace the old DC10? Show working to explain your answer. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ( 4 marks) 01/09/10v1 15 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 This scatter graph shows the average amount of fuel used and the average CO2 emissions per flight of the five types of aeroplane shown in the table in question 2. Average fuel used and CO2 emissions per flight (kg) 5 What type of correlation does the scatter graph show? Explain what this tells you. …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… (2 marks) 01/09/10v1 16 Functional Skills Mathematics Level 2 END OF EXAM 01/09/10v1 17