HM: Memory Lesson Plan - Multistore Model & AO3
Volume 21, Number 3, February 2016
Lesson plan
HM: the man with no memory
Matt Jarvis
The big picture
Learning objectives
Starter activity
Lesson activities
AQA 3.1.2 Memory. HM’s case (see pages 18–21) is important in the multistore model as evidence for the distinction between long-term memory and short-term memory. HM’s particular long-term memory problems are also useful for discussing the nature of long-term memory, in particular the distinction between declarative and procedural memory. This lesson assumes that AO1 material for multistore model and types of long-term memory have been covered. It also assumes students are familiar with the concept of AO3.
To practise graph interpretation (numeracy)
To recap on the distinction between qualitative and quantitative data
To consolidate understanding of the multistore model
To consolidate understanding of the distinction between different long-term memory systems
To practise working in groups (employability)
To improve understanding of the experience of amnesia (diversity)
To improve ability to produce AO3 answers on the memory topic
Numeracy exercise
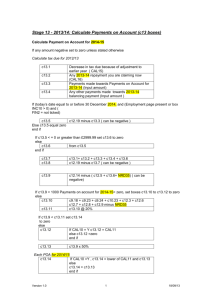
1 Looking at Figure 3 on page 20. In normal control subjects estimate how many trials it typically took to learn eight word definitions, synonyms or sentences.
2 What do the bars fo r HM’s results show?
3 Figure 2 shows an example of qualitative data. Explain the difference between quantitative and qualitative data.
1 Recap quiz in student teams addressing structural models of memory including the multistore model and the distinction between procedural, episodic and semantic memory.
2 Class divides into two groups (or multiples depending on group size). Group 1 works with the article to produce AO3 material for the multistore model. Group 2 works with the article to produce AO3 material for procedural memory.
3 Each group displays their ideas to the other using either a powerpoint presentation or A3 paper (depending on available resources).
4 All students individually complete an exam-type question requiring AO3 answers on memory using HM.
Philip Allan Publishers © 2016 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/psychologyreview
Plenary
Homework task
Assessment opportunities
Differentiation
5 Extension: students peer-mark question using an exam-style mark scheme.
Around the room, ask each student to identify one new thing they have learned about HM, memory or AO3.
HM loved crosswords. All students complete an HM and memory crossword
(generated at www.eclipsecrossword.com
)
Targeted questions in starter
Teacher assessment of participation in group task and peer presentation
Peer assessment of AO3 question
Teacher assessment of plenary
Targeting of questions in starter
Teacher and peer prompts and targeted elaboration questions in peer presentations
Different AO3 questions (if appropriate)
Targeted elaboration questions in plenary
This resource is part of P SYCHOLOGY R EVIEW , a magazine written for A-level students by subject experts.
To subscribe to the full magazine go to: http://www.hoddereducation.co.uk/psychologyreview
Philip Allan Publishers © 2016 www.hoddereducation.co.uk/psychologyreview