Diffraction and Interference of Waves
advertisement
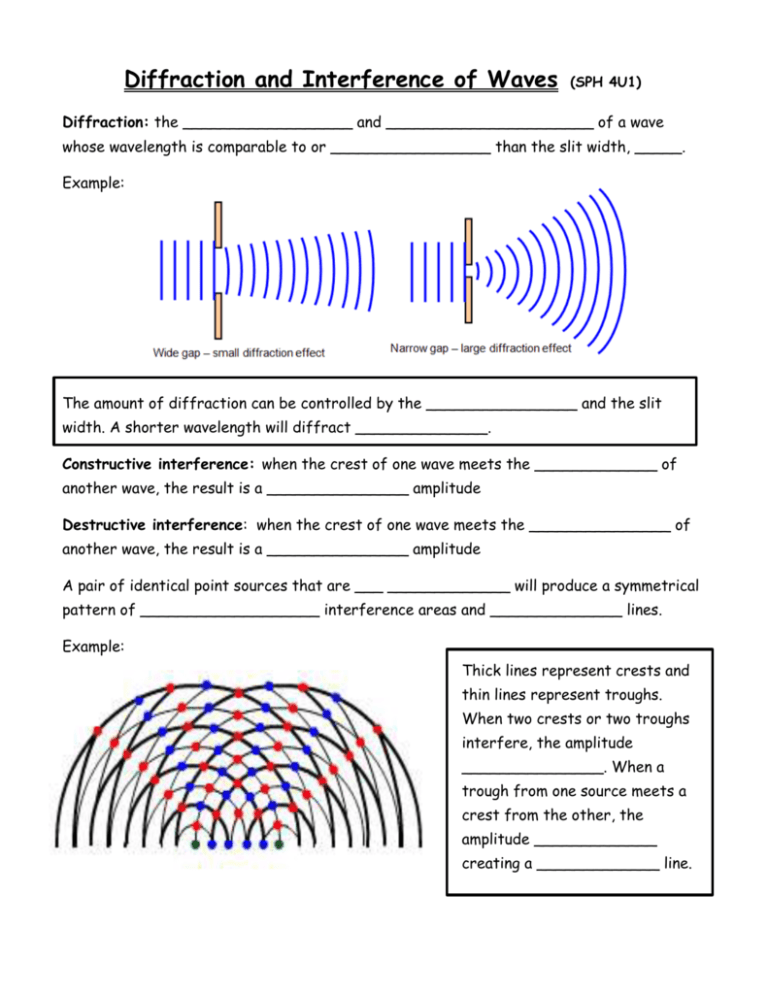
Diffraction and Interference of Waves (SPH 4U1) Diffraction: the __________________ and ______________________ of a wave whose wavelength is comparable to or _________________ than the slit width, _____. Example: The amount of diffraction can be controlled by the ________________ and the slit width. A shorter wavelength will diffract ______________. Constructive interference: when the crest of one wave meets the _____________ of another wave, the result is a _______________ amplitude Destructive interference: when the crest of one wave meets the _______________ of another wave, the result is a _______________ amplitude A pair of identical point sources that are ___ _____________ will produce a symmetrical pattern of ___________________ interference areas and ______________ lines. Example: Thick lines represent crests and thin lines represent troughs. When two crests or two troughs interfere, the amplitude _______________. When a trough from one source meets a crest from the other, the amplitude _____________ creating a _____________ line. Mathematics of Two Point Source Interference The key to understanding the mathematics of the pattern is looking at the ___________ length from each source, S1 and S2 to the interested point which is either at a location of constructive interference or at a nodal line. When the difference in path length is a __________________ multiple of λ, constructive interference is occurring When the difference in path length is a ___________ multiple of λ, destructive interference is occurring and it must be a nodal line Results: 1 |𝑃𝑛 𝑆1 − 𝑃𝑛 𝑆2 | = (𝑛 − )λ 2 1 λ sin 𝜃𝑛 = (𝑛 − ) 2 𝑑 Where Pn is any point on the nth nodal line Where 𝜃𝑛 is the angle for the nth nodal line and d is the distance between the point sources sin 𝜃𝑛 = 𝑥𝑛 𝐿 Where 𝑥𝑛 is the perpendicular distance from the right bisector to the point Pn and L is the distance from Pn to the midpoint of the two sources 𝑥𝑚 = 𝑚𝐿λ 𝑑 Where 𝑥𝑚 is the perpendicular distance from the right bisector to the point Pm on the mth line of constructive interference Practice Questions: 1. Two sources are 10.0 cm apart. An interference pattern is observed at a distance of 25.0cm along the right bisector of the line segment joining the sources. The third nodal line is 33.6 cm from the right bisector at this distance. What is the wavelength of the waves? 2. Two identical point sources are 5.0cm apart, in phase and vibrating with a frequency of 12 Hz. They produce an interference pattern. A point on the first nodal line is 5cm from one source and 5.5 cm from the other. Determine the wavelength and speed of the waves.