Elbow Chart Conditions
advertisement
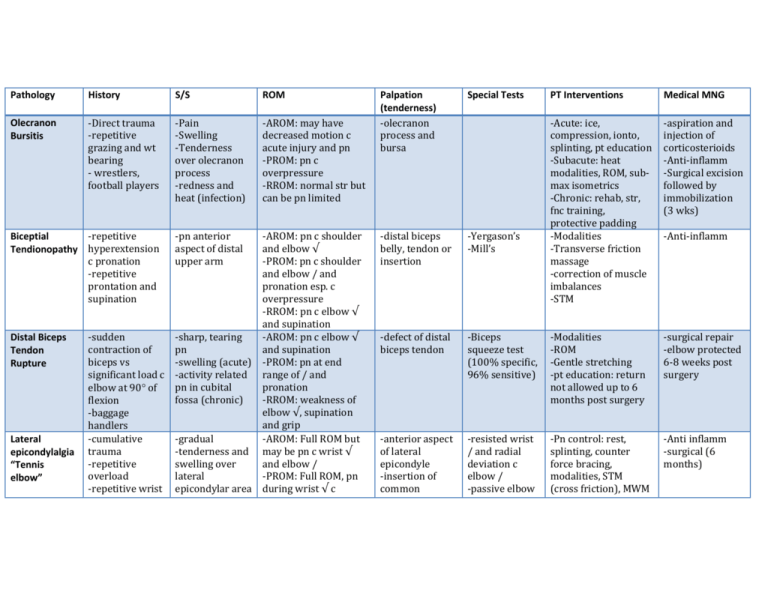
Pathology History S/S ROM Olecranon Bursitis -Direct trauma -repetitive grazing and wt bearing - wrestlers, football players -Pain -Swelling -Tenderness over olecranon process -redness and heat (infection) -AROM: may have decreased motion c acute injury and pn -PROM: pn c overpressure -RROM: normal str but can be pn limited Biceptial -repetitive Tendionopathy hyperextension c pronation -repetitive prontation and supination -pn anterior aspect of distal upper arm Distal Biceps Tendon Rupture Lateral epicondylalgia “Tennis elbow” -AROM: pn c shoulder and elbow √ -PROM: pn c shoulder and elbow / and pronation esp. c overpressure -RROM: pn c elbow √ and supination -sudden -sharp, tearing -AROM: pn c elbow √ contraction of pn and supination biceps vs -swelling (acute) -PROM: pn at end significant load c -activity related range of / and pn in cubital pronation elbow at 90 of fossa (chronic) -RROM: weakness of flexion elbow √, supination -baggage and grip handlers -cumulative -gradual -AROM: Full ROM but trauma -tenderness and may be pn c wrist √ -repetitive swelling over and elbow / overload lateral -PROM: Full ROM, pn -repetitive wrist epicondylar area during wrist √ c Palpation (tenderness) -olecranon process and bursa Special Tests PT Interventions Medical MNG -Acute: ice, compression, ionto, splinting, pt education -Subacute: heat modalities, ROM, submax isometrics -Chronic: rehab, str, fnc training, protective padding -Modalities -Transverse friction massage -correction of muscle imbalances -STM -aspiration and injection of corticosterioids -Anti-inflamm -Surgical excision followed by immobilization (3 wks) -distal biceps belly, tendon or insertion -Yergason’s -Mill’s -defect of distal biceps tendon -Biceps squeeze test (100% specific, 96% sensitive) -Modalities -ROM -Gentle stretching -pt education: return not allowed up to 6 months post surgery -surgical repair -elbow protected 6-8 weeks post surgery -anterior aspect of lateral epicondyle -insertion of common -resisted wrist / and radial deviation c elbow / -passive elbow -Pn control: rest, splinting, counter force bracing, modalities, STM (cross friction), MWM -Anti inflamm -surgical (6 months) -Anti-inflamm * most common ECRB /, rotation and grasping Medial Epicondylalgia “Golfers elbow” -overuse -repetitive and Elbow sprains -isolated varus or valgus force -hyperextension force -FOOSH Elbow dislocations -trauma: hyperextension *most -aching at night -nocturnal pn -stiffness in AM -dropping things in pronated position forearm pronated and elbow / -RROM: pn c wrist /, radial deviation c elbow extended, grip strength, weak shoulder girdle m, muscle imbalances in forearm and shoulder -pn over medial -AROM: normal c slight epicondyle and pn c wrist √ flexor forearm -PROM: pn c wrist /, -pn may radiate supination, elbow / into wrist -RROM: pn c wrist √ and pronation -generalized pn -AROM: non capsular, / c pt tenderness limited greater than √ over ligament -PROM: pn c /, mucle involved guarding end feel -worse c elbow / -RROM: initially (+) for may be relieved pn c elbow √ -Accessory motion: -ecchymosis laxity c distraction, -guarding of arm medial and lateral glides depending on ligament -Neuro: may get (+) ulnar nerve - severe, -AROM: non-capsular constant pn pattern, / limited -possible n/t greater than √ -PROM: pn c /, spasm and guarding end feel extensor tendon -radial head / c wrist √ -Cozen’s -Mill’s -3rd finger -DIFFERENTIAL DX -Exercise: stretching, prox. Stabilization, plyo, fnc training -pt education: modification of aggravating factors, stretching, ice after activity -flexor-pronator origin -Golfer’s elbow -Modalities -Rest -ROM and stretching -Strengthening -Activity modification -Anti-inflamm -corticosteriod injection - pt tender over ligament -Varus or Valgus stress -Posterolateral pivot shift apprehension -moving valgus stress (100% sensitive, 75% specific) -Modalities -ROM -Sub-max isometrics progressing to isotonic -Throwing and conditioning -taping/bracing for sports -anti-inflamm -immobilization c sling that prevents full / -surgical repair (competitive athletes) -over ligaments -monitor for neural tension -Immobilization (2-3 weeks): AROM of shoulder, wrist and hand, sub-max isometetrics, -immediate reduction -immobilization for 2-3 weeks post injury -↑temperature common is posterior Pulled (Nursemaid’s) elbow -sudden traction on the pronated wrist and / elbow -pn in forearm or wrist -arm hangs limply c elbow / and forearm pronated Little Leaguer’s Elbow -insidious or suddenly -usually sudden onset 2nd to fx at sight of lesion -pn medial aspect of elbow -persistent discomfort or stiffness -locking or catching (if loose body) -RROM: acute phase all tests are painful -Accessory motion: laxity c humeroulnar and humeroradial glides -Neuro: possible ulnar or median nerve injury -AROM: prior to reduction child resists any mvt -PROM: child will resist attempt to supinate forearm at elbow -RROM: may make reduction more difficult -AROM: all motions may be pn or limited -PROM: acutely all motions are pn -RROM: may not be accurate due to pn -Acessory: muscle guarding, laxity c medial glide -radial head -deformity -medial aspect of elbow modalities (for pn and edema -Post-immobilization: active stretching, ROM, restricted strengthening working into fnc, fnc training -reduction -parental education: AVOID longitudinal traction -possible sling for 1-2 days -surgical repair of ligaments -ulnar nerve transposition may be needed -Parent/coach education -rest and elimination of aggravating factors (3-6 wks) -Adhere to little league rules: limit # of pitches per game, per week, per session, # of days btw pitching -modalities -ROM -Correction of muscle imbalances -Gradual return to activity -Anti-inflamm -surgery only for pt c loose bodies -reduction of dislocated radial head Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Radial nerve entrapment at the elbow High radial nerve compression Posterior interosseous syndrome -repetitive activities -trauma -chronic compression (sleeping c elbows bent) -parasthesias in ulnar nerve distribution of hand -pn that radiates prox. Or distally along medial aspect of elbow -↓sensation along ulnar n -loss of grip power and dexterity -atrophy of ulnar intrinsics -clawing of ring and small finger -fx of humerus -strenuous muscular exercise -extended crutch ambulation -insidious onset -repetitive activity -previous -loss of wrist / -loss of finger and thumb / -loss of sensation in 1st dorsal web space -weakness (NO pn or paresthesias) -cramping -AROM: WNL, late -cubital fossa -elbow flexion -Non-surgical: -anti-inflamm stages difficulty / ring test (99% modalities, night -Ulnar nerve and small fingers and specific, 75% decompression splinting at 40-60, adducting the thumb sensitive) elbow pads, ulnar -PROM: WNL, may -Tinel’s nerve glides, reproduce pn c -Froment’s strengthening, activity overpressure of elbow -Wrinkle test modification, sleeping √ -ULNT 3 posture -RROM: weakness in -Pinch strength -Post-surgical: wrist ulnar deviation, √ -Grip strength modalities, splinting, of ring and pinky, scar mng, ROM, adduction of thumb, strengthening, ADD/ABD/oppostion desensitization, ulnar of pinky nerve glides, pt -Accessory: may have education some laxity of UCL -Neuro: sensory loss of ulnar in hand * RADIAL NERVE IS MOST FREQUENTLY INJURED NERVE IN FX OF HUMERUS -most common entrapments are a high radial nerve palsy, posterior interosseous syndrome, and radial tunnel syndrome -AROM: difficulty / fingers and thumb at MP joints and abducting thumb -increased muscle tone -soft tissue tightness -3rd finger sign -direct pressure over course of nerve -dynamic splinting with finger / assist allowing full finger √ -static night splint in -therapy referral Radial Tunnel syndrome * dynamic compression syndrome Median nerve entrapment Humerus Supracondylar Process syndrome *compression at ligament of Struthers trauma -difficulty to / fingers and thumb -difficulty grasping objects -difficulty stabilizing wrist during activity -PROM: WNL -RROM: weak wrist /, finger /, thumb radial abduction - Neuro: Semmes Weinstein monofiliament testing, 2 pt discrimination, ULNT 2b -insideous onset -repetitive activities -pn and cramping that is poorly localized over radial aspect of proximal forearm -worse at night -AROM: WLN, pn c wrist /, supination and elbow / -PROM: WNL, pn wrist √, pronation, elbow / -RROM: pn c wrist / and finger / -Neuro: Semmes Weinstein monofilament test, 2 pt discrimination, ULNT 2b -insidious -Gradual -onset of symptoms unknown -pn in the wrist or medial forearm exacerbated by full elbow / and pronation -paresthesias in index and long finger - wrist and finger / -STM -thermal modalities -Radial nerve glides -Stretching -Activity modification -very tender over radial tunnel -resisted middle finger / -resisted supination c elbow extended -wrist-cock up splint -thermal modalities -STM -Radial nerve glides -stretching -activity modification -therapy referral -occasional surgical release Pronator Syndrome *compression btw humeral and ulnar heads of pronator teres -Insidious -Gradual -Repetitive activities -pn radial aspect of palm and palmer aspect of thumb, index, middle and radial aspect of ring finger -experience heaviness in forearm -NO nocturnal Anterior Interosseous Syndrome * compression btw 2 heads of pronator teres -insidious -some forearm pn -WEAKNESS -inability to make OK sign Elbow Fractures (General) -50-60% in children -60-70% occur in boys age 4-10 years -AROM: WNL, pn c prontation and wrist √ -PROM: WNL, pn c supination and wrist / c overpressure -RROM: pn and weakness c pronation, wrist √, wrist radial deviation, thumb oppostition, thub radal and palmer ABD, and long finger √ -Neuro: Semmes Weinstein monofilament test, 2 pt discrimination, ULNT 1, 2a -AROM: WNL -PROM: WNL -RROM: weakness in thumb IP √ and index finger DIP √ -Neuro: Semmes Weinstein monofilament test, 2 pt discrimination, ULNT 1, 2a -pronator teres 4 cm distal to cubital crease c resistance vs pronation, elbow √ and wrist / -Grip strength -Pinch strength -Wrinkle test -thermal modalities -splinting in neutral position (4-6 weeks) -STM -Stretching -Median nerve glides -Correction of muscle imbalances -activity modification - NO tenderness -increased tone/soft tissue tightness -Pinch test -Grip test -minimal intervention bc it usually resolves spontaneously -strengthening for pinch and grip -Pn management -edema control -scar management -ROM of shoulder, elbow, forearm, and wrist -therapy referral -Closed reduction: posterior splint or cast in 120 √ -Open reduction: treatment of Condylar fractures -uncommon -FOOSH (lateral column Intercondylar fractures -difficult to estimate -wedge effect of the longitudinal groove of the olecranon -“t” and “Y” fractures -common due to subcutaneous position -fall backwards onto the elbow -FOOSH Olecranon Fractures Radial head fractures -FOOSH due to axial loading through the radial head -Joint mobilization -Gradual return to activities -Pn management -Edema control -Scar management -ROM -Strengthening -Gradual return to fnc activities -Pn management -Edema control -Scar management -ROM (all joints) -Strengthening -Joint mobilizations -Gradual return to fnc activities -Pn management -Scar management -Edema control -ROM (all joints) -Stregthening -Gradual return to fnc activities -Pn mangement -Edema control -Early AROM -Stregthening: choice, plates and screws -Closed reduction: splint 4-5 weeks -Open reduction: screw fixation provides stable fixation, single plate may enhance stability in presence of communion -closed reduction: rarely fone -open reduction: screws, plates, wires -Closed type: cast 2-3 weeks -Open reduction: internal fixation -Closed reduction: sling for 3 days (Type I), sling 2-3 Monteggia fracture Essex-Lopresti fractures -relatively rare -direct blow to the forearm -FOOSH c arm in hyperextension or hyperpronation -fx of radial head c proximal radius migration and disruption of the DRUJ and interosseous membrane -fall from height isometrics at 3 weeks progressiong to isotonics at 5-6 weeks, heavy resistance not performed until at least 8 weeks -Joint mobilization -Progressive return to activity -Pn management -Edema control -Scar management -AROM -Strengthening -Return to fnc activities -Pn management -Edema control -Scar management -AROM -Strengthening -Return to fnc activities weeks (Type II) -Open reduction: internal fixation, immobilization for 4 weeks in 90-120 of elbow √ -ORIF: immobilization in cast for 6 weeks