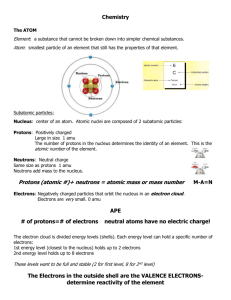
This Study guide can help your child grasp the main ideas that we
advertisement

This Study guide can help your child grasp the main ideas that we are studying in sixth grade science. Please visit the YouTube links and other links for lessons on the topics that we are studying in class. The students have been doing much of this in class for the last two weeks. There will be a short test late next week over these concepts. Some of the online resources go deeper into some concepts than we are. Therefore, don’t expect that they will know everything in all of the online resources. The major terms and concepts are listed that will be tested late next week. Matter: Atoms, Molecules, Pure Substances and Mixtures, Density 6th Grade Study Guide Key terms: Atoms Protons Neutrons Electrons Molecule (the smallest unit of a compound) Atomic mass unit Pure substances Mixtures Density Mass Volume Triple beam balance Graduated cylinder Concepts and Skills Be able to organize the following particles according to size (mass) from smallest to largest: beginning with smallest they are as follows—electron, neutron and proton, atom, molecule. Know that the smallest particle of an element is the atom. Anything smaller than an atom of an element does not have the characteristic properties of the element. Know that atoms bond together to make molecules, so molecules are far larger than single atoms and molecules have characteristic properties that are different from the atoms that are in them. Atoms of any one element represent a pure substance. Molecules of only one type represent a pure substance. Mixtures are substances of more than one type of element or are substances of more than one type of element or both. Be able to use the periodic table to determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in an atom of any particular element (using the atomic number for number of protons and the same number for number of electrons) Know the mass of each particle (proton = 1 AMU, neutron = 1 AMU, electron = 1/2000 AMU) Be able to represent solids, liquids, gases in terms of particle ability to move around (solids: very dense where particles cannot move around or change locations, liquids: not as dense as solids where molecules and atoms can move relatively freely, gases: not dense where particles move rapidly and freely from place to place) Calculate the volume of rectangular prisms: V = L x W x H Determine the density of irregular-shape objects of pure substances such as solids or liquids by using the displacement method in a graduated cylinder Calculate density: D = M/V (density equals mass divided by volume) Units for density: grams/ cm3 (grams per cubic centimeter) SI units for mass: grams SI units for volume: cm3 Mass of: protons, neutrons, electrons Electric charge of: protons, neutrons, electrons Online Resources (These videos are very helpful in understanding the above concepts) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-1En9PykvN4 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ndw9XYA4iF0 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KCL8zqjXbME https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HgLrMKEN4Iw This video goes deeper in mathematics of converting units that we will in class. Simply learn the basics of calculating density. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HgLrMKEN4Iw (only concern yourself with the first half of the video. http://www.auburnschools.org/ajhs/lmcrowe/Week%205/Density%20problems%20without%20answers. pdf This video is more comprehensive than the material we are currently studying, but watching this video will help students better understand matter in all its forms. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ukaeyMU2RoM