further information
advertisement

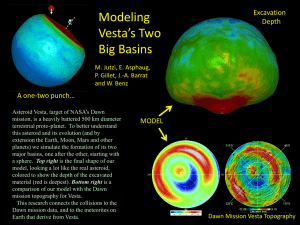
Distal Terrains on Asteroid 4 Vesta Resulting from the Rheasilvia Impact The geologically recent (~1 Gya) Rheasilvia basin on asteroid 4 Vesta is one of the most spectacular impact structures in the solar system, with a diameter nearly equal in size to that of Vesta itself. To date, much of the numerical modeling of this impact has concentrated on the morphology of the Rheasilvia basin. However, the stress wave produced by an impact of this size is capable of causing deformation at considerable distance from the basin itself. We use high resolution hydrocodes modeling coupled with a strain analysis routine in order to understand the modes and magnitudes of deformation expected globally on Vesta following the Rheasilvia impact. These simulations give insight into several interesting observations by NASA’s Dawn spacecraft. First, our results suggest that the major system of graben circling Vesta’s equator opened shortly after the passage of the Rheasilvia related impact shock wave. Secondly, we find that the deficiency of small craters at Vesta’s north pole is likely a result of antipodal focusing of Rheasilvia impact related stresses. The details behind both of these findings are dependent on material parameters of Vesta’s interior, including core strength, mantle porosity, and damage to the body from previous major impacts. By matching model output to observation, we can perform a crude sort of seismology and gain insight into both Vesta’s internal rheology as well as its impact history.