File
advertisement

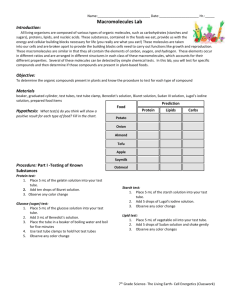
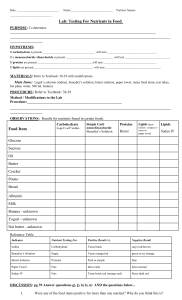
Name_______________________________________ Period____ Macromolecules Lab Introduction: Most matter in your body that is not water is made up of organic compounds. Organic compounds contain carbon atoms. There are four principle classes of organic compounds made or used by living things: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids . Without these compounds, cells could not function. Carbohydrates are made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and are key sources of energy. They include glucose, fructose, galactose, sucrose, ribose, deoxyribose, cellulose and chitin. The monomers for carbohydrates are monosaccharides. Lipids include fats (a source of stored energy), phospholipids (key components of the cell membrane), steroids and waxes. Proteins are large molecules made up of chains of amino acids. Proteins are important molecules in living things because they are responsible for the proper functioning of all cells and the structure of some cells. Proteins include: muscle tissue, skin, bone, hair, enzymes and antibodies. Purpose: This lab activity provides an opportunity for the development of skills involved in chemically testing for the presence of the carbohydrates, lipids and proteins found in food samples. You will learn how to test for the presence of proteins using the Biuret test, to test for the presence of monosaccharides using the Benedict’s test, to test for the presence of starches (polysaccharides) using Lugol’s iodine solution and to detect the presence of lipids using Sudan III. Using the skills that you develop, you should be able to determine which organic compounds are present in the unknown solutions provided in this lab. Materials: Lugol’s iodine in dropper bottle Benedict’s solution in dropper bottle Biuret Reagent in dropper bottle Sudan III in dropper bottle Unknown Solution A Unknown Solution B Unknown Solution C Unknown Solution D Plastic cups Test tubes Pipettes Hot Plate Test tube holder (beaker) Safety Alert 1. Do not touch, taste, or smell any substances. 2. Point test tubes away from all people when heating samples. 3. Handle hot test tubes with test tube clamp. Background Information On Solution Testing: Part I: Testing for Lipids Sudan III can be used to detect the presence of lipids. In the presence of a lipid-rich solution and water, Sudan III will diffuse through the solution producing an orange-pink color ring at the top. DO NOT mix or shake the solution. Record observations for the lipid test in Data Table 1. *Add 3 drops of Sudan III to the test tube Part II: Testing for Proteins Biuret reagent can be used to test for the presence of protein. Biuret reagent will change color from light blue to violet in the presence of protein. Record observations for the protein test in Data Table 1. * Add 6 drops of Biuret’s reagent Part III: Testing for a Polysaccharide called Starch Lugol’s Iodine solution can be used to test for the presence of the polysaccharide called starch. In the presence of starch, the Lugol’s Iodine solution will change color from amber to dark blue/black. Record observations for the starch test in Data Table 1. * Add 1 drop of Lugol’s iodine solution Part IV: Testing for Monosaccharides Benedict’s solution can be used to detect the presence of monosaccharides. In the presence of a monosaccharide like glucose, Benedict’s solution will change color from blue to orange when heated. Record observations for the glucose test in Data Table 1. * Add 1 dropperful of Benedict’s solution. Place the tube in a beaker of boiling water and boil for 5 minutes. (Use test tube clamps to hold hot test tubes.) Procedure: Each group will be assigned 1 Solution to test Solution A: 1. Place 2 dropperfuls of the unknown solution A in each of your test tubes and cups. Complete Testing for Parts I - IV. Note any change in color! 2. Rinse out your test tube and determine whether or not the unknown Solution A you've been assigned contains any Macromolecules. Record your findings in Data Table 2. Solution B: 1. Place 2 dropperfuls of the unknown solution B into each of your test tubes and cups. Complete Testing for Parts I - IV. Note any change in color! 2. Rinse out your test tube and determine whether or not the unknown B solution you’ve been assigned contains any Macromolecules. Record your findings in Data Table 2. Solution C: 1. Place 2 dropperfuls of the unknown solution C in each of your test tubes and cups. Complete Testing for Parts I - IV. Note any change in color! 2. Rinse out your test tube and determine whether or not the unknown C solution you’ve been assigned contains any Macromolecules. Record your findings in Data Table 2. Solution D: 1. Place 2 dropperfuls of the unknown solution D in each of your test tubes and cups. Complete Testing for Parts I - IV. Note any change in color! 2. Rinse out your test tube and determine whether or not the unknown D solution you’ve been assigned contains any Macromolecules. Record your findings in Data Table 2. Data and Observations: Data Table 1: Positive Test Observations Test Performed Sudan III Biuret's Test Lugol's Test Benedict's Test Data Table 2: Results Test Performed 1. Sudan III 2. Biuret Test 3. Lugol’s Iodine Test 4. Benedict’s Test Which Organic Compound is it ? Positive Result Put “+” If Color Change Sol A Sol B Put “-“ If No Color Change Sol C Sol D Conclusion Questions: 1. What are the monomers for each of these macromolecules? a. Carbohydrates _____________________ b. Lipids ____________________________ c. Proteins __________________________ 2. Circle any of the following compounds that would be classified as carbohydrates. a. Amino acids e. fructose b. Triglycerides f. hemoglobin c. Glucose g. chitin d. cellulose h. starch 3. If you were given an unknown food sample and asked to identify its contents, which chemical identification test would you use to determine the presence of: a. Lipids _______________________________ b. Proteins______________________________ c. Glucose_______________________________ d. Starch________________________________ 4. Was the data collected in this experiment qualitative or quantitative? Explain? _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ 5. Predict the primary macromolecule that should be present in the following food substance and indicate which test you would apply in order to detect the presence of that macromolecule. You may need to consult additional resources. Food Substance a. Potato b. Cracker c. Gelatin d. Honey Predicted Macromolecule Test to be used