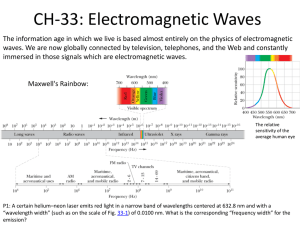
File
advertisement

Name:_______________________________ K/U - /7 T/I- /11 Date:________________________ C- /7 Unit 4 Test Multiple Choice (7 marks) Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. Which of the following properties of light provides the strongest evidence that light is a wave rather than a particle? a. reflection b. refraction c. dispersion d. diffraction e. photoelectric effect 2. The diagram shows the interference pattern formed by two coherent light sources S1 and S2. The curves in full lines represent the crests and the curves in broken lines represent the troughs. Which of the following lines, A, B, C, D, or E, are antinodal lines? a. A and C b. A, C, and E c. C d. B and D e. A, B, C, D, and E 3. Which of the following might be a valid conclusion for the Young's double-slit experiment? a. Light travels in a straight line. b. Light is an electromechanical wave. c. Collisions among light particles account for the interference pattern on the screen. d. Light travels at a very high speed. e. Light behaves as a wave in this experiment. 4. Which of the following is true? a. All electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed. b. Electromagnetic waves can travel only in vacuum. c. Electromagnetic waves can be reflected, refracted, and diffracted. d. An electromagnetic wave is an electron waving in a magnetic field. e. Electromagnetic waves can travel only in material media that support wave motion, such as water and air. 5. The name given to an electromagnetic wave (for example, X ray, radio wave) depends on the wave’s a. colour b. speed c. amplitude d. wavelength e. intensity ____ ____ 6. A beam of vertically polarized light passes through a polarizer with virtually no changes. When a beam of horizontally polarized light passes through the same polarizer, which of the following occurs? a. No light is transmitted through the polarizer. b. The light is transmitted, but becomes unpolarized. c. The transmitted light becomes vertically polarized. d. The light is partially reflected and partially transmitted. e. none of the above 7. Radio waves with a wavelength of 1 m are transmitted into a room in phase with sound waves of wavelength 1 m. The radio waves and the sound waves a. experience constructive and destructive interference b. experience constructive interference only c. experience destructive interference only d. combine so that the sound waves modulate the radio waves e. none of the above Short Answer For the following questions, write the most appropriate answer in the space provided. 8. Unpolarized sunlight strikes the smooth water surface of Lake Ontario and is reflected. a) Draw a diagram to show the difference between the polarizations of the incident ray and the reflected ray. Explain why the difference occurs. (2 marks) 9. Explain how polarized sunglasses reduce glare off a water surface. (2 marks) 2 10. In 1660, Isaac Newton proposed that light is made up of particles. Describe how the particle theory (corpuscular theory) explained the law of refraction. (3 marks) Problem Solving For the following questions, write the answer in the space provided. If the question requires mathematical calculations, show all of your work. 11. a) Why are the edges of shadows not perfectly sharp? (1 mark) b) What is the phenomenon described in part (a) called? (1 mark) c) Can you explain this phenomenon by using Isaac Newton's corpuscular theory? If your answer is yes, explain how. If not, which theory can be used to explain the phenomenon, and how? (2 marks) 3 12. a) Describe the interference pattern formed by a single slit. (1 mark) b) Explain how single-slit diffraction causes dark fringes and bright fringes. (2 marks) 13. Suppose that the inside length of a microwave-oven is 30 cm. If the length of a microwave oven is half of the wavelength of microwaves used by the oven, find the frequency of the microwaves used in the oven.(3 marks) 14. Determine the force that Earth’s gravity exerts on an electromagnetic wave of frequency 3.7 1015 Hz travelling at Earth’s surface. (1 mark) 4 AEW Answer Section MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: D D E C D A E DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: DIF: easy average average easy easy difficult difficult REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: REF: K/U K/U K/U K/U K/U K/U K/U LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: LOC: WA V.01, WA 1.01 WA V.01, WA 1.03 WA V.01, WA 2.03 WA V.01, WA 1.01 WA V.01, WA 1.01 WA V.01, WA 1.02 WA V.01, WA 1.02 SHORT ANSWER 8. ANS: a) When light strikes a water surface at an oblique angle, the electric field vectors vibrating perpendicular to the surface are transmitted or absorbed. The reflected rays are polarized with the electric field vectors vibrating horizontally. b) Polarization supports the hypothesis that light is formed from waves, and that furthermore they are transverse waves. Analysis of various polarization experiments confirms that the vibration of electric field vectors of an electromagnetic wave is perpendicular to the direction of the wave motion. DIF: difficult REF: K/U,C LOC: WA V.01, WA 1.02 9. ANS: When light strikes a surface such as a street or pool of water, the reflected light is horizontally polarized. The polarized lenses in sunglasses are oriented to block the transmission of horizontally polarized light. DIF: average REF: K/U, C LOC: WA V.01, WA 1.02 PROBLEM 10. ANS: 5 Isaac Newton stated that when light travels from air to water, a force of attraction acts on the particles once they move close enough to the surface. The velocity component perpendicular to the boundary increases and the velocity component parallel to the boundary remains constant. When the light particles move a little beyond the surface, the velocity remains constant at its increased value. This causes the light particles to bend toward the normal line, which is seen as refraction. The explanation of refraction in the previous paragraph is not valid, because it suggests that the speed of light in water is greater than its speed in air. Experiments show that, contrary to this, the speed of light in water is 2.25 108 m/s, which is less than its speed in air, 3.00 108 m/s. DIF: average REF: I, C LOC: WA V.01, WA 1.05 11 ANS: a) The bending of light waves around the edges of barriers causes the fuzzy edges of shadows. b) This bending phenomenon is called “diffraction.” c) No. Diffraction can be explained by Huygens' wave theory. Every point on an advancing wavefront can be considered to be a source of tiny secondary waves called "wavelets." The new position of the wavefront is the envelope of the wavelets emitted from all points of the wavefront in its previous position. DIF: average REF: C LOC: WA V.01, WA 1.05 12. ANS: a) There is a bright central band, with narrower, dimmer, equally spaced bands to the sides. b) No light is seen when the paths of two light waves differ in length by n, due to destructive interference. Light can be seen when the paths of two light waves differ in length by approximately (n , due to constructive interference. In both cases, n = 1, 2, 3, … . DIF: average REF: C 13. ANS: Length of microwave oven 0.3 m Wavelength of microwaves 0.6 m LOC: WA V.01, WA 2.03 Frequency of microwaves DIF: easy REF: K/U, MC LOC: WA V.01, WA 1.01 14. ANS: Earth’s gravity does not exert any force on electromagnetic waves, since electromagnetic waves have no mass. DIF: average REF: K/U, C LOC: WA V.03, WA 3.02 6