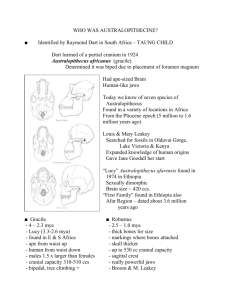
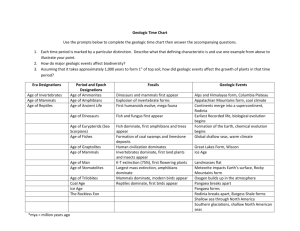
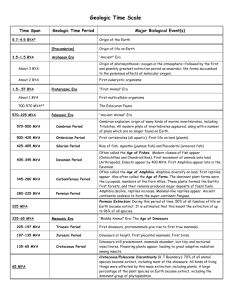
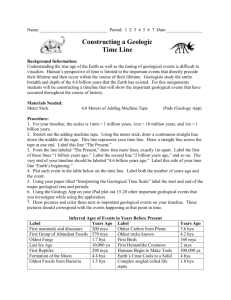
Geologic Time What is Geologic Time? A ______ scale which
advertisement

Geologic Time What is Geologic Time? A _____________ scale which divides geologic time into units. Relative time is ________________ to something. Units are from largest to smallest o Eon ______ Period ______________ Age Basis For Subdivision of Time Law of ___________________ Age of Earth ______ ______________ yrs oldest rock 4 billion yrs _____________________ Precambrian Era Vast time in earth history _________ the deposition of Cambrian _____________ bearing rocks. Fossils are _____ because animals were ______ bodied. Example: Jellyfish, paramecium, and trail marks from animals. Plants & Animals Paleozoic Era Life increased in _______________ The continents collided to form ____________ Cambrian Period Also has “Age of __________” in it Divided into ___-___ periods 1st common and ________________ fossils (index) o example: Algae, sponges, worms, mollusks All lived in the Sea o ________ large but few o ______ :clams Cambrian Environment o sea cucumbers Ordovician Period 540 – 425 mya Rise of new ____________ groups of importance. Oldest _________________- fragments of bone o example: bryozoans, brachiopods, echnoids Sea covered land o ________ & _____________ building Trilobites Silurian Period 425-405 mya New ____________ rather than new groups of animals Most important ___________ (fossil of oldest plant) Trilobites, crinoids, etc. from ancient reefs near Chicago types of ___________ starting Crinoids Environment Devonian Period 405-345 mya Expansion of _______ and land plants 1st ______ animals (primitive amphibians) First developed fish o _____________ fish o plate-skinned fish o sharks o 1st _________ fish o From lobed-fin fish -amphibians Oldest _________, millipedes and insects Fresh water clams Great ___________ starting Coral reefs Carboniferous 345-280 mya Mississippian period 345-310 mya o ______________ warm seas o _____ animals and plants ___________ o Amphibians and land plants spread o ______ swamp forests (most US under water) Permian Period 280-230 mya o o o o o o o o Pennsylvanian Period 310-280 mya Scale trees, seed ________ develop _________ dragonflies o (30 inch wing span) Reptiles from amphibians Primitive ___________________ New insects (beetles, and true dragonflies) Active ________________ o different from skull and vertebrae fossil eggs example: o ____________-back lizard (sail as ________________ control) o Theriodonts – carnivore ( mammals are descendents) A lot become _________________ (trilobites, corals, blastoids) Mesozoic Era o o o Known as ______________ Life Also has the “______ of the _____________” in it. New pattern of lands and seas, formed _______________ ranges Triassic Period 230-180 mya o o o o A lot of ____________ activity _______________ dominate o advanced body structure o __________-protected eggs o both _______ and __________ reptiles 1st appeared lobster like creature ______________ forest- Petrified forest Jurassic Period 180-145 mya o o o o Flying reptiles and herbivores in water __________ mammals-fragments of rat sized jaws & teeth. Oldest known _______ Over thousand species of insects Dinosaurs o o o 3 main groups _____________: long-necked, long-tailed, four-legged o (largest land animal 87 ft long) ________________: armored reptiles, weighed up to 10 tons _________________ Theropods: walk on ________ legs Dinosaur Hips Dinosaurs are also classified by the _______ types of hips. Saurischian- _____________ hipped ornithischian- _________ hipped Cretaceous Period 135-63 mya o o o o o o Major advanced of ________ ________ arrivals- flowering plants, trees-magnolia, oaks, maple, etc. New sources of food provided for mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects _______________ roamed over all continents ____________ mammals, marsupials At the ________ of period _________________ of dinosaurs. Cenozoic Era 63-1 mya (last 70 my) o o o o o o _______ Periods and __________ epochs Includes the age of the ________________ Includes the age of Man Birds are numerous ______________ fish dominate Our era of ___________ Tertiary Period o o o Has __________ epochs. A lot of changes taking place examples: o -___________ mammals to _____________ mammals o -_____________ plants to _______________ o -Single animals to __________ -Alps, Himalayas, Rockies, Andes and Glacier formation Paleocene Epoch o o Mammals are _________ ____________ plants Eocene Epoch o o Mammals becoming _______________ Ancestors of modern ____________ and _____________ Oligocene Epoch o ________________ plants _____________ by grasses and pines o Apes, elephants, cats and dogs families Miocene Epoch o __________ of grass eating animals o Land bridge between ___________ and ______________Mastodans cross. Pliocene Epoch o ____________began to form o Sea level ________ o Animals crossed __________ bridges and new land formed o Animals hunting herds o (Near End of Epoch) o Ice age ________________ o ___________ _______________ was carved out of rising rock layers Quaternary Period o Includes _______ Epochs o Climate much ___________ o Includes the __________ Age o Includes the age of _______ o Our period of ________________ Pleistocene Epoch o _________ mya Ice Age o ___________________ advanced at least _________ different times o Animals either developed ________________ covering or moved __________ o example: mastodons, saber-tooth tigers, ________________ o (At end of the epoch) o 10,000 yrs ago Ice sheets __________________ o Large mammals became _________________ Holocene Epoch Earth’s climate became ______________ o Human civilization arose (Age of man) o The epoch of _______________