File
advertisement

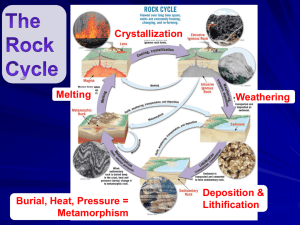
Name_________________________________Date____________Per_____ Plutons Diagram Matching ___1. This type of pluton forms closest to the surface. A. Felsic / Sialic ___2. This type of pluton solidifies at the highest temperature. B. Intermediate ___3. This is the type of pluton in which granite forms. C. Mafic ___4. This is the type of pluton in which peridotite forms. D. Ultra-mafic ___5. This is the type of pluton in which diorite forms. ___6. This pluton form so deep down that its magma rarely makes it to the surface as lava. ___7. This type of pluton is the source for basalt lava flows. ___8. This type of pluton is the source for rhyolite lava flows. ___9. This is the type of pluton in which gabbro forms. ___10.This type of pluton is the source for andesite lava flows. Notes - Plutons and Bowen’s Reactions Series 11. Plutons are molten blobs of magma that move upward by _____________ their way upward through the solid overlying rock layers. 12. As a mafic pluton melts its way upward through felsic overlying solid rock, its chemical composition becomes more _______________. 13. Igneous rocks start to crystallize at a temperature of ______ o C and finish at ______ o C. ____ 14. At which temperature would an igneous rock be completely solid? a) 550 o C b) 750 o C c) 1000 o C d) 1350 o C T or F 15. All of the minerals in a pluton’s magma crystallize at the same time. 16. The first minerals to crystallize are ___ - rich feldspar and ______________. 17. The last mineral to crystallize is ________________. 18. As a general rule, the ( mafic / felsic ) minerals crystallize first and the ( mafic / felsic ) minerals crystallize last. ____19. Which of these minerals would not be found in the same rock with the other three? a) K-spar b) Biotite c) Na-spar d) Ca-spar ____20. If a plutonic magma body was low on silica to begin with, which of these minerals would probably not get a chance to form in the rock? a) Olivine b) Quartz c) Biotite d) Ca-spar 21. The gray mineral in gabbro is probably ______________ ( Na-spar or Quartz? ). 22 - 24. You are looking at a freshly broken piece of granite which contains large pink blocky crystals, shiny black plates, clear glassy gray crystals and chunky black minerals. 22. The shiny black plates are probably _____________ mica. 23. The crystals are probably clear, glassy _____________ and pink blocks of ___-______ . 24. a) The chunky black minerals are more likely to be ( pyroxene / amphibole ). b) Why? _______________________________________________________ 25. Which mineral on Bowen’s R.S. is the most stable at the earth’s surface? ___________ 26. Which mineral is most likely to weather (wear down) first? __________________ (Hint: it’s common in ultra-mafic rocks such as peridotite.) ____ 27. Which of the following minerals forms deepest in the crust? a) Quartz b) Olivine c) Biotite d) K-spar o ____ 28. Which of the following minerals would crystallize at 1800 C ? a) Quartz b) Olivine c) Biotite d) none of these ____ 29. Which mineral forms at the same time as Biotite? a) Quartz b) Muscovite c) Na-spar d) Ca-spar ____ ____ 30. Which two feldspars would you expect to find in granite? a) K-spar b) Na-spar d) Ca-spar ____ 31. Which feldspar is the last to form (last to turn solid in a cooling magma)? a) K-spar b) Na-spar d) Ca-spar 32. Rhyolite is felsic and Basalt is mafic, yet they both form at the surface. This is possible because basalt’s source pluton is located ______ __________ than rhyolite’s. 33. Put a check in the blank for each trait that describes a rock that formed from cooling magma deep in the crust: _____ light colored _____ dark-colored ____ glassy _____ felsic _____ mafic or ultra-mafic _____ vesicular _____ coarse - grained _____ fine-grained _____ volcanic _____ contains Quartz and K-spar _____ contains Olivine and Ca-spar _____ weathers badly at the surface _____ shows little sign of weathering 34-37. Look at your silicate structure diagrams on the edge of the Bowen’s Chart. For each mineral, write in the name of the S.S. group and the number of oxygen atoms shared: 34. Olivine - ___________ ______________ ; _____ oxygen “corners” shared 35. Pyroxene - ____________ Structure ; _____ oxygen “corners” shared 36. Muscovite - ___________ Structure ; _____ oxygen “corners” shared 37. Quartz - 3 - D _____________________ ; _____ oxygen “corners” shared Bonus (+5) - Describe what happens to the structure of the silicates as you go from the bottom to the top of the left-hand columns of Bowen’s Reaction Series: ______________________________________________________________